
Ostracods, or ostracodes, are a class of the Crustacea, sometimes known as seed shrimp. Some 33,000 species have been identified, grouped into 7 valid orders. They are small crustaceans, typically around 1 mm (0.04 in) in size, but varying from 0.2 to 30 mm in the case of the marine Gigantocypris. The largest known freshwater species is Megalocypris princeps, which reach 8mm in length. In most cases, their bodies are flattened from side to side and protected by a bivalve-like valve or "shell" made of chitin, and often calcium carbonate. The family Entocytheridae and many planktonic forms do not have calcium carbonate. The hinge of the two valves is in the upper (dorsal) region of the body. Ostracods are grouped together based on shell and soft part morphology, and molecular studies have not unequivocally supported the group's monophyly. They have a wide range of diets, and the class includes carnivores, herbivores, scavengers and filter feeders, but most ostracods are deposit feeders.

Isopoda is an order of crustaceans. Members of this group are called Isopods and include both terrestrial and aquatic species such as woodlice. All have rigid, segmented exoskeletons, two pairs of antennae, seven pairs of jointed limbs on the thorax, and five pairs of branching appendages on the abdomen that are used in respiration. Females brood their young in a pouch under their thorax.

Bathynomus giganteus is a species of aquatic crustacean, of the order Isopoda. It is a member of the giant isopods (Bathynomus), and as such it is related—albeit distantly—to shrimps and crabs. It was the first Bathynomus species ever documented and was described in 1879 by French zoologist Alphonse Milne Edwards after the isopod was found in fishermen's nets off the coast of the Dry Tortugas in the Gulf of Mexico.
Epicaridea is a former suborder of isopods, now treated as an infraorder in suborder Cymothoida. They are ectoparasites that inhabit other crustaceans, namely ostracods, copepods, barnacles and malacostracans. Epicarideans are found globally. Epicaridea are generally less well researched than other isopods.

In zoology, deep-sea gigantism or abyssal gigantism is the tendency for species of deep-sea dwelling animals to be larger than their shallower-water relatives across a large taxonomic range. Proposed explanations for this type of gigantism include necessary adaptation to colder temperature, food scarcity, reduced predation pressure and increased dissolved oxygen concentrations in the deep sea. The harsh conditions and inhospitality of the underwater environment in general, as well as the inaccessibility of the abyssal zone for most human-made underwater vehicles, have hindered the study of this topic.

Archaeoniscus is a genus of prehistoric isopods that first appeared during the Bajocian stage of the Middle Jurassic. It is a widespread genus with a paleogeographic distribution encompassing the continental margin environments of the central Atlantic Ocean and the western Tethys Ocean. Fossils of Archaeoniscus suggest that this genus lived in diverse aquatic habitats, including the marine, paralic, and freshwater environments. While earlier descriptions suggested that it may have had an ectoparasitic association with fishes, some researchers argue that at least two species, A. aranguthyorum and A. coreaensis, lived a benthic free-living lifestyle based on morphological characteristics that are either unsuitable for or unrelated to parasitic behavior.
The Microcerberidea are a suborder of isopod crustaceans. They are less than 2 mm (0.079 in) long, and live interstitially. They may be found in the eastern Pacific Ocean, and around the coasts of South America, Africa, the Mediterranean Sea, and India.

Paracerceis sculpta is a species of marine isopod between 1.3 millimetres (0.05 in) and 10.3 mm (0.41 in) in length. The species lives mainly in the intertidal zone, and is native to the Northeast Pacific from Southern California to Mexico, but has since been introduced to many other countries. Adults are herbivorous and consume algae but juveniles are carnivorous and consume moulting females. They reproduce in sponges but do not feed near them.

Gibbonsia elegans, the spotted kelpfish, is a species of clinid native to subtropical waters of the Pacific Ocean from central California, U.S. to southern Baja California, Mexico. It prefers subtidal rocky habitats with seaweed down to a depth of about 56 metres (184 ft). This species can reach a maximum length of 16 centimetres (6.3 in) TL. This species feeds on benthic crustaceans, gastropods, and polychaete worms. The genus Gibbonsia is named after William P. Gibbons who was a naturalist in the California Academy of Science. It is found in three different colors depending on their habitat. Males and females do not show sexual dimorphism.
Hemioniscus balani, a species of isopod crustacean, is a widespread parasitic castrator of barnacles in the northern Atlantic Ocean. Its range extends from Norway to the Atlantic coast of France, and as far west as Massachusetts. It is also commonly found on the Pacific coast of North America; it is not known if the Pacific and Atlantic populations are the same species, or if the Pacific population exists following human-assisted introduction.
Serolidae is a family of isopod crustaceans, containing the following genera :

Ligia dilatata is a woodlouse in the family Ligiidae.
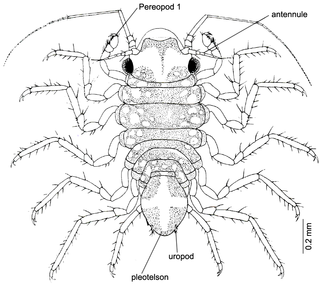
Uromunna sheltoni is a species of isopod first described by Brian Kensley in 1977. U. sheltoni is included in the genus Uromunna and family Munnidae. No subspecies are listed. The species was first collected by Peter Shelton of the University of Cape Town, for whom it is named.
Perisesarma guttatum, the red-claw mangrove crab, is a crab species in the genus Parasesarma and the family Sesarmidae. It is distributed in coastal brackish water habitats of the western Indian Ocean.

Anilocra capensis is a species of parasitic isopod in the family Cymothoidae. It is endemic to southern Africa. The species preferentially attaches itself to the hottentot seabream.

Pachymetopon blochii, the hottentot seabream or hottentot, is a species of sea bream in the family Sparidae, native to the southwestern coast of Africa.

Glyptidotea is a monotypic genus of isopod in the family Idoteidae. Its sole member is Glyptidotea lichtensteini, the keeled isopod, a medium-sized isopod found on the coast of southern Africa.

Exosphaeroma laeviusculum is a species of isopod in the family Sphaeromatidae, native to the west coast of southern Africa.

Deto is a genus of woodlice in the family Detonidae. Members of this genus can be found along the coasts in areas of New Zealand, Namibia, South Africa and Australia.

Notothenia cyanobrancha, the blue rockcod, bluegillnotothen, or bluegill rockcod, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes. It is native to the Kerguelen and Heard Islands in the Southern Ocean.
















