
The German Empire, also referred to as Imperial Germany, the Second Reich or simply Germany, was the period of the German Reich from the unification of Germany in 1871 until the November Revolution in 1918, when the German Reich changed its form of government from a monarchy to a republic.

The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk was a separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Soviet Russia and the Central Powers, by which Russia withdrew from World War I. The treaty, which followed months of negotiations after the armistice on the Eastern Front in December 1917, was signed at Brest-Litovsk.

Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin is a Russian politician and former intelligence officer who has served as President of Russia since 2012, having previously served from 2000 to 2008. Putin also served as Prime Minister of Russia from 1999 to 2000 and again from 2008 to 2012. At 24 years, 11 months and 24 days, he is the longest-serving Russian or Soviet leader since the 30-year tenure of Joseph Stalin.
A casus belli is an act or an event that either provokes or is used to justify a war. A casus belli involves direct offenses or threats against the nation declaring the war, whereas a casus foederis involves offenses or threats against its ally—usually one bound by a mutual defense pact. Either may be considered an act of war. A declaration of war usually contains a description of the casus belli that has led the party in question to declare war on another party.

The term "Soviet empire" collectively refers to the world's territories that the Soviet Union dominated politically, economically, and militarily. This phenomenon, particularly in the context of the Cold War, is also called Soviet imperialism by Sovietologists to describe the extent of the Soviet Union's hegemony over the Second World.

In the field of international relations, a sphere of influence (SOI) is a spatial region or concept division over which a state or organization has a level of cultural, economic, military, or political exclusivity.
German Reich was the constitutional name for the German nation state that existed from 1871 to 1945. The Reich became understood as deriving its authority and sovereignty entirely from a continuing unitary German Volk, with that authority and sovereignty being exercised at any one time over a unitary German "state territory" with variable boundaries and extent. Although commonly translated as "German Empire", the word Reich here better translates as "realm" or territorial "reach", in that the term does not in itself have monarchical connotations.

A great power is a sovereign state that is recognized as having the ability and expertise to exert its influence on a global scale. Great powers characteristically possess military and economic strength, as well as diplomatic and soft power influence, which may cause middle or small powers to consider the great powers' opinions before taking actions of their own. International relations theorists have posited that great power status can be characterized into power capabilities, spatial aspects, and status dimensions.
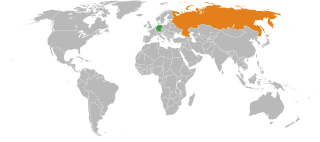
Germany–Russia relations display cyclical patterns, moving back and forth from cooperation and alliance to strain and to total warfare. Historian John Wheeler-Bennett says that since the 1740s:

The United States and Russia maintain one of the most important, critical, and strategic foreign relations in the world. Both nations have shared interests in nuclear safety and security, nonproliferation, counterterrorism, and space exploration.

Russia–United Kingdom relations, also Anglo-Russian relations, are the bilateral relations between Russia and the United Kingdom. Formal ties between the nations started in 1553. Russia and Britain became allies against Napoleon in the early-19th century. They were enemies in the Crimean War of the 1850s, and rivals in the Great Game for control of central Asia in the latter half of the 19th century. They allied again in World Wars I and II, although the Russian Revolution of 1917 strained relations. The two countries again became enemies during the Cold War (1947–1989). Russia's business tycoons developed strong ties with London financial institutions in the 1990s after the dissolution of the USSR in 1991. Due to the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, relations became very tense after the United Kingdom imposed sanctions against Russia. It was subsequently added to Russia's list of "unfriendly countries".

Italy–Russia relations are the bilateral foreign relations between the two countries, embodied in the so-called privileged relationship. Both countries are full members of the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe.
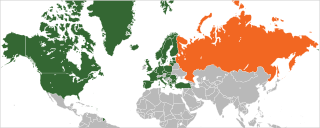
Relations between the NATO military alliance and the Russian Federation were established in 1991 within the framework of the North Atlantic Cooperation Council. In 1994, Russia joined the Partnership for Peace program, and on 27 May 1997, the NATO–Russia Founding Act (NRFA) was signed at the 1997 Paris NATO Summit in France, enabling the creation of the NATO–Russia Permanent Joint Council (NRPJC). Through the early part of 2010s NATO and Russia signed several additional agreements on cooperation. The NRPJC was replaced in 2002 by the NATO-Russia Council (NRC), which was established in an effort to partner on security issues and joint projects together.

The Allied Control Council (ACC) or Allied Control Authority, and also referred to as the Four Powers, was the governing body of the Allied occupation zones in Germany (1945–1949/1991) and Austria (1945–1955) after the end of World War II in Europe. After the defeat of the Nazis, Germany and Austria were occupied as two different areas, both by the same four Allies. Both were later divided into four zones by the 1 August 1945 Potsdam Agreement. Its members were the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, the United States, and France. The organisation was based in Schöneberg, Berlin.

On 18 March 2014, Russian president Vladimir Putin gave a speech to both chambers of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation in connection with the request for admission by the Crimean parliament of the republic in the Russian Federation. He spoke in the St. George Hall of the Grand Kremlin Palace in the Moscow Kremlin.
A Second Cold War, Cold War II, or the New Cold War has been used to describe heightened geopolitical tensions in the 21st century between usually, on one side, the United States and, on the other, either China or Russia—the successor state of the Soviet Union, which led the Eastern Bloc during the original Cold War.

The Valdai speech of Vladimir Putin is a press-coined name for the speech that the Russian President Vladimir Putin delivered at the Valdai International Discussion Club XI session on 24 October 2014, in Sochi.

The French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars, sometimes called the Great French War, were a series of conflicts between the French and several European monarchies between 1792 and 1815. They encompass first the French Revolutionary Wars against the newly declared French Republic and from 1803 onwards the Napoleonic Wars against First Consul and later Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. They include the Coalition Wars as a subset: seven wars waged by various military alliances of great European powers, known as Coalitions, against Revolutionary France – later the First French Empire – and its allies between 1792 and 1815:

Russian irredentism refers to territorial claims made by the Russian Federation to regions that were historically part of the Russian Empire and the Soviet Union, which Russian nationalists regard as part of the "Russian world". It seeks to create a Greater Russia by politically incorporating ethnic Russians and Russian speakers living in territories bordering Russia. This ideology has been significantly defined by the regime of Vladimir Putin, who has governed the country since 1999. It is linked to Russian neo-imperialism.

Russian imperialism is the political, economic and cultural influence, as well as military power, exerted by Russia and its predecessor states, over other countries and territories. It includes the conquests of the Tsardom of Russia, the Russian Empire, the imperialism of the Soviet Union, and the neo-imperialism of the Russian Federation. Some postcolonial scholars have noted the lack of attention given to Russian and Soviet imperialism in the discipline.
















