
In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall.

Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. They are characterized by their cell envelopes, which are composed of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall sandwiched between an inner cytoplasmic cell membrane and a bacterial outer membrane.

A mitochondrion is an organelle found in the cells of most eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used throughout the cell as a source of chemical energy. They were discovered by Albert von Kölliker in 1857 in the voluntary muscles of insects. The term mitochondrion was coined by Carl Benda in 1898. The mitochondrion is popularly nicknamed the "powerhouse of the cell", a phrase coined by Philip Siekevitz in a 1957 article of the same name.
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell, that has a specific function. The name organelle comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as organs are to the body, hence organelle, the suffix -elle being a diminutive. Organelles are either separately enclosed within their own lipid bilayers or are spatially distinct functional units without a surrounding lipid bilayer. Although most organelles are functional units within cells, some function units that extend outside of cells are often termed organelles, such as cilia, the flagellum and archaellum, and the trichocyst.
In biological taxonomy, a domain, also dominion, superkingdom, realm, or empire, is the highest taxonomic rank of all organisms taken together. It was introduced in the three-domain system of taxonomy devised by Carl Woese, Otto Kandler and Mark Wheelis in 1990.

Exocytosis is a form of active transport and bulk transport in which a cell transports molecules out of the cell. As an active transport mechanism, exocytosis requires the use of energy to transport material. Exocytosis and its counterpart, endocytosis, are used by all cells because most chemical substances important to them are large polar molecules that cannot pass through the hydrophobic portion of the cell membrane by passive means. Exocytosis is the process by which a large amount of molecules are released; thus it is a form of bulk transport. Exocytosis occurs via secretory portals at the cell plasma membrane called porosomes. Porosomes are permanent cup-shaped lipoprotein structure at the cell plasma membrane, where secretory vesicles transiently dock and fuse to release intra-vesicular contents from the cell.

An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific cell rapidly rises and falls. This depolarization then causes adjacent locations to similarly depolarize. Action potentials occur in several types of animal cells, called excitable cells, which include neurons, muscle cells, and in some plant cells. Certain endocrine cells such as pancreatic beta cells, and certain cells of the anterior pituitary gland are also excitable cells.

Membrane proteins are common proteins that are part of, or interact with, biological membranes. Membrane proteins fall into several broad categories depending on their location. Integral membrane proteins are a permanent part of a cell membrane and can either penetrate the membrane (transmembrane) or associate with one or the other side of a membrane. Peripheral membrane proteins are transiently associated with the cell membrane.

A transmembrane protein (TP) is a type of integral membrane protein that spans the entirety of the cell membrane. Many transmembrane proteins function as gateways to permit the transport of specific substances across the membrane. They frequently undergo significant conformational changes to move a substance through the membrane. They are usually highly hydrophobic and aggregate and precipitate in water. They require detergents or nonpolar solvents for extraction, although some of them (beta-barrels) can be also extracted using denaturing agents.

A steroid hormone is a steroid that acts as a hormone. Steroid hormones can be grouped into two classes: corticosteroids and sex steroids. Within those two classes are five types according to the receptors to which they bind: glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids and androgens, estrogens, and progestogens. Vitamin D derivatives are a sixth closely related hormone system with homologous receptors. They have some of the characteristics of true steroids as receptor ligands.

An antifungal medication, also known as an antimycotic medication, is a pharmaceutical fungicide or fungistatic used to treat and prevent mycosis such as athlete's foot, ringworm, candidiasis (thrush), serious systemic infections such as cryptococcal meningitis, and others. Such drugs are usually obtained by a doctor's prescription, but a few are available over the counter (OTC). The evolution of antifungal resistance is a growing threat to health globally.

The periplasm is a concentrated gel-like matrix in the space between the inner cytoplasmic membrane and the bacterial outer membrane called the periplasmic space in gram-negative bacteria. Using cryo-electron microscopy it has been found that a much smaller periplasmic space is also present in gram-positive bacteria, between cell wall and the plasma membrane.

Gas mixtures can be effectively separated by synthetic membranes made from polymers such as polyamide or cellulose acetate, or from ceramic materials.

