Related Research Articles

Vitamin K is a family of structurally similar, fat-soluble vitamers found in foods and marketed as dietary supplements. The human body requires vitamin K for post-synthesis modification of certain proteins that are required for blood coagulation or for controlling binding of calcium in bones and other tissues. The complete synthesis involves final modification of these so-called "Gla proteins" by the enzyme gamma-glutamyl carboxylase that uses vitamin K as a cofactor.
Liver function tests, also referred to as a hepatic panel, are groups of blood tests that provide information about the state of a patient's liver. These tests include prothrombin time (PT/INR), activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), albumin, bilirubin, and others. The liver transaminases aspartate transaminase and alanine transaminase are useful biomarkers of liver injury in a patient with some degree of intact liver function.

Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer in adults and is currently the most common cause of death in people with cirrhosis. HCC is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide.

Alpha-fetoprotein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AFP gene. The AFP gene is located on the q arm of chromosome 4 (4q13.3). Maternal AFP serum level is used to screen for Down syndrome, neural tube defects, and other chromosomal abnormalities.
Liver tumors are abnormal growth of liver cells on or in the liver. Several distinct types of tumors can develop in the liver because the liver is made up of various cell types. Liver tumors can be classified as benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous) growths. They may be discovered on medical imaging, and the diagnosis is often confirmed with liver biopsy. Signs and symptoms of liver masses vary from being asymptomatic to patients presenting with an abdominal mass, hepatomegaly, abdominal pain, jaundice, or some other liver dysfunction. Treatment varies and is highly specific to the type of liver tumor.

Hepatoblastoma is a malignant liver cancer occurring in infants and children and composed of tissue resembling fetal liver cells, mature liver cells, or bile duct cells. They usually present with an abdominal mass. The disease is most commonly diagnosed during a child's first three years of life. Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) levels are commonly elevated, but when AFP is not elevated at diagnosis the prognosis is poor.
In oncology, AFP-L3 is an isoform of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), a substance typically used in the triple test during pregnancy and for screening chronic liver disease patients for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). AFP can be fractionated by affinity electrophoresis into three glycoforms: L1, L2, and L3 based on the reactivity with the lectin Lens culinaris agglutinin (LCA). AFP-L3 binds strongly to LCA via an additional α 1-6 fucose residue attached at the reducing terminus of N-acetylglucosamine; this is in contrast to the L1 isoform. It is the L1 isoform which is typically associated with non-HCC inflammation of liver disease condition. The L3 isoform is specific to malignant tumors and its detected presence can serve to identify patients whom need increased monitoring for the development of HCC in high risk populations. AFP-L3% is now being considered as a tumor marker for the North American demographic.

Fetal proteins are high levels of proteins present during the fetal stage of development. Often related proteins assume similar roles after birth or in the embryo, in which case the fetal varieties are called fetal isoforms. Sometimes, the genes coding fetal isoforms occur adjacent to their adult homologues in the genome, and in those cases a locus control region often coordinates the transition from fetal to adult forms. In other cases fetal isoforms can be produced by alternate splicing using fetal exons to produce proteins that differ in only a portion of their amino acid sequence. In some situations the continuing expression of fetal forms can reveal the presence of a disease condition or serve as a treatment for diseases such as sickle cell anemia. Some well known examples include:

Liver cancer, also known as hepatic cancer, primary hepatic cancer, or primary hepatic malignancy, is cancer that starts in the liver. Liver cancer can be primary in which the cancer starts in the liver, or it can be liver metastasis, or secondary, in which the cancer spreads from elsewhere in the body to the liver. Liver metastasis is the more common of the two liver cancers. Instances of liver cancer are increasing globally.

Vitamin K-dependent carboxylation/gamma-carboxyglutamic (GLA) domain is a protein domain that contains post-translational modifications of many glutamate residues by vitamin K-dependent carboxylation to form γ-carboxyglutamate (Gla). Proteins with this domain are known informally as Gla proteins. The Gla residues are responsible for the high-affinity binding of calcium ions.

Glypican-3 is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the GPC3 gene. The GPC3 gene is located on human X chromosome (Xq26) where the most common gene encodes a 70-kDa core protein with 580 amino acids. Three variants have been detected that encode alternatively spliced forms termed Isoforms 1 (NP_001158089), Isoform 3 (NP_001158090) and Isoform 4 (NP_001158091).

Golgi membrane protein 1 (GOLM1) also known as Golgi phosphoprotein 2 or Golgi membrane protein GP73 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GOLM1 gene. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been described for this gene.

