
Tankwa Karoo National Park is a national park in South Africa. The park lies about 70 km west of Sutherland and along the border of the Northern Cape and Western Cape in Succulent Karoo habitat; a biodiversity hotspot and one of the most arid regions of South Africa.

Ardea is a genus of herons. These herons are generally large in size, typically 80–100 cm or more in length.

The terrestrial fauna of the Cocos (Keeling) Islands is unsurprisingly depauperate, because of the small land area of the islands, their lack of diverse habitats, and their isolation from large land-masses. However, the fauna dependent on marine resources is much richer.

Nature's Valley is a holiday resort and small village on the Garden Route along the southern Cape coast of South Africa. Nature's Valley lies between the Salt River, the foothills of the Tsitsikamma Mountains, the Indian Ocean and the Groot River lagoon. Nature's Valley has a balmy climate and is surrounded by the de Vasselot Nature Reserve which is part of the Tsitsikamma Park, and in turn part of the Garden Route National Park.

Rietvlei Nature Reserve, located in southern Pretoria, is about 4,000 hectares (40 km2) in size, and includes the entirety of the Rietvlei Dam which impounds the Rietvlei River, in Gauteng, South Africa. The reserve is wedged between the R21 highway on the western side and the R50 (Delmas-Bapsfontein) road on the north-east. The mean elevation above sea level is approximately 1,525 meters, with the highest point at 1,542 m and the lowest at 1,473 m, the dam’s outflow in Sesmylspruit. The reserve covers a surface area of approximately 4,003 ha or 40 km2, of which the dam constitutes some 20ha. A network of roads criss-cross the entire area, which facilitates access to visitors and management.
Sipacate-Naranjo National Park is located along the Pacific coast of Escuintla in Guatemala. The park includes mangrove forests, lagoons and sandy beaches and covers an area of 20 km long and 1 km wide, stretching between the coastal towns of Sipacate and El Naranjo.
Moeyungyi Wetland Wildlife Sanctuary is a protected area in Myanmar's Bago Division, covering an area of 103.6 km2 (40.0 sq mi). It was established in 1988 and gained the status of an Important Bird Area in 2003.

Ilanda Wilds is a nature reserve along the aManzimtoti River in the town of eManzimtoti, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. This small area of land contains various habitat types, ranging from steep rocky slopes to various riverine habitats, forest and small patches of grassland.

The Rietvlei Wetland Reserve is a 663-hectare (1,640-acre) nature reserve situated in Table View, Western Cape, South Africa. It is managed by the City of Cape Town's Environmental Resource Management Department.
The Milnerton Racecourse Nature Reserve is a lowland conservation area located in the City of Cape Town, South Africa.
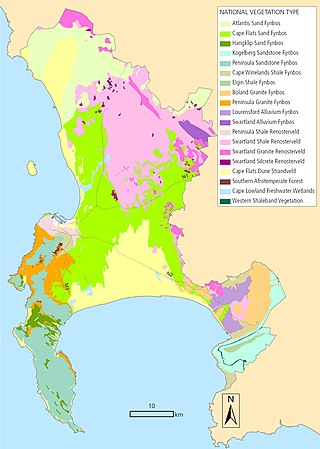
The biodiversity of Cape Town is the variety and variability of life within the City of Cape Town, excluding the Prince Edward Islands. The terrestrial vegetation is particularly diverse and much of it is endemic to the city and its vicinity. Terrestrial and freshwater animals are heavily impacted by urban development and habitat degradation. Marine life of the waters immediately adjacent to the city along the Cape Peninsula and in False Bay is also diverse, and while also impacted by human activity, the habitats are relatively intact.

The Table Bay Nature Reserve is an 880-hectare (2,200-acre) nature reserve in Milnerton, Western Cape, South Africa. It consists of several smaller constituent reserves including Rietvlei Wetland Reserve, Diep River Fynbos Corridor, Zoarvlei Wetlands, Milnerton Racecourse Nature Reserve, and Milnerton Lagoon, as well as surrounding protected areas. These adjacent reserves were amalgamated on 27 June 2012, in order to improve the biodiversity management in the built-up area. It is managed by the City of Cape Town's Environmental Resource Management Department, with offices at Rietvlei.

Kaludiya Pokuna Archeological Forest Site is a forest with archeological remains in Kandalama, in the Dry Zone of Sri Lanka. The site has been handed over to the Girls' High School, Kandy in accordance with the "Urumaya Thani Nokaramu" program organized by the Department of Archeology. For the first time in Sri Lanka, a school was given custody of an archeological site.
Nanda lake is a Ramsar site located in the Indian state of Goa. It is situated in Curchorem. Covering an area of 0.42 square kilometres, it is the only Ramsar wetland site in Goa.










