

Cape Flats Sand Fynbos (CFSF), previously known as Sand Plain Fynbos, is a critically endangered vegetation type that occurs only within the city of Cape Town. Less than 1% of this unique lowland fynbos vegetation is conserved. [1]


Cape Flats Sand Fynbos (CFSF), previously known as Sand Plain Fynbos, is a critically endangered vegetation type that occurs only within the city of Cape Town. Less than 1% of this unique lowland fynbos vegetation is conserved. [1]
This is the richest and most diverse type of Sand Fynbos. It also has the highest number of threatened plant species. It is the wettest and coolest of all West Coast Sand Fynbos, growing primarily in deep, white, acidic sands. It is dominated by Proteoid and Restioid fynbos, but Ericaceous fynbos also occurs in wetter areas and Asteraceous fynbos in drier spots. In winter, seasonal wetlands appear in many areas, and mists often cover the landscape. [2]
Lying as it does entirely within the limits of Cape Town, over 85 percent of what was once Cape Town's commonest vegetation type is now destroyed and covered by urban sprawl. Half of what remains is badly infested with invasive alien plants (Acacia saligna, Acacia cyclops, Pinus, Eucalyptus and Kikuyu grass), and less than 1 percent is actually statutorily conserved.
Surviving pockets exist in several small nature reserves within the city, such as Rondevlei, Kenilworth Racecourse, Rondebosch Common and Tokai Park. These are identified as “Core Conservation Sites”. However, these sites alone are too small to preserve this vegetation type, and they themselves are threatened by invasive alien plants and the destructive practise of mowing (which eliminates all the tall and serotinous species).
Nature preserves with Cape Flats Sand Fynbos habitat include:
Historically, areas of Cape Town that were not developed for housing were often planted with commercial plantations of invasive European Pines. A fire at Tokai Park in 1998 revealed that this pine plantation is located on top of intact CFSF seed beds from its original vegetation. [3] To date over 340 indigenous plants have emerged from the seed bank, and 22 threatened plant species and 2 threatened amphibian species are present. [4]
Cape Flats Sand Fynbos is particularly rich in Protea and Erica species, many of which are endemic to this vegetation type and occur nowhere else. This was also the habitat of several species of plant which are now extinct, such as the Aspalathus variegata (the Cape Flats Capegorse), Erica pyramidalis (the Pyramid Heath), Erica turgida (the Showy Heath), Erica verticillata (the Whorl Heath) and Liparia graminifolia (Grass Mountainpea). [5] [6]



Fynbos is a small belt of natural shrubland or heathland vegetation located in the Western Cape and Eastern Cape provinces of South Africa. This area is predominantly coastal and mountainous, with a Mediterranean climate and rainy winters. The fynbos ecoregion is within the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub biome. In fields related to biogeography, fynbos is known for its exceptional degree of biodiversity and endemism, consisting of about 80% species of the Cape floral kingdom, where nearly 6,000 of them are endemic. This land continues to face severe human-caused threats, but due to the many economic uses of the fynbos, conservation efforts are being made to help restore it.

The Rondevlei Nature Reserve is located in Grassy Park, Zeekoevlei and Lavenderhill, suburbs of Cape Town, South Africa. The bird sanctuary covers approximately 290 hectares of mostly permanent wetland and consists of a single large brackish lagoon. The nature reserve is among the most important wetlands for birds in South Africa despite being situated directly alongside the Zeekoevlei. A number of islands on the vlei act as vital breeding sites. Rondevlei is home to about 230 bird species, a variety of small mammals and reptiles like caracal, porcupine, Cape fox, grysbuck, steenbuck and mongoose, as well as a hippopotamus population which was re-introduced in 1981 as a means to control an alien grass species from South America, which had covered the shoreline and was threatening to engulf the vlei itself. It boasts unusual and threatened ecosystems like strandveld, sand plains fynbos, Cape lowland wetland vegetation and indigenous coastal fynbos vegetation with unique plants found nowhere else in the world.

The Cape Floral Region is a floristic region located near the southern tip of South Africa. It is the only floristic region of the Cape Floristic Kingdom, and includes only one floristic province, known as the Cape Floristic Province.

Newlands Forest is a conservancy area on the eastern slopes of Table Mountain, beside the suburb of Newlands, Cape Town. It is owned and maintained by the Table Mountain National Parks Board, along with the City Parks Department of Cape Town, and includes a Fire Station, Nursery and Reservoir.

