 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
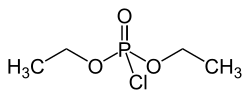
| Preferred IUPAC name Diethyl phosphorochloridate | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.011.270 |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| (C2H5O)2P(O)Cl | |
| Molar mass | 172.54 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.1915 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 60 °C (140 °F; 333 K) (2 mm Hg) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Diethyl chlorophosphate is an organophosphorus compound with the formula (C2H5O)2P(O)Cl. As a reagent in organic synthesis, it is used to convert alcohols to the corresponding diethylphosphate esters. It is a colorless liquid with a fruity odor. It is a corrosive, and as a cholinesterase inhibitor, highly toxic through dermal absorption. [1] The molecule is tetrahedral.