| Blaauwberg Nature Reserve | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| Location | Blaauwberg, Western Cape |
| Coordinates | 33°46′05″S18°27′10″E / 33.76806°S 18.45278°E |
| Area | 1,445 ha (3,570 acres) 2,000 ha (4,900 acres) planned |
| Established | 2007 |
| City of Cape Town - Blaauwberg Nature Reserve | |
Blaauwberg Nature Reserve was proclaimed a local and provincial nature reserve in 2007. The reserve has views down fynbos slopes, across the city,[ where? ] to seven kilometres of rocky and sandy coastline and the ocean and beyond. The reserve presents itself as one of the few viewpoints in the world from where you can see two proclaimed world heritage sites, namely Table Mountain and Robben Island.[ citation needed ]
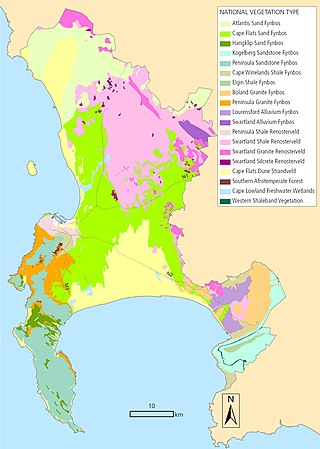
Blaauwberg Nature Reserve conserves three threatened vegetation types: Cape Flats Dune Strandveld (endangered), Swartland Shale Renosterveld (critically endangered) and Cape Flats Sand Fynbos (critically endangered). The rich biodiversity embraces a wetland, 624 plant species, 41 mammal species (including whales, dolphins and seals), 166 bird species, 30 reptile species and four amphibians. The reserve is one of the few City of Cape Town nature reserves where it is possible to find white-tailed rat (Mystromys albicaudatus) and aardvark (Orycteropus afer).
The holotype of Blaauwberg dwarf burrowing skink (Scelotes montispectus) was collected within Blaauwberg Nature Reserve. Besides the population of white-tailed rat, which is listed as endangered in the Red List of mammals of South Africa, another seven Red List fauna species occur here.[ citation needed ]
Within the current 1,445 ha, there is evidence of early human occupation,[ citation needed ] with shell middens dating back approximately 15,000 years. The reserve also conserves the site of the 1806 Battle of Blaauwberg, when the British took possession of the Cape from the Dutch for the second time and retained ownership until South Africa's independence. On Blaauwberg Hill, several buildings were constructed during World War II, including a radar station, a lookout and a mess room.
Since the then Blaauwberg Conservation Area's (BCA) inception, conservation in the area has progressed rapidly.[ citation needed ] Simple bollards in the coastal parking areas have stopped 4x4s from accessing and ultimately driving on the beach, and, already, the endangered vegetation has recovered and the African oystercatcher (Haematopus moquini) has since returned. Illegal vehicles had not only endangered the vegetation and oystercatcher, but had destroyed a number of the shell middens.[ citation needed ]
The conservation area is also used for recreational activities such as surfing, hiking, wind surfing, whale watching and picnics. [1]