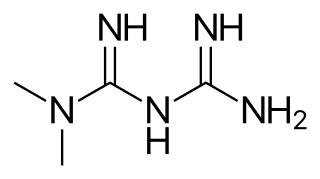
Metformin, sold under the brand name Glucophage, among others, is the main first-line medication for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, particularly in people who are overweight. It is also used in the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome, and is sometimes used as an off-label adjunct to lessen the risk of metabolic syndrome in people who take antipsychotic medication. It has been shown to inhibit inflammation, and is not associated with weight gain. Metformin is taken by mouth.

The connecting peptide, or C-peptide, is a short 31-amino-acid polypeptide that connects insulin's A-chain to its B-chain in the proinsulin molecule. In the context of diabetes or hypoglycemia, a measurement of C-peptide blood serum levels can be used to distinguish between different conditions with similar clinical features.

Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), also called somatomedin C, is a hormone similar in molecular structure to insulin which plays an important role in childhood growth, and has anabolic effects in adults. In the 1950s IGF-1 was called "sulfation factor" because it stimulated sulfation of cartilage in vitro, and in the 1970s due to its effects it was termed "nonsuppressible insulin-like activity" (NSILA).

The Canadian Medical Association Journal is a peer-reviewed open-access general medical journal published by the Canadian Medical Association. It publishes original clinical research, analyses and reviews, news, practice updates, and editorials.
Thrifty phenotype refers to the correlation between low birth weight of neonates and the increased risk of developing metabolic syndromes later in life, including type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. Although early life undernutrition is thought to be the key driving factor to the hypothesis, other environmental factors have been explored for their role in susceptibility, such as physical inactivity. Genes may also play a role in susceptibility of these diseases, as they may make individuals predisposed to factors that lead to increased disease risk.

Type 1 diabetes (T1D), formerly known as juvenile diabetes, is an autoimmune disease that occurs when pancreatic cells are destroyed by the body's immune system. In healthy persons, beta cells produce insulin. Insulin is a hormone required by the body to store and convert blood sugar into energy. T1D results in high blood sugar levels in the body prior to treatment. Common symptoms include frequent urination, increased thirst, increased hunger, weight loss, and other complications. Additional symptoms may include blurry vision, tiredness, and slow wound healing. While some cases take longer, symptoms usually appear within weeks or a few months.
Slowly evolving immune-mediated diabetes, or latent autoimmune diabetes in adults (LADA), is a form of diabetes that exhibits clinical features similar to both type 1 diabetes (T1D) and type 2 diabetes (T2D), and is sometimes referred to as type 1.5 diabetes. It is an autoimmune form of diabetes, similar to T1D, but patients with LADA often show insulin resistance, similar to T2D, and share some risk factors for the disease with T2D. Studies have shown that LADA patients have certain types of antibodies against the insulin-producing cells, and that these cells stop producing insulin more slowly than in T1D patients. Since many people develop the disease later in life, it is often misdiagnosed as type 2 diabetes.

HNF1 homeobox B, also known as HNF1B or transcription factor 2 (TCF2), is a human gene.