Epithelial membrane protein 3 (EMP3) is a trans-membrane signaling molecule that is encoded by the myelin-related gene EMP3. EMP3 is a member of the peripheral myelin protein gene family 22-kDa (PMP22), which is mainly responsible for the formation of the sheath of compact myelin. Although the detailed functions and mechanisms of EMP3 still remain unclear, it is suggested that EMP3 is possibly epigenetically linked to certain carcinomas.
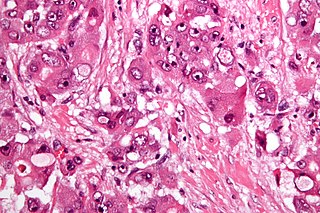
Fibrolamellar carcinoma (FLC) is a rare form of carcinoma that typically affects young adults and is characterized, under the microscope, by laminated fibrous layers interspersed between the tumor cells. It has been estimated that 200 new cases are diagnosed worldwide each year. However, in light of recent advances in our molecular understanding, this has recently been revised to suggest it may be at least ten times more common. FLC, also known as fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma, is different from the more common hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in that it afflicts young people with normal liver function and no known risk factors.
In transplantation medicine, the Milan criteria are set of criteria applied in consideration of patients with cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) for liver transplantation with intent to cure their disease. Their significance derives from a landmark 1996 study in 48 patients by Mazzaferro et al which showed that selecting cases for transplantation according to specific strict criteria led to improved overall and disease-free survival at a four-year time point. These same criteria have since been adopted by the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network (OPTN) in the evaluation of patients for potential transplantation.The threshold Milan criteria are as follows:
Elevated alpha-fetoprotein refers to a state where alpha-fetoprotein levels are outside of the reference range.
Patrizia Paterlini-Bréchot, born in the Italian city of Reggio Emilia, is an Italian scientist and a professor of cell biology and oncology working at the Faculté de Médecine Necker-Enfants Malades, Université Paris Descartes and at INSERM in Paris.

The Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System is a quality assurance tool created and trademarked by the American College of Radiology in 2011 to standardize the reporting and data collection of CT and MR imaging patients at risk for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), or primary cancer of the liver cells. It provides a standardized framework for classification of liver lesions by a radiologist, and only applies in patients with chronic liver disease, the main risk factor for liver cancer. The hierarchical classification, from LR1 to LR5, is based on specific imaging features of the lesion in question, and corresponds to the degree of suspicion for malignancy. For example, a lesion with features corresponding to the highest category, LR5, is "definitely" HCC. Importantly, the increasing acceptance of the LI-RADS system of reporting by referring clinicians has reduced the need for tissue biopsy confirmation of cancer in patients with chronic liver disease.
George K. Michalopoulos is a Greek-American pathologist and academic. He served as Maud L. Menten Professor of Experimental Pathology and Chair of the Department of Pathology at the University of Pittsburgh and UPMC from 1991 to 2023.
Ultrasonography of liver tumors involves two stages: detection and characterization.
References
- ↑ Liebman HA, Furie BC, Tong MJ, et al. (1984). "Des-gamma-carboxy (abnormal) prothrombin as a serum marker of primary hepatocellular carcinoma". N. Engl. J. Med. 310 (22): 1427–31. doi:10.1056/NEJM198405313102204. PMID 6201741.
- ↑ Tsai SL, Huang GT, Yang PM, Sheu JC, Sung JL, Chen DS (1990). "Plasma des-gamma-carboxyprothrombin in the early stage of hepatocellular carcinoma". Hepatology. 11 (3): 481–8. doi:10.1002/hep.1840110321. PMID 2155866.
- ↑ Cui R, Wang B, Ding H, Shen H, Li Y, Chen X (2002). "Usefulness of determining a protein induced by vitamin K absence in detection of hepatocellular carcinoma". Chin. Med. J. 115 (1): 42–5. PMID 11930656.
- 1 2 Marrero JA, Su GL, Wei W, et al. (2003). "Des-gamma carboxyprothrombin can differentiate hepatocellular carcinoma from nonmalignant chronic liver disease in American patients". Hepatology. 37 (5): 1114–21. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2003.50195 . PMID 12717392.
- ↑ Volk ML, Hernandez JC, Su GL, Lok AS, Marrero JA (2007). "Risk factors for hepatocellular carcinoma may impair the performance of biomarkers: a comparison of AFP, DCP, and AFP-L3". Cancer Biomark. 3 (2): 79–87. doi:10.3233/cbm-2007-3202. PMID 17522429.
- ↑ Lamerz R, Runge M, Stieber P, Meissner E (1999). "Use of serum PIVKA-II (DCP) determination for differentiation between benign and malignant liver diseases". Anticancer Res. 19 (4A): 2489–93. PMID 10470180.
- ↑ Ertle, JM; Heider, D; Wichert, M; Keller, B; Kueper, R; Hilgard, P; Gerken, G; Schlaak, JF (2013). "A combination of α-fetoprotein and des-γ-carboxy prothrombin is superior in detection of hepatocellular carcinoma". Digestion. 87 (2): 121–31. doi:10.1159/000346080. PMID 23406785.
- ↑ Lefrere JJ, Gozin D (1987). "Use of des-gamma-carboxyprothrombin in retrospective diagnosis of hidden intoxication of anticoagulants". J. Clin. Pathol. 40 (5): 589. doi:10.1136/jcp.40.5.589-b. PMC 1141034 . PMID 3584512.