
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom bonded to two organyl groups. They have the general formula R−O−R′, where R and R′ represent the organyl groups. Ethers can again be classified into two varieties: if the organyl groups are the same on both sides of the oxygen atom, then it is a simple or symmetrical ether, whereas if they are different, the ethers are called mixed or unsymmetrical ethers. A typical example of the first group is the solvent and anaesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether". Ethers are common in organic chemistry and even more prevalent in biochemistry, as they are common linkages in carbohydrates and lignin.
In organic chemistry, butyl is a four-carbon alkyl radical or substituent group with general chemical formula −C4H9, derived from either of the two isomers (n-butane and isobutane) of butane.
In chemistry, radical initiators are substances that can produce radical species under mild conditions and promote radical reactions. These substances generally possess weak bonds—bonds that have small bond dissociation energies. Radical initiators are utilized in industrial processes such as polymer synthesis. Typical examples are molecules with a nitrogen-halogen bond, azo compounds, and organic and inorganic peroxides.

tert-Butyl alcohol is the simplest tertiary alcohol, with a formula of (CH3)3COH (sometimes represented as t-BuOH). Its isomers are 1-butanol, isobutanol, and butan-2-ol. tert-Butyl alcohol is a colorless solid, which melts near room temperature and has a camphor-like odor. It is miscible with water, ethanol and diethyl ether.

In organic chemistry, organic peroxides are organic compounds containing the peroxide functional group. If the R′ is hydrogen, the compounds are called hydroperoxides, which are discussed in that article. The O−O bond of peroxides easily breaks, producing free radicals of the form RO•. Thus, organic peroxides are useful as initiators for some types of polymerization, such as the acrylic, unsaturated polyester, and vinyl ester resins used in glass-reinforced plastics. MEKP and benzoyl peroxide are commonly used for this purpose. However, the same property also means that organic peroxides can explosively combust. Organic peroxides, like their inorganic counterparts, are often powerful bleaching agents.

tert-Butyllithium is a chemical compound with the formula (CH3)3CLi. As an organolithium compound, it has applications in organic synthesis since it is a strong base, capable of deprotonating many carbon molecules, including benzene. tert-Butyllithium is available commercially as solutions in hydrocarbons (such as pentane); it is not usually prepared in the laboratory.

The tert-butyloxycarbonyl protecting group or tert-butoxycarbonyl protecting group is an acid-labile protecting group used in organic synthesis.
In chemistry, dehydrohalogenation is an elimination reaction which removes a hydrogen halide from a substrate. The reaction is usually associated with the synthesis of alkenes, but it has wider applications.
2-Methyl-2-nitrosopropane (MNP or t-nitrosobutane) is the organic compound with the formula (CH3)3CNO. It is a blue liquid that is used in chemical research as a spin trap, i.e. it binds to radicals.

Trimethyltin chloride is an organotin compound with the formula (CH3)3SnCl. It is a white solid that is highly toxic and malodorous. It is susceptible to hydrolysis.
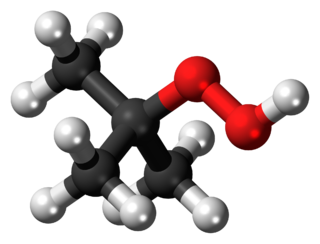
tert-Butyl hydroperoxide (tBuOOH) is the organic compound with the formula (CH3)3COOH. It is one of the most widely used hydroperoxides in a variety of oxidation processes, like the Halcon process. It is normally supplied as a 69–70% aqueous solution. Compared to hydrogen peroxide and organic peracids, tert-butyl hydroperoxide is less reactive and more soluble in organic solvents. Overall, it is renowned for the convenient handling properties of its solutions. Its solutions in organic solvents are highly stable.
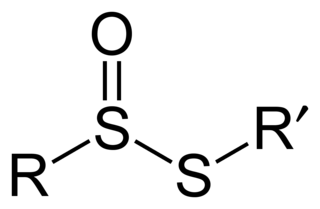
In organosulfur chemistry, thiosulfinate is a functional group consisting of the linkage R-S(O)-S-R. Thiolsulfinates are also named as alkanethiosulfinic acid esters.

Jacobsen's catalyst is the common name for N,N'-bis(3,5-di-tert-butylsalicylidene)-1,2-cyclohexanediaminomanganese(III) chloride, a coordination compound of manganese and a salen-type ligand. It is used as an asymmetric catalyst in the Jacobsen epoxidation, which is renowned for its ability to enantioselectively transform prochiral alkenes into epoxides. Before its development, catalysts for the asymmetric epoxidation of alkenes required the substrate to have a directing functional group, such as an alcohol as seen in the Sharpless epoxidation. This compound has two enantiomers, which give the appropriate epoxide product from the alkene starting material.
tert-Amyl methyl ether (TAME) is an ether used as a fuel oxygenate. TAME derives from C5 distillation fractions of naphtha. It has an ethereous odor. Unlike most ethers, it does not require a stabilizer as it does not form peroxides on storage.

The Jones oxidation is an organic reaction for the oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols to carboxylic acids and ketones, respectively. It is named after its discoverer, Sir Ewart Jones. The reaction was an early method for the oxidation of alcohols. Its use has subsided because milder, more selective reagents have been developed, e.g. Collins reagent.

Bis(trifluoromethyl)peroxide (BTP) is a fluorocarbon derivative first produced by Frédéric Swarts. It has some utility as a radical initiator for polymerisation reactions. BTP is unusual in the fact that, unlike many peroxides, it is a gas, is non-explosive, and has good thermal stability.
Di-tert-butyl-iminodicarboxylate is an organic compound that can be described with the formula [(CH3)3COC(O)]2NH. It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents. The compound is used as a reagent for the preparation of primary amines from alkyl halides. It was popularized as an alternative to the Gabriel synthesis for the same conversion. Amines can also be prepared from alcohols by dehydration using the Mitsunobu reaction.

tert-Butyl peroxybenzoate (TBPB) an organic compound with the formula C6H5CO3CMe3 (Me = CH3). It is the most widely produced perester; it is an ester of peroxybenzoic acid (C6H5CO3H). It is often used as a radical initiator in polymerization reactions, such as the production of LDPE from ethylene, and for crosslinking, such as for unsaturated polyester resins.

2,4,6-Tri-tert-butylphenol (2,4,6-TTBP) is a phenol symmetrically substituted with three tert-butyl groups and thus strongly sterically hindered. 2,4,6-TTBP is a readily oxidizable aromatic compound and a weak acid. It oxidizes to give the deep-blue 2,4,6-tri-tert-butylphenoxy radical. 2,4,6-TTBP is related to 2,6-di-tert-butylphenol, which is widely used as an antioxidant in industrial applications. These compounds are colorless solids.

Tetramethoxymethane is a chemical compound which is formally formed by complete methylation of the hypothetical orthocarbonic acid C(OH)4.