Diabetes Care is a monthly peer-reviewed medical journal published since 1978 by the American Diabetes Association. The journal covers research in the following five categories: 1) clinical care/education/nutrition/psychosocial research, 2) epidemiology/health services research, 3) emerging treatments and technologies, 4) pathophysiology/complications, and 5) cardiovascular and metabolic risk. The journal also publishes clinically relevant review articles, letters to the editor, and commentaries.
MODY 3 or HNF1A-MODY is a form of maturity-onset diabetes of the young. It is caused by mutations of the HNF1-alpha gene, a homeobox gene on human chromosome 12. This is the most common type of MODY in populations with European ancestry, accounting for about 70% of all cases in Europe. HNF1α is a transcription factor that is thought to control a regulatory network important for differentiation of beta cells. Mutations of this gene lead to reduced beta cell mass or impaired function. MODY 1 and MODY 3 diabetes are clinically similar. About 70% of people develop this type of diabetes by age 25 years, but it occurs at much later ages in a few. This type of diabetes can often be treated with sulfonylureas with excellent results for decades. However, the loss of insulin secretory capacity is slowly progressive and most eventually need insulin.
Douglas L. Coleman was a scientist and professor emeritus at the Jackson Laboratory, in Bar Harbor, Maine. His work predicted that there exists a hormone that can cause mice to feel full, and that a mutation in the gene encoding this hormone can lead to obesity. The gene and corresponding hormone were discovered about 20 years later by Jeffrey M. Friedman, Rudolph Leibel, and their research teams at Rockefeller University, which Friedman named leptin.
Complications of diabetes are secondary diseases that are a result of elevated blood glucose levels that occur in diabetic patients. These complications can be divided into two types: acute and chronic. Acute complications are complications that develop rapidly and can be exemplified as diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state (HHS), lactic acidosis (LA), and hypoglycemia. Chronic complications develop over time and are generally classified in two categories: microvascular and macrovascular. Microvascular complications include neuropathy, nephropathy, and retinopathy; while cardiovascular disease, stroke, and peripheral vascular disease are included in the macrovascular complications.
Derek LeRoith is a South African endocrinologist. He is a Professor of Medicine and the current Chief of the Hilda and J. Lester Gabrilove, M.D. Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Bone Disease and Director of the Metabolism Institute of the Mount Sinai Medical Center in New York City. He is an international expert in insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1).
Bernhard Ludvik is a Specialist in Internal Medicine, board certified in Endocrinology and Metabolism. He is currently an associate professor of medicine at the Medical University of Vienna. He serves as the deputy head of the Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism at the General Hospital Vienna.
The European Journal of Preventive Cardiology is a peer-reviewed medical journal that covers research on the cardiovascular system. The journal's editor-in-chief is Prof Victor Aboyans. It was established in 1994 as the European Journal of Cardiovascular Prevention & Rehabilitation and obtained its current title in 2012. It is currently published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.

Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough insulin, or the cells of the body becoming unresponsive to the hormone's effects. Classic symptoms include polydipsia, polyuria, weight loss, and blurred vision. If left untreated, the disease can lead to various health complications, including disorders of the cardiovascular system, eye, kidney, and nerves. Diabetes accounts for approximately 4.2 million deaths every year, with an estimated 1.5 million caused by either untreated or poorly treated diabetes.

Pierre De Meyts is a Belgian physician and biochemist known for his research on fine chemical and kinetic aspects of ligand-receptor interaction, subunit assembly, and specific metabolic effects of hormones typically causing receptor tyrosine kinase activation such as insulin and insulin-like growth factors (IGFs). He has also studied receptor signalling for other peptide hormones such as growth hormone and relaxin, and key pathophysiological aspects of diabetes mellitus. De Meyts held professorial posts for over three decades at several European and United States institutions and currently is an emeritus professor in the Science Faculty at the Université catholique de Louvain. While living in Denmark (1990-2010) he occupied executive research positions at Novo Nordisk. De Meyts is also known as a science cartoonist.
Professor Aly Saad, is a professor of cardiology at Zagazig University and a member of the higher committee of promotion of professors and assistant professors of cardiovascular diseases and critical care subspecialty in Egypt.

The Journal of Diabetes Investigation is a bimonthly peer-reviewed medical journal covering the study of diabetes. It was established in 2010 and is published by John Wiley & Sons on behalf of the Asian Association for the Study of Diabetes, of which it is the official journal. The editor-in-chief is Nigishi Hotta. In 2014, the journal became open-access. According to the Journal Citation Reports, the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 4.232.

Brian M. Frier is a Scottish physician, diabetologist, clinical scientist, and an Honorary Professor of Diabetes at the University of Edinburgh. He is best known for his many scientific contributions to the pathophysiological understanding of hypoglycemia, a common adverse effect of insulin therapy in diabetic patients whose societal impact has deserved increasing media attention worldwide. His honors include the R.D. Lawrence Lecture of the British Diabetic Association in 1986, the Banting Memorial Lecture at Diabetes UK in 2009, the Camillo Golgi Prize and lecture at the 53rd annual EASD conference in 2017, and the Michael Somogyi Award from the Hungarian Diabetes Association in 2004. Frier is a science book author and editor, and a science journal Chief editor. He is also regarded as an authority on the field of driving and diabetes. In 2023, Frier was accorded Honorary Life Membership by the European Association of Diabetes.









