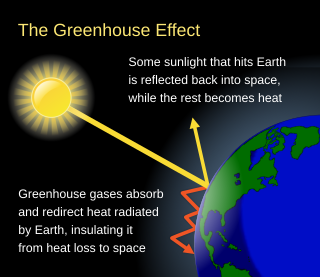
The greenhouse effect occurs when greenhouse gases in a planet's atmosphere trap some of the heat radiated from the planet's surface, raising its temperature. This process happens because stars emit shortwave radiation that passes through greenhouse gases, but planets emit longwave radiation that is partly absorbed by greenhouse gases. That difference reduces the rate at which a planet can cool off in response to being warmed by its host star. Adding to greenhouse gases further reduces the rate a planet emits radiation to space, raising its average surface temperature.

Global warming potential (GWP) is an index to measure of how much infrared thermal radiation a greenhouse gas would absorb over a given time frame after it has been added to the atmosphere. The GWP makes different greenhouse gases comparable with regards to their "effectiveness in causing radiative forcing". It is expressed as a multiple of the radiation that would be absorbed by the same mass of added carbon dioxide, which is taken as a reference gas. Therefore, the GWP is one for CO2. For other gases it depends on how strongly the gas absorbs infrared thermal radiation, how quickly the gas leaves the atmosphere, and the time frame being considered.

The Paleogene is a geologic period and system that spans 43 million years from the end of the Cretaceous Period 66 million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Neogene Period 23.03 Mya. It is the beginning of the Cenozoic Era of the present Phanerozoic Eon. The earlier term Tertiary Period was used to define the span of time now covered by the Paleogene Period and subsequent Neogene Period; despite no longer being recognized as a formal stratigraphic term, "Tertiary" still sometimes remains in informal use. Paleogene is often abbreviated "Pg".
Atmospheric pressure, also known as air pressure or barometric pressure, is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere is a unit of pressure defined as 101,325 Pa (1,013.25 hPa), which is equivalent to 1,013.25 millibars, 760 mm Hg, 29.9212 inches Hg, or 14.696 psi. The atm unit is roughly equivalent to the mean sea-level atmospheric pressure on Earth; that is, the Earth's atmospheric pressure at sea level is approximately 1 atm.
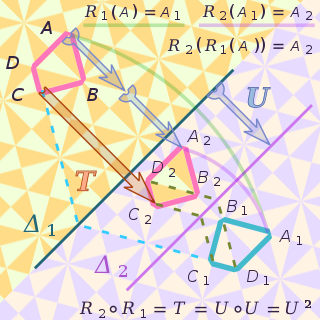
In mathematics, an isometry is a distance-preserving transformation between metric spaces, usually assumed to be bijective. The word isometry is derived from the Ancient Greek: ἴσος isos meaning "equal", and μέτρον metron meaning "measure". If the transformation is from a metric space to itself, it is a kind of geometric transformation known as a motion.
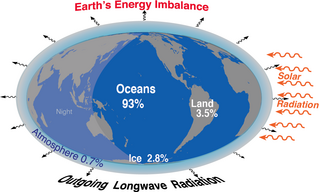
Earth's energy budget accounts for the balance between the energy that Earth receives from the Sun and the energy the Earth loses back into outer space. Smaller energy sources, such as Earth's internal heat, are taken into consideration, but make a tiny contribution compared to solar energy. The energy budget also accounts for how energy moves through the climate system. Because the Sun heats the equatorial tropics more than the polar regions, received solar irradiance is unevenly distributed. As the energy seeks equilibrium across the planet, it drives interactions in Earth's climate system, i.e., Earth's water, ice, atmosphere, rocky crust, and all living things. The result is Earth's climate.

The Group of Seven (G7) is an intergovernmental political & economic forum consisting of Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom and the United States; additionally, the European Union (EU) is a "non-enumerated member". It is organized around shared values of pluralism, liberal democracy, and representative government. G7 members are the major IMF advanced economies.

The NatureServe conservation status system, maintained and presented by NatureServe in cooperation with the Natural Heritage Network, was developed in the United States in the 1980s by The Nature Conservancy (TNC) as a means for ranking or categorizing the relative imperilment of species of plants, animals, or other organisms, as well as natural ecological communities, on the global, national or subnational levels. These designations are also referred to as NatureServe ranks, NatureServe statuses, or Natural Heritage ranks. While the Nature Conservancy is no longer substantially involved in the maintenance of these ranks, the name TNC ranks is still sometimes encountered for them.

The G20 or Group of 20 is an intergovernmental forum comprising 19 sovereign countries, the European Union (EU), and the African Union (AU). It works to address major issues related to the global economy, such as international financial stability, climate change mitigation and sustainable development.
Internet Low Bitrate Codec (iLBC) is a royalty-free narrowband speech audio coding format and an open-source reference implementation (codec), developed by Global IP Solutions (GIPS) formerly Global IP Sound. It was formerly freeware with limitations on commercial use, but since 2011 it is available under a free software/open source license as a part of the open source WebRTC project. It is suitable for VoIP applications, streaming audio, archival and messaging. The algorithm is a version of block-independent linear predictive coding, with the choice of data frame lengths of 20 and 30 milliseconds. The encoded blocks have to be encapsulated in a suitable protocol for transport, usually the Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP).
internet Speech Audio Codec (iSAC) is a wideband speech codec, developed by Global IP Solutions (GIPS). It is suitable for VoIP applications and streaming audio. The encoded blocks have to be encapsulated in a suitable protocol for transport, e.g. RTP.

Urodidae, whose species are commonly known as false burnet moths, is a family of moths in the lepidopteran order. It is the type genus in the superfamily, Urodoidea, with three genera, one of which, Wockia, occurs in Europe.
Agathiphaga is a genus of moths, known as kauri moths. It is the only living in the family Agathiphagidae. This caddisfly-like lineage of primitive moths was first reported by Lionel Jack Dumbleton in 1952, as a new genus of Micropterigidae.

Methane is a chemical compound with the chemical formula CH4. It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane on Earth makes it an economically attractive fuel, although capturing and storing it poses technical challenges due to its gaseous state under normal conditions for temperature and pressure.
G-Sat is a subscription-based direct-to-home (DTH) satellite television service commercially available in the Philippines. G-Sat is owned by Global Satellite Technology Services (GSTS), registered in the Philippines with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). G-Sat also carried pay TV channels from Hong Kong, Macau and Taiwan, which TV shows and movies subtitled in Cantonese and Mandarin.

In physics, a gauge theory is a type of field theory in which the Lagrangian, and hence the dynamics of the system itself, do not change under local transformations according to certain smooth families of operations. Formally, the Lagrangian is invariant.
Trade globalization is a type of economic globalization and a measure of economic integration. On a national scale, it loosely represents the proportion of all production that crosses the boundaries of a country, as well as the number of jobs in that country dependent upon external trade. On a global scale, it represents the proportion of all world production that is used for imports and exports between countries.

Gen.G, previously known as KSV Esports, is a professional esports organization with headquarters in Santa Monica, Seoul, and Shanghai. According to Forbes, Gen.G is the sixth most valuable esports organization in the world as of December 2020, worth US$185 million.