The tectoria membrane (TM) is one of two acellular membranes in the cochlea of the inner ear, the other being the basilar membrane (BM). "Tectorial" in anatomy means forming a cover. The TM is located above the spiral limbus and the spiral organ of Corti and extends along the longitudinal length of the cochlea parallel to the BM. Radially the TM is divided into three zones, the limbal, middle and marginal zones. Of these the limbal zone is the thinnest (transversally) and overlies the auditory teeth of Huschke with its inside edge attached to the spiral limbus. The marginal zone is the thickest (transversally) and is divided from the middle zone by Hensen's Stripe. It overlies the sensory inner hair cells and electrically-motile outer hair cells of the organ of Corti and during acoustic stimulation stimulates the inner hair cells through fluid coupling, and the outer hair cells via direct connection to their tallest stereocilia.

The plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase (PMCA) is a transport protein in the plasma membrane of cells that functions as a calcium pump to remove calcium (Ca2+) from the cell. PMCA function is vital for regulating the amount of Ca2+ within all eukaryotic cells. There is a very large transmembrane electrochemical gradient of Ca2+ driving the entry of the ion into cells, yet it is very important that they maintain low concentrations of Ca2+ for proper cell signalling. Thus, it is necessary for cells to employ ion pumps to remove the Ca2+. The PMCA and the sodium calcium exchanger (NCX) are together the main regulators of intracellular Ca2+ concentrations. Since it transports Ca2+ into the extracellular space, the PMCA is also an important regulator of the calcium concentration in the extracellular space.
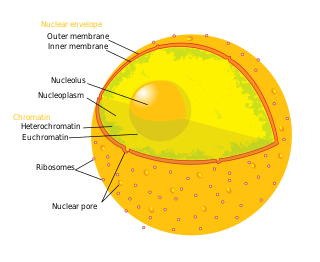
The nuclear envelope, also known as the nuclear membrane, is made up of two lipid bilayer membranes that in eukaryotic cells surround the nucleus, which encloses the genetic material.

Voltage-dependent anion channels, or mitochondrial porins, are a class of porin ion channel located on the outer mitochondrial membrane. There is debate as to whether or not this channel is expressed in the cell surface membrane.
Reverse osmosis (RO) is a water purification process that uses a semi-permeable membrane to separate water molecules from other substances. RO applies pressure to overcome osmotic pressure that favors even distributions. RO can remove dissolved or suspended chemical species as well as biological substances, and is used in industrial processes and the production of potable water. RO retains the solute on the pressurized side of the membrane and the purified solvent passes to the other side. It relies on the relative sizes of the various molecules to decide what passes through. "Selective" membranes reject large molecules, while accepting smaller molecules.

Myosin IG, also known as myosin 1G and MYO1G, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MYO1G gene. MYO1G is a member of class I unconventional myosins. Its expression is highly restricted to hematopoietic tissues and cells. It localises exclusively to the plasma membrane and is dependent on both the motor domain and the tail domain. MYO1G regulates cell elasticity possibly by interaction plasma membrane and cortical actin in Jurkat T-cells.
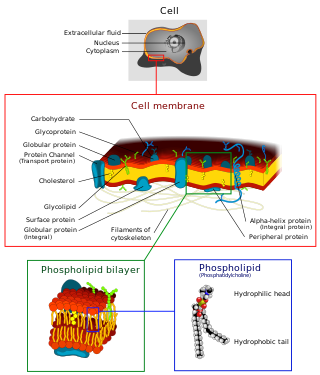
The cell membrane is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment. The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, made up of two layers of phospholipids with cholesterols interspersed between them, maintaining appropriate membrane fluidity at various temperatures. The membrane also contains membrane proteins, including integral proteins that span the membrane and serve as membrane transporters, and peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer (peripheral) side of the cell membrane, acting as enzymes to facilitate interaction with the cell's environment. Glycolipids embedded in the outer lipid layer serve a similar purpose. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of a cell, being selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules. In addition, cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity, and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall and the carbohydrate layer called the glycocalyx, as well as the intracellular network of protein fibers called the cytoskeleton. In the field of synthetic biology, cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.

















