
A doctor's office in American English, a doctor's surgery in British English, or a doctor's practice, is a medical facility in which one or more medical doctors, usually general practitioners (GP), receive and treat patients. [1] [2]

A doctor's office in American English, a doctor's surgery in British English, or a doctor's practice, is a medical facility in which one or more medical doctors, usually general practitioners (GP), receive and treat patients. [1] [2]
Doctors' offices are the primary place where ambulatory care is given, and are often the first place that a sick person would go for care, except in an emergency, in which case one would go to an emergency department at a hospital. [3]
In developed countries, where health services are guaranteed by the state in some form, most medical visits to doctors take place in their offices. In the United States, where this is not the case, many people who cannot afford health insurance or doctor's visits must either go to free or reduced-cost clinics or an emergency department at a hospital for care, instead of a doctor's office. [4]
For healthy people, most visits to doctors' offices revolve around a once-yearly recommended physical examination. This exam usually consists of gathering information such as a patient's blood pressure, heart rate, weight, and height, along with checking for any irregularities or signs of illness around the body. [5] GPs will also ask the patients about any mental health problems that they may be experiencing, and may refer them to a psychiatrist for further examination in the event that they do indeed have such problems. If there are any other health problems that must be addressed by a medical specialist, such as a cardiologist, a referral will be given. [5]
The staff of a doctor's office usually consists of nurses, receptionists, and doctors. Sometimes, many doctors of different medical specialties may be housed in one building, allowing easy referrals.
Doctors' offices can range from spartan to luxurious. A basic office usually consists of a waiting room and examination room(s). Examination rooms usually consist of an examination table, upon which the patient sits or lies down, and various other equipment, depending on the office. Examples of the equipment found in an examination room include: [6]

Medicine is the science and practice of caring for patients, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness. Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, genetics, and medical technology to diagnose, treat, and prevent injury and disease, typically through pharmaceuticals or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, external splints and traction, medical devices, biologics, and ionizing radiation, amongst others.
Obstetrics and gynaecology is the medical specialty that encompasses the two subspecialties of obstetrics and gynaecology. The specialization is an important part of care for women's health.

An emergency department (ED), also known as an accident and emergency department (A&E), emergency room (ER), emergency ward (EW) or casualty department, is a medical treatment facility specializing in emergency medicine, the acute care of patients who present without prior appointment; either by their own means or by that of an ambulance. The emergency department is usually found in a hospital or other primary care center.

A general practitioner (GP) or family physician is a doctor who is a consultant in general practice.
A patient is any recipient of health care services that are performed by healthcare professionals. The patient is most often ill or injured and in need of treatment by a physician, nurse, optometrist, dentist, veterinarian, or other health care provider.

In a physical examination, medical examination, clinical examination, or medical checkup, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a medical condition. It generally consists of a series of questions about the patient's medical history followed by an examination based on the reported symptoms. Together, the medical history and the physical examination help to determine a diagnosis and devise the treatment plan. These data then become part of the medical record.
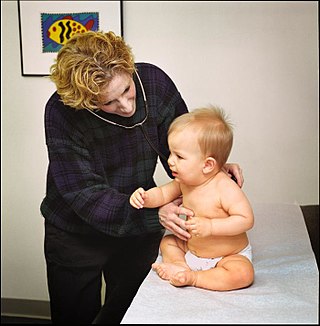
General practice is personal, family, and community-orientated comprehensive primary care that includes diagnosis, continues over time and is anticipatory as well as responsive.

