
Trastuzumab, sold under the brand name Herceptin among others, is a monoclonal antibody used to treat breast cancer and stomach cancer. It is specifically used for cancer that is HER2 receptor positive. It may be used by itself or together with other chemotherapy medication. Trastuzumab is given by slow injection into a vein and injection just under the skin.
Inflammatory breast cancer (IBC) is one of the most aggressive types of breast cancer. It can occur in women of any age. It is referred to as "inflammatory" due to its frequent presentation with symptoms resembling a skin inflammation, such as erysipelas.

Tamoxifen, sold under the brand name Nolvadex among others, is a selective estrogen receptor modulator used to prevent breast cancer in women and men. It is also being studied for other types of cancer. It has been used for Albright syndrome. Tamoxifen is typically taken daily by mouth for five years for breast cancer.

Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ERBB2 gene. ERBB is abbreviated from erythroblastic oncogene B, a gene originally isolated from the avian genome. The human protein is also frequently referred to as HER2 or CD340.
Adjuvant therapy, also known as adjunct therapy, adjuvant care, or augmentation therapy, is a therapy that is given in addition to the primary or initial therapy to maximize its effectiveness. The surgeries and complex treatment regimens used in cancer therapy have led the term to be used mainly to describe adjuvant cancer treatments. An example of such adjuvant therapy is the additional treatment usually given after surgery where all detectable disease has been removed, but where there remains a statistical risk of relapse due to the presence of undetected disease. If known disease is left behind following surgery, then further treatment is not technically adjuvant.
MammaPrint is a prognostic and predictive diagnostic test for early stage breast cancer patients that assess the risk that a tumor will metastasize to other parts of the body. It gives a binary result, high-risk or low-risk classification, and helps physicians determine whether or not a patient will benefit from chemotherapy. Women with a low risk result can safely forego chemotherapy without decreasing likelihood of disease free survival. MammaPrint is part of the personalized medicine portfolio marketed by Agendia.
In medicine, a biomarker is a measurable indicator of the severity or presence of some disease state. It may be defined as a "cellular, biochemical or molecular alteration in cells, tissues or fluids that can be measured and evaluated to indicate normal biological processes, pathogenic processes, or pharmacological responses to a therapeutic intervention." More generally a biomarker is anything that can be used as an indicator of a particular disease state or some other physiological state of an organism. According to the WHO, the indicator may be chemical, physical, or biological in nature - and the measurement may be functional, physiological, biochemical, cellular, or molecular.

Lapatinib (INN), used in the form of lapatinib ditosylate (USAN) is an orally active drug for breast cancer and other solid tumours. It is a dual tyrosine kinase inhibitor which interrupts the HER2/neu and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) pathways. It is used in combination therapy for HER2-positive breast cancer. It is used for the treatment of patients with advanced or metastatic breast cancer whose tumors overexpress HER2 (ErbB2).

Pertuzumab, sold under the brand name Perjeta, is a monoclonal antibody used in combination with trastuzumab and docetaxel for the treatment of metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer; it also used in the same combination as a neoadjuvant in early HER2-positive breast cancer.
Hormonal therapy in oncology is hormone therapy for cancer and is one of the major modalities of medical oncology, others being cytotoxic chemotherapy and targeted therapy (biotherapeutics). It involves the manipulation of the endocrine system through exogenous or external administration of specific hormones, particularly steroid hormones, or drugs which inhibit the production or activity of such hormones. Because steroid hormones are powerful drivers of gene expression in certain cancer cells, changing the levels or activity of certain hormones can cause certain cancers to cease growing, or even undergo cell death. Surgical removal of endocrine organs, such as orchiectomy and oophorectomy can also be employed as a form of hormonal therapy.
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is any breast cancer that either lacks or shows low levels of estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR) and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) overexpression and/or gene amplification. Triple-negative is sometimes used as a surrogate term for basal-like.
Breast cancer management takes different approaches depending on physical and biological characteristics of the disease, as well as the age, over-all health and personal preferences of the patient. Treatment types can be classified into local therapy and systemic treatment. Local therapy is most efficacious in early stage breast cancer, while systemic therapy is generally justified in advanced and metastatic disease, or in diseases with specific phenotypes.
The estrogen receptor test (ERT) uses the estrogen receptor (ER) tumor marker that allows for immunohistochemical techniques to be performed for diagnostic purposes. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) methods involve the selective identification of antigen proteins by exploiting these antigen-antibody relationships to characterize your analyte of interest. Previously, the ligand binding assay has been used to determine ER activity. However, this method was limited because of the large quantities of fresh tissue needed for each assay. IHC serves as a more efficient method as this technique allows for the tissue morphology to be observed in a tumor-specific manner. This increases the practicability of this technique as in many cases, patients’ tissue samples are limited in the applications of biomarker analysis. Anti-estrogen receptor antibodies were among the first of biomarkers that introduced a semi-quantitative assessment of the ER activity. Today, ER analysis is one of many routinely performed immunohistochemical assays performed to classify the hormone receptor status and to serve as a means of insight into the determination of cancer prognosis and management.
Breast cancer classification divides breast cancer into categories according to different schemes criteria and serving a different purpose. The major categories are the histopathological type, the grade of the tumor, the stage of the tumor, and the expression of proteins and genes. As knowledge of cancer cell biology develops these classifications are updated.

