
Italy is located in southern Europe and comprises the long, boot-shaped Italian Peninsula, the southern side of Alps, the large plain of the Po Valley and some islands including Sicily and Sardinia. Corsica, although belonging to the Italian geographical region, has been a part of France since 1769. Italy is part of the Northern Hemisphere.

The Dolomites are a mountain range located in northeastern Italy. They form a part of the Southern Limestone Alps and extend from the River Adige in the west to the Piave Valley in the east. The northern and southern borders are defined by the Puster Valley and the Sugana Valley. The Dolomites are nearly equally shared between the provinces of Belluno, South Tyrol and Trentino.

The Apennines or Apennine Mountains are a mountain range consisting of parallel smaller chains extending c. 1,200 km (750 mi) along the length of peninsular Italy. In the northwest they join with the Ligurian Alps at Altare. In the southwest they end at Reggio di Calabria, the coastal city at the tip of the peninsula. Since 2000 the Environment Ministry of Italy, following the recommendations of the Apennines Park of Europe Project, has been defining the Apennines System to include the mountains of north Sicily, for a total distance of 1,500 kilometres (930 mi). The system forms an arc enclosing the east side of the Ligurian and Tyrrhenian Seas.

Rocky Mountain National Park is an American national park located approximately 76 mi (122 km) northwest of Denver International Airport in north-central Colorado, within the Front Range of the Rocky Mountains. The park is situated between the towns of Estes Park to the east and Grand Lake to the west. The eastern and westerns slopes of the Continental Divide run directly through the center of the park with the headwaters of the Colorado River located in the park's northwestern region. The main features of the park include mountains, alpine lakes and a wide variety of wildlife within various climates and environments, from wooded forests to mountain tundra.

The Italian Peninsula or Apennine Peninsula extends 1,000 km (620 mi) from the Po Valley in the north to the central Mediterranean Sea in the south. The peninsula's shape gives it the nickname lo Stivale. Three smaller peninsulas contribute to this characteristic shape, namely Calabria, Salento and Gargano.

Gran Sasso d'Italia (Italian: [ɡran ˈsasso diˈtaːlja] is an Apennine secondary mountain massif. Its highest peak, Corno Grande, is the highest mountain in the Apennines and outside the Alps. Included in Gran Sasso e Monti della Laga National Park, is a popular touristic attraction and ski resort, used several times as filming locations.

The Brenta Group or Brenta Dolomites is a mountain range, and a subrange of the Rhaetian Alps in the Southern Limestone Alps mountain group. They are located in the Province of Trentino, in northeastern Italy. It is the only dolomitic group west of river Adige. Therefore, geographically, they have not always been considered a part of the Dolomites mountain ranges. Geologically, however, they definitely are - and therefore sometimes called the "Western Dolomites". As part of the Dolomites, the Brenta Group has been officially recognized as UNESCO World Heritage Site under the World Heritage Convention.

The Province of Belluno is a province in the Veneto region of Italy. Its capital is the city of Belluno.
The Monti Simbruini are a mountain range in central Italy, a part of Apennines mountain system.

The Dolomites Railway, originally the Ampezzaner Bahn or Ampezzaner Railway, was a railway in Northern Italy crossing the Dolomites mountains. The 64.9-kilometre (40.3-mile) long railway began in Calalzo and ended in Toblach. Its gauge was 950 mm — "Italian metre gauge". The Cortina d'Ampezzo - Toblach part was closed in 1962 and the Cortina d'Ampezzo - Calalzo di Cadore in 1964. Two EMUs went to the Trento - Malè railway and are still in use. Other vehicles went to the Apulo-Lucane railway.
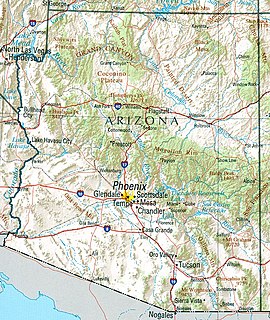
Arizona is a landlocked state situated in the southwestern region of the United States of America. It has a vast and diverse geography famous for its deep canyons, high- and low-elevation deserts, numerous natural rock formations, and volcanic mountain ranges. Arizona shares land borders with Utah to the north, the Mexican state of Sonora to the south, New Mexico to the east, and Nevada to the northwest, as well as water borders with California and the Mexican state of Baja California to the southwest along the Colorado River. Arizona is also one of the Four Corners states and is diagonally adjacent to Colorado.

Cimon della Pala, sometimes called Cimone and The Matterhorn of the Dolomites, is the best-known peak of the Pale di San Martino group, in the Dolomites, northern Italy. Although it is not the highest peak of the group, the Cima Vezzana being a few metres higher, its slender point, which can be seen from the Rolle Pass, dominates the landscape.

Tofane is a mountain group in the Dolomites of northern Italy, west of Cortina d'Ampezzo in the province of Belluno, Veneto. Most of the Tofane lies within Parco naturale delle Dolomiti d'Ampezzo, a nature park.

The flora of Italy was traditionally estimated to comprise about 5,500 vascular plant species. However, as of 2005, 6,759 species are recorded in the Data bank of Italian vascular flora. Geobotanically, the Italian flora is shared between the Circumboreal Region and Mediterranean Region. According to the index compiled by the Italian Ministry for the Environment in 2001, 274 vascular plant species were protected.

The Llogara National Park is a national park centered on the Ceraunian Mountains along the Albanian Riviera in Southwestern Albania, spanning an surface area of 1,010 ha (10.1 km2). The park's terrain includes large alpine meadows, vertical rock faces, precipices and dense forests. The most area of land is covered by forests and was established in 1966 to protect several ecosystems and biodiversity of national importance. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has listed the park as Category II. The region has been recognised as an important Bird and Plant Area, because it support significant numbers of various bird and plant species.

Cinque Torri are a small group belonging to Nuvolao group, in the Dolomiti Ampezzane north-west of San Vito di Cadore and south-west of Cortina d'Ampezzo.

The Alburni are an Italian mountain range of the Province of Salerno, Campania, part of the Apennines. Due to their geomorphology, they are popularly known as the "Dolomites of Campania" or of Southern Italy. The highest mountain is the Panormo. Its second name, Alburno, gives the name to the whole range.

The Fiemme Mountains, sometimes also the Fleimstal Alps or Fiemme Dolomites, are a mountain range of the Southern Limestone Alps in the Italian region of Trentino-South Tyrol. The range was named after the Fiemme Valley.

The Dolomiti Bellunesi National Park is a national park in the province of Belluno, Veneto, in the northern Italy.
































