
The Brahmaputra is a trans-boundary river which flows through Tibet (China), Northeastern India, and Bangladesh. It is known as Brahmaputra or Luit in Assamese, Yarlung Tsangpo in Tibetan, the Siang/Dihang River in Arunachali, and Jamuna River in Bengali. It is the 9th largest river in the world by discharge, and the 15th longest.

Northeast India, officially known as the North Eastern Region (NER), is the easternmost region of India representing both a geographic and political administrative division of the country. It comprises eight states—Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland and Tripura, and the "brother" state of Sikkim.
Tezu is a census town and the headquarters of Lohit district in the Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh. It is the fifth largest town in Arunachal Pradesh and one of its most developed.

The Lohit River, which name came from the Assamese word Lohit meaning blood, also known as the Zayul Chu by the Tibetans and Tellu by the Mishmis, is a river in China and India, which joins the Brahmaputra River in the state of Assam. It is formed in the Zayul County of the Tibet Autonomous Region, through a merger of two rivers: the Kangri Karpo Chu, which originates in the Kangri Karpo range, and Zayul Chu, which originates to its northeast. The two rivers merge below the town of Rima. The combined river descends through this mountainous region and surges through Arunachal Pradesh in India for 200 kilometres (120 mi) before entering the plains of Assam where it is known as the Lohit River. Tempestuous and turbulent, and known as the river of blood partly attributable to the lateritic soil, it flows through the Mishmi Hills, to meet the Siang (Brahmaputra) at the head of the Brahmaputra valley.

Bhupen Hazarika was an Indian playback singer, lyricist, musician, poet, actor, artist, editor, filmmaker, professor and politician from Assam, widely known as Sudha Kontho. His songs were written and sung mainly in the Assamese language by himself, are marked by humanity and universal brotherhood and have been translated and sung in many languages, most notably in Bengali and Hindi.

Roing is the district headquarter of Lower Dibang Valley district in the Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh. It is the last major township at the north-eastern frontier of India.
The Ministry of Development of North Eastern Region is a Government of India ministry, established in September 2001, which functions as the nodal Department of the Central Government to deal with matters related to the socio-economic development of the eight States of Northeast India: Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Tripura and Sikkim. It acts as a facilitator between the Central Ministries/ Departments and the State Governments of the North Eastern Region in the economic development including removal of infrastructural bottlenecks, provision of basic minimum services, creating an environment for private investment and to remove impediments to lasting peace and security in the North Eastern Region.
The Trans-Arunachal Highway (TAH), which includes an existing 1,811 km (1,125 mi) route comprising NH-13 and parts of NH-15, NH-215 and SH-25, is an under-construction 2-lane more than 2,407 km (1,496 mi) long highway passing through 16 districts in Arunachal Pradesh state in India. It runs from LAC in Tawang in northwest to Kanubari in southeast at tri-junction of Assam-Nagaland-Arunachal Pradesh. It connects at least 16 districts of Arunachal Pradesh.
Rupai Siding is a fast developing township situated in the district of Tinsukia in Assam,(in North East) India. The place is approximately 540 km from the state capital. It was a small village about 50 years ago, which is now the Industrial Township surrounded by numerous Tea gardens and Factories and Other Allied Industries. It is said that it had one of the oldest railway tracks until few years back which was used by the Britishers to transport goods and materials. This railway track connects Dibrugarh to Dangari and runs through Rupai and hence the place is a siding and came to be known as RUPAI SIDING. Beesakopie Tea Factory, the largest tea factory in Asia is very near.

The Subansiri is a trans-Himalayan river and a tributary of the Brahmaputra River that flows through Tibet's Lhuntse County in the Shannan Prefecture, and the Indian states of Arunachal Pradesh and Assam. The Subansiri is approximately 518 kilometres (322 mi) long, with a drainage basin 32,640 square kilometres (12,600 sq mi). It is the largest tributary of the Brahmaputra contributing 7.92% of the Brahmaputra's total flow.

The Bogibeel Bridge is a combined road and rail bridge over the Brahmaputra River in the northeastern Indian state of Assam between Dhemaji district and Dibrugarh district, which was started in the year 2002 and took a total of 200 months to complete, Bogibeel river bridge is the longest rail-cum-road bridge in India, measuring 4.94 kilometres over the Brahmaputra river. As it is situated in an earthquake-prone area it is India's first bridge to have fully welded steel-concrete support beams that can withstand earthquakes of magnitudes up to 7 on the Richter scale. It is Asia's second longest rail-cum-road bridge and has a serviceable period of around 120 years.