Family medicine is a medical specialty within primary care that provides continuing and comprehensive health care for the individual and family across all ages, genders, diseases, and parts of the body. The specialist, who is usually a primary care physician, is named a family physician. It is often referred to as general practice and a practitioner as a general practitioner. Historically, their role was once performed by any doctor with qualifications from a medical school and who works in the community. However, since the 1950s, family medicine / general practice has become a specialty in its own right, with specific training requirements tailored to each country. The names of the specialty emphasize its holistic nature and/or its roots in the family. It is based on knowledge of the patient in the context of the family and the community, focusing on disease prevention and health promotion. According to the World Organization of Family Doctors (WONCA), the aim of family medicine is "promoting personal, comprehensive and continuing care for the individual in the context of the family and the community". The issues of values underlying this practice are usually known as primary care ethics.
Clinical audit is a process that has been defined as a quality improvement process that seeks to improve patient care and outcomes through systematic review of care against explicit criteria and the implementation of change

NHS Scotland, sometimes styled NHSScotland, is the publicly–funded healthcare system in Scotland and one of the four systems that make up the National Health Service in the United Kingdom. It operates 14 territorial NHS boards across Scotland, supported by seven special non-geographic health boards, and Public Health Scotland.
Emergency Medical Service in Germany is a service of public pre-hospital emergency healthcare, including ambulance service, provided by individual German cities and counties. It is primarily financed by the German public health insurance system.
An admission note is part of a medical record that documents the patient's status, reasons why the patient is being admitted for inpatient care to a hospital or other facility, and the initial instructions for that patient's care.

The National Health Service (NHS) is the publicly funded healthcare system in England, and one of the four National Health Service systems in the United Kingdom. It is the second largest single-payer healthcare system in the world after the Brazilian Sistema Único de Saúde. Primarily funded by the government from general taxation, and overseen by the Department of Health and Social Care, the NHS provides healthcare to all legal English residents and residents from other regions of the UK, with most services free at the point of use for most people. The NHS also conducts research through the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR).
SystmOne is a centrally hosted clinical computer system developed by Horsforth-based The Phoenix Partnership (TPP). It is used by healthcare professionals in the UK predominantly in primary care. The system is being deployed as one of the accredited systems in the government's programme of modernising IT in the NHS.
Healthcare in England is mainly provided by the National Health Service (NHS), a public body that provides healthcare to all permanent residents in England, that is free at the point of use. The body is one of four forming the UK National Health Service as health is a devolved matter; there are differences with the provisions for healthcare elsewhere in the United Kingdom, and in England it is overseen by NHS England. Though the public system dominates healthcare provision in England, private health care and a wide variety of alternative and complementary treatments are available for those willing and able to pay.

Pediatric dentistry is the branch of dentistry dealing with children from birth through adolescence. The specialty of pediatric dentistry is recognized by the American Dental Association, Royal College of Dentists of Canada, and Royal Australasian College of Dental Surgeons.

Italy's healthcare system is consistently ranked among the best in the world. The Italian healthcare system employs a Beveridge model, and operates on the assumption that health care is a human right that should be provided to everyone regardless of their ability to pay. Life expectancy is the 4th highest among OECD countries and the world's 8th highest according to the WHO. Healthcare spending accounted for 9.7% of GDP in 2020.

NHS Pathways is a triage software utilised by the National Health Service of England to triage public telephone calls for medical care and emergency medical services – such as 999 or 111 calls – in some NHS trusts and five of the ambulance services in the country. In its emergency capacity, it has replaced the Advanced Medical Priority Dispatch System for some trusts, and in non-emergency telephone triage it is found in many medical care triage systems, such as NHS 111.
Dentistry provided by the National Health Service in the United Kingdom is supposed to ensure that dental treatment is available to the whole population. Most dentistry is provided by private practitioners, most of whom also provide, on a commercial basis, services which the NHS does not provide, largely cosmetic. Most adult patients have to pay some NHS charges, although these are often significantly cheaper than the cost of private dentistry. The majority of people choose NHS dental care rather than private care: as of 2005, the national average proportion of people forced to use private care was 23%. NHS dentistry is not always available and is not managed in the way that other NHS services are managed.
Out-of-hours services are the arrangements to provide access to healthcare at times when General Practitioner surgeries are closed; in the United Kingdom this is normally between 6.30pm and 8am, at weekends, at Bank Holidays and sometimes if the practice is closed for educational sessions.