A prism is a transparent optical component with flat surfaces that refract light.

Binoculars or field glasses are two refracting telescopes mounted side-by-side and aligned to point in the same direction, allowing the viewer to use both eyes when viewing distant objects. Most binoculars are sized to be held using both hands, although sizes vary widely from opera glasses to large pedestal-mounted military models.
In geometry, a cuboid is a hexahedron, a six-faced solid. Its faces are quadrilaterals. "Cuboid" means "like a cube", in the sense that by adjusting the length of the edges or the angles between edges and faces a cuboid can be transformed into a cube. In math language a cuboid is convex polyhedron, whose polyhedral graph is the same as that of a cube.

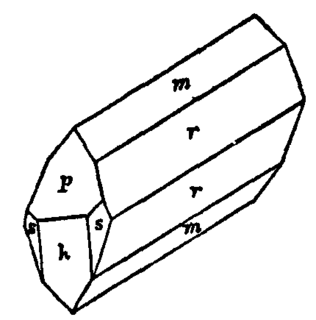
An optical prism is a transparent optical element with flat, polished surfaces that are designed to refract light. At least one surface must be angled — elements with two parallel surfaces are not prisms. The traditional geometrical shape of an optical prism is that of a triangular prism with a triangular base and rectangular sides, and in colloquial use "prism" usually refers to this type. Some types of optical prism are not in fact in the shape of geometric prisms. Prisms can be made from any material that is transparent to the wavelengths for which they are designed. Typical materials include glass, acrylic and fluorite.

In geometry, a prism is a polyhedron comprising an n-sided polygon base, a second base which is a translated copy of the first, and n other faces, necessarily all parallelograms, joining corresponding sides of the two bases. All cross-sections parallel to the bases are translations of the bases. Prisms are named after their bases; example: a prism with a pentagonal base is called a pentagonal prism. Prisms are a subclass of prismatoids.
In crystallography, the monoclinic crystal system is one of the seven crystal systems. A crystal system is described by three vectors. In the monoclinic system, the crystal is described by vectors of unequal lengths, as in the orthorhombic system. They form a rectangular prism with a parallelogram as its base. Hence two pairs of vectors are perpendicular, while the third pair makes an angle other than 90°.
In crystallography, the orthorhombic crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems. Orthorhombic lattices result from stretching a cubic lattice along two of its orthogonal pairs by two different factors, resulting in a rectangular prism with a rectangular base and height (c), such that a, b, and c are distinct. All three bases intersect at 90° angles, so the three lattice vectors remain mutually orthogonal.

Prism is a Canadian rock band formed in Vancouver in 1977. They were originally active from 1977 to 1984 and have been active again from 1987 to present. Their classic line-up consisted of lead singer Ron Tabak, guitarist Lindsay Mitchell, keyboardist John Hall, bass guitarist Allen Harlow and drummer Rocket Norton.

In geometry, a uniform 4-polytope is a 4-dimensional polytope which is vertex-transitive and whose cells are uniform polyhedra, and faces are regular polygons.

PRISM was an American regional premium cable television channel in the Philadelphia metropolitan area. Launched in September 1976, PRISM was primarily distributed through area cable systems, although it was also available through a scrambled over-the-air signal on WWSG-TV from 1983 to 1985.

In geometry, a triangular prism is a three-sided prism; it is a polyhedron made of a triangular base, a translated copy, and 3 faces joining corresponding sides. A right triangular prism has rectangular sides, otherwise it is oblique. A uniform triangular prism is a right triangular prism with equilateral bases, and square sides.
In geometry, the pentagonal prism is a prism with a pentagonal base. It is a type of heptahedron with 7 faces, 15 edges, and 10 vertices.

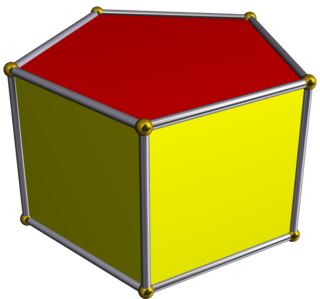
In geometry, the hexagonal prism is a prism with hexagonal base. This polyhedron has 8 faces, 18 edges, and 12 vertices.
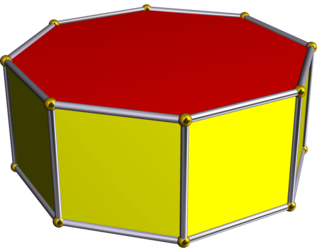
In geometry, the octagonal prism is the sixth in an infinite set of prisms, formed by square sides and two regular octagon caps.
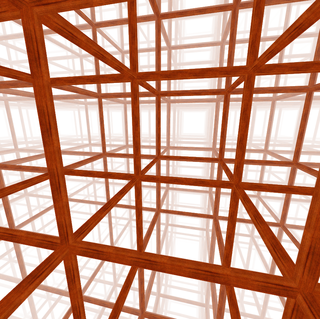
The cubic honeycomb or cubic cellulation is the only proper regular space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space made up of cubic cells. It has 4 cubes around every edge, and 8 cubes around each vertex. Its vertex figure is a regular octahedron. It is a self-dual tessellation with Schläfli symbol {4,3,4}. John Horton Conway called this honeycomb a cubille.

The triangular prismatic honeycomb or triangular prismatic cellulation is a space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed entirely of triangular prisms.
The wedge prism is a prism with a shallow angle between its input and output surfaces. This angle is usually 3 degrees or less. Refraction at the surfaces causes the prism to deflect light by a fixed angle. When viewing a scene through such a prism, objects will appear to be offset by an amount that varies with their distance from the prism.

In geometry, an apeirogonal prism or infinite prism is the arithmetic limit of the family of prisms; it can be considered an infinite polyhedron or a tiling of the plane.

PRISM is a code name for a program under which the United States National Security Agency (NSA) collects internet communications from various U.S. internet companies. The program is also known by the SIGAD US-984XN. PRISM collects stored internet communications based on demands made to internet companies such as Google LLC under Section 702 of the FISA Amendments Act of 2008 to turn over any data that match court-approved search terms. Among other things, the NSA can use these PRISM requests to target communications that were encrypted when they traveled across the internet backbone, to focus on stored data that telecommunication filtering systems discarded earlier, and to get data that is easier to handle.

Prism is the fourth studio album by American singer Katy Perry. It was released by Capitol Records on October 18, 2013. While the album was initially planned to be "darker" than her previous material, Prism ultimately became a prominently dance-inspired record. Perry worked with several past collaborators, while enlisting new producers and guest vocals. Much of Prism revolves around the themes of living in the present, relationships, and self-empowerment. The album garnered generally positive reviews with critics praising its lyrics for being more "mature" and personal, while others considered Prism to be more formulaic than her previous material.
