Trastuzumab emtansine, sold under the brand name Kadcyla, is an antibody-drug conjugate consisting of the humanized monoclonal antibody trastuzumab (Herceptin) covalently linked to the cytotoxic agent DM1. Trastuzumab alone stops growth of cancer cells by binding to the HER2 receptor, whereas trastuzumab emtansine undergoes receptor-mediated internalization into cells, is catabolized in lysosomes where DM1-containing catabolites are released and subsequently bind tubulin to cause mitotic arrest and cell death. Trastuzumab binding to HER2 prevents homodimerization or heterodimerization (HER2/HER3) of the receptor, ultimately inhibiting the activation of MAPK and PI3K/AKT cellular signalling pathways. Because the monoclonal antibody targets HER2, and HER2 is only over-expressed in cancer cells, the conjugate delivers the cytotoxic agent DM1 specifically to tumor cells. The conjugate is abbreviated T-DM1.

A cancer biomarker refers to a substance or process that is indicative of the presence of cancer in the body. A biomarker may be a molecule secreted by a tumor or a specific response of the body to the presence of cancer. Genetic, epigenetic, proteomic, glycomic, and imaging biomarkers can be used for cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and epidemiology. Ideally, such biomarkers can be assayed in non-invasively collected biofluids like blood or serum.
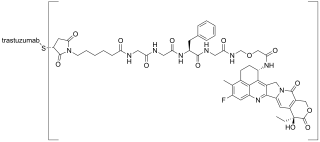
Trastuzumab deruxtecan, sold under the brand name Enhertu, is an antibody-drug conjugate consisting of the humanized monoclonal antibody trastuzumab (Herceptin) covalently linked to the topoisomerase I inhibitor deruxtecan. It is licensed for the treatment of breast cancer or gastric or gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma. Trastuzumab binds to and blocks signaling through epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2/neu) on cancers that rely on it for growth. Additionally, once bound to HER2 receptors, the antibody is internalized by the cell, carrying the bound deruxtecan along with it, where it interferes with the cell's ability to make DNA structural changes and replicate its DNA during cell division, leading to DNA damage when the cell attempts to replicate itself, destroying the cell.
Metronomic therapy is a new type of chemotherapy in which anti-cancer drugs are administered in a lower dose than the maximum tolerated dose repetitively over a long period to treat cancers with fewer side effects. Metronomic therapy is shown to affect both tumor microenvironment and tumor cells to achieve its therapeutic effects. Metronomic therapy is also cost-effective as a lower dose is used compared to conventional chemotherapy. The use of metronomic therapy has been extensively investigated and can be advantageous in selected group of patients. Yet, more clinical trials are necessary to generalize the method.
Trastuzumab/hyaluronidase, sold under the brand name Herceptin SC among others, is a fixed-dose combination medication for the treatment of HER2-overexpressing breast cancer in adults. It is a combination of trastuzumab and hyaluronidase.
Endocrine therapy is a common treatment for estrogen receptor positive breast cancer. However, resistance to this therapy can develop, leading to relapse and progression of disease. This highlights the need for new strategies to combat this resistance.






