
Mountain View is a city in Santa Clara County, California, United States, part of the San Francisco Bay Area. Named for its views of the Santa Cruz Mountains, the population was 82,376 at the 2020 census.

The Humboldt–Toiyabe National Forest (HTNF) is the principal U.S. National Forest in the U.S. state of Nevada, and has a smaller portion in Eastern California. With an area of 6,289,821 acres (25,454.00 km2), it is the largest U.S. National Forest outside of Alaska.

The Blue Ridge Mountains are a physiographic province of the larger Appalachian Highlands range. The mountain range is located in the Eastern United States and extends 550 miles southwest from southern Pennsylvania through Maryland, West Virginia, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, and Georgia. The province consists of northern and southern physiographic regions, which divide near the Roanoke River gap. To the west of the Blue Ridge, between it and the bulk of the Appalachians, lies the Great Appalachian Valley, bordered on the west by the Ridge and Valley province of the Appalachian range.

The Catskill Mountains, also known as the Catskills, are a physiographic province and subrange of the larger Appalachian Mountains, located in southeastern New York. As a cultural and geographic region, the Catskills are generally defined as those areas close to or within the borders of the Catskill Park, a 700,000-acre (2,800 km2) forest preserve protected from many forms of development under New York state law.

A summit is a point on a surface that is higher in elevation than all points immediately adjacent to it. The topographic terms acme, apex, peak, and zenith are synonymous.
Orbe District was a district of the canton of Vaud, Switzerland.

An ice field is a mass of interconnected valley glaciers on a mountain mass with protruding rock ridges or summits. They are often found in the colder climates and higher altitudes of the world where there is sufficient precipitation for them to form. The higher peaks of the underlying mountain rock that protrude through the icefields are known as nunataks. Ice fields are larger than alpine glaciers, but smaller than ice caps and ice sheets. The topography of ice fields is determined by the shape of the surrounding landforms, while ice caps have their own forms overriding underlying shapes.
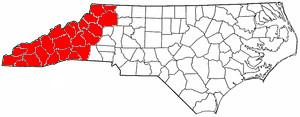
Western North Carolina is the region of North Carolina which includes the Appalachian Mountains; it is often known geographically as the state's Mountain Region. It contains the highest mountains in the Eastern United States, with 125 peaks rising to over 5,000 feet in elevation. Mount Mitchell at 6,684 feet, is the highest peak of the Appalachian Mountains and mainland eastern North America. The population of the 23 most commonly associated counties for the region, as measured by the 2020 U.S. Census, is 1,149,405. The region accounts for approximately 11% of North Carolina's total population.

Col du Mont d'Orzeires is a high mountain pass in the Jura Mountains in the canton of Vaud in Switzerland.

The Mountain states form one of the nine geographic divisions of the United States that are officially recognized by the United States Census Bureau. It is a subregion of the Western United States.

Bellvale Mountain is a mountain range located near Bellvale in Orange County, New York. It is a continuation of Bearfort Mountain in New Jersey. The Appalachian Trail is located along the ridge of the mountain. Puddingstone of the Skunnemunk Conglomerate is visible along the ridge.

Mont d'Or is a mountain of the Jura, located in the French department of Doubs and extending into the Swiss canton of Vaud. Its main summit is 1,463 metre-high and lies within France, 500 metres north of the border with Switzerland. The mountain is located between Jougne, France and Vallorbe, Switzerland.

Dun Brook Mountain is a mountain located in Adirondack Mountains of New York located in the town of Indian Lake east-northeast of Blue Mountain Lake. Tirrell Mountain is located west and Tirrel Pond is located west-southwest of Dun Brook Mountain.
Irish Mountain is a mountain located in the Catskill Mountains of New York southwest of Grand Gorge. Irish Mountain is located southeast of Moresville Range and north of Schultice Mountain.

Huntersfield Mountain is a mountain located in the Catskill Mountains of New York north-northwest of Ashland. Ashland Pinnacle is located east, and Tower Mountain is located south-southeast of Huntersfield Mountain. It is the highest point in Schoharie County and it is ranked 9 of 62 on the list of New York County High Points.
Richmond Mountain is a mountain located in the Catskill Mountains of New York east-northeast of Hunter. Richtmyer Peak is located northeast, Bump Mountain is located south, Steenburg Mountain is located north, and Ashland Pinnacle is located west-southwest of Richmond Mountain.
Bump Mountain is a mountain located in the Catskill Mountains of New York northeast of Ashland. Richtmyer Peak is located north-northeast, The Knob is located west, and Ashland Pinnacle is located west-southwest of Bump Mountain.
Mount Pisgah is a mountain located in the Catskill Mountains of New York north of Windham. Steenburg Mountain is located northwest, Richtmyer Peak is located west, and Mount Nebo is located southeast of Mount Pisgah.
The Knob is a mountain in Greene County, New York. It is located in the Catskill Mountains north-northeast of Ashland. Ashland Pinnacle is located north, and Huntersfield Mountain is located northwest of The Knob. The mountain has an elevation of 2,638 feet.
