The Rangiya-Murkongselek section is a 450 km (280 mi) long railway line connecting Rangiya in Kamrup district with Murkongselek in Dhemaji district in the Indian state of Assam. The entire section is under the jurisdiction of Northeast Frontier Railway.
Arunachal Frontier Highway (AFH), officially notified as the National Highway NH-913 and also called Bomdila-Vijaynagar Highway (BVH), connecting Bomdila Airstrip ALG & HQ in northwest to Vijaynagar Airstrip ALG & HQ in southeast via Nafra HQ-Sarli HQ-Huri Helipad ALG & HQ-Nacho HQ-Mechuka Airstrip ALG & HQ-Monigong HQ-Jido -Hunli HQ-Hayuliang Airstrip ALG HQ-Chenquenty-Hawai HQ-Miao HQ including 800 km greenfield section and network of new tunnels & bridges, is a 2-lane paved-shoulder under-construction national highway along the India-China LAC-McMahon Line border in the Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh. The 1,748 km-long (1,086 mi) highway itself will cost ₹27,000 crore and total cost including 6 additional inter-corridors is ₹40,000 crore. In some places, this highway will run as close as 20 km from the LAC. To be constructed by MoRTH in 9 packages, all packages will be approved by the end of fy 2024-25 and construction will be completed in 2 years by 31 March 2027. Of the total route, 800km is greenfield, rest brownfield will be upgraded and tunnels will be built. This highway in the north & east Arunachal along the China border, would complement the Trans-Arunachal Highway and the Arunachal East-West Corridor as major highways spanning the whole state, pursuing the Look East connectivity policy.
East-West Industrial Corridor Highway of Arunachal Pradesh, a 2-lane and 966.78 km long including existing 274.20 km Pasighat-Manmao route, is a proposed highway across lower foothills of Arunachal Pradesh state in India from Bhairabkunda in Assam at tri-junction of Bhutan-Assam-Arunachal Pradesh in west to Kanubari tri-junction of Nagaland-Assam-Arunachal Pradesh in east.

Jagadish Bhuyan is an Indian student leader and politician associated with the Assam Movement, who served two terms as an MLA of the Assam Legislative Assembly from the Sadiya legislative assembly constituency in Tinsukia district, and as tourism minister in the Prafulla Kumar Mahanta government from 1998 to 2001. Originally a leader in the Asom Gana Parishad, in June 2015 he abandoned the faltering AGP for the Bharatiya Janata Party. He served as the chairman of Assam Petro-Chemicals until 2019.

The Dibang River Bridge is a beam bridge across Dibang River which connects Bomjir and Malek villages and provides all-weather connectivity between Dambuk and Roing in eastern part of Arunachal Pradesh, India. At 6.2 km long, it is the second-longest bridge above water in India and was completed in 2018 as part of NH13 Trans-Arunachal Highway. This strategically important bridge helps Indian military combat anti-national activities and Chinese military threat in the easter sector of Line of Actual Control border areas. It is known as "Sikang" in Adi Language and "Talon" in Idu Mishmi language.
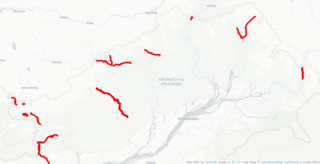
India–China Border Roads is a Government of India project for developing infrastructure along the Sino-Indian border by constructing strategic roads, including bridges and tunnels. The ICBR project is largely in response to Chinese infrastructure development along the borderlands with India.

The National Highways and Infrastructure Development Corporation Limited (NHIDCL) is a fully owned company of the Government of India, set up in 2014 and is responsible for management of a network of over 10,000 km of National Highways out of 1,15,000 km in India. It is a nodal agency of the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways. Krishan Kumar (IAS) is the present Managing Director of NHIDCL since 14th February 2024.
Sumitra Hazarika is an Indian activist. She was born in a village near to Titabor in Assam, India. She was married to Manindra Gogoi until his death in 2015 and was sister-in-law to Bhupen Hazarika. She is president of the Mission for Integration, Gender Equalization, Harmony and Fight against Threat (MIGHT). She also works for the Assam State Commission for Women. In 2022, she filed a first information report (FIR) against politician Sherman Ali Ahmed regarding his televised comments on rape. In recognition of her achievements, Hazarika received the Nari Shakti Puraskar on 8 March 2017 from President Pranab Mukherjee. She also was awarded the Prag Perona in 2018.