Rondebosch Common is an open common of about 40 hectares in Rondebosch, Cape Town in South Africa. A common is defined as "A piece of open land for public use, esp. in a village or town." It contains one of the few surviving pockets of the critically endangered “Cape Flats Sand Fynbos” vegetation type, which exists nowhere else in the world.
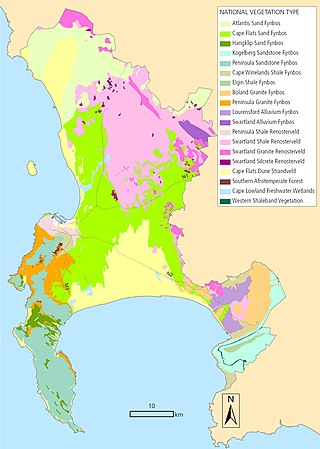
The Biodiversity of Cape Town is the variety and variability of life within the geographical extent of the City of Cape Town metropolitan municipality, excluding the Prince Edward Islands. The terrestrial vegetation is particularly diverse and much of it is endemic to the city and its vicinity. Terrestrial and freshwater animal life is heavily impacted by urban development and habitat degradation. Marine life of the waters immediately adjacent to the city along the Cape Peninsula and in False Bay is also diverse, and while also impacted by human activity, the habitats are relatively intact.

Cape Flats Dune Strandveld is an endangered vegetation type. This is a unique type of Cape Strandveld that is endemic to the coastal areas around Cape Town, including the Cape Flats.

Lourensford Alluvium Fynbos is a critically endangered vegetation type that is endemic to Cape Town. Though closest to Fynbos, it has characteristics of both Fynbos and Renosterveld vegetation and is thus actually a unique hybrid vegetation type.

Peninsula Granite Fynbos is an endangered Fynbos vegetation type which is endemic to the city of Cape Town and occurs nowhere else. It is a unique type of tall, dense and diverse scrubland, scattered with trees. It can be found all along the belt of granite that encircles Table Mountain.

Swartland Shale Renosterveld is a critically endangered vegetation type of the Western Cape, South Africa.

Kenilworth Racecourse Conservation Area is a 52-hectare (130-acre) nature reserve, situated in the centre of Kenilworth Racecourse, in Cape Town, South Africa. Due to its location, it has been left undisturbed for more than 100 years, making it now the best preserved patch of “Cape Flats Sand Fynbos” in the world.
Witzands Aquifer Nature Reserve is a 3,000-hectare (7,400-acre) protected natural area in Cape Town, South Africa, located on the city’s northern outskirts. This reserve protects an important part of Cape Town’s natural and cultural heritage, including the Atlantis Aquifer.

Durbanville Nature Reserve is a 6-hectare (15-acre) piece of protected land, located next to the Durbanville Racecourse in the Western Cape, South Africa.
Blaauwberg Nature Reserve was proclaimed a local and provincial nature reserve in 2007. The reserve has views down fynbos slopes, across the city, to seven kilometres of rocky and sandy coastline and the ocean and beyond. The reserve presents itself as one of the few viewpoints in the world from where you can see two proclaimed world heritage sites, namely Table Mountain and Robben Island.

Kogelberg Nature Reserve is a nature reserve of 3,000 ha comprising the Kogelberg Mountain Range, to the east of Cape Town, South Africa.

Cape Lowland Freshwater Wetland is a critically endangered vegetation type of the Western Cape, South Africa.

Erica verticillata is a species of Erica that was naturally restricted to the city of Cape Town but is now classified as Extinct in the Wild.

Erica turgida, the showy heath or Kenilworth heath, is a species of Erica that was naturally restricted to the city of Cape Town, South Africa, but is now classified as Extinct in the Wild.

Tokai Park, previously known as "Tokai Forest", is a small wing, about 600 ha, of the greater Table Mountain National Park in Cape Town, South Africa. Tokai Park is made up of two sections: upper and lower Tokai Park. Lower Tokai Park is flat, and characterized by the threatened Cape Flats Sand Fynbos. Upper Tokai Park is on the slopes of Constantiaberg Mountain, and consists of conservation area as well as the Tokai Arboretum. Upper Tokai Park is characterized by Peninsula Granite Fynbos, Peninsula Sandstone Fynbos and Afromontane Forest and noted for its diversity.