Related Research Articles

Gegenschein or counterglow is a faintly bright spot in the night sky centered at the antisolar point. The backscatter of sunlight by interplanetary dust causes this optical phenomenon.

Astronomy is the oldest of the natural sciences,dating back to antiquity,with its origins in the religious,mythological,cosmological,calendrical,and astrological beliefs and practices of prehistory:vestiges of these are still found in astrology,a discipline long interwoven with public and governmental astronomy. It was not completely separated in Europe during the Copernican Revolution starting in 1543. In some cultures,astronomical data was used for astrological prognostication.

Taurus is one of the constellations of the zodiac and is located in the northern celestial hemisphere. Taurus is a large and prominent constellation in the Northern Hemisphere's winter sky. It is one of the oldest constellations,dating back to the Early Bronze Age at least,when it marked the location of the Sun during the spring equinox. Its importance to the agricultural calendar influenced various bull figures in the mythologies of Ancient Sumer,Akkad,Assyria,Babylon,Egypt,Greece,and Rome. Its old astronomical symbol is (♉︎),which resembles a bull's head.

Tycho Brahe,generally called Tycho for short,was a Danish astronomer of the Renaissance,known for his comprehensive and unprecedentedly accurate astronomical observations. He was known during his lifetime as an astronomer,astrologer,and alchemist. He was the last major astronomer before the invention of the telescope.

The zodiac is a belt-shaped region of the sky that extends approximately 8°north and south of the ecliptic,which is the apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere over the course of the year. The orbital paths of the Moon and major planets are within the belt of the zodiac.
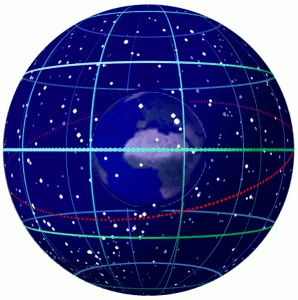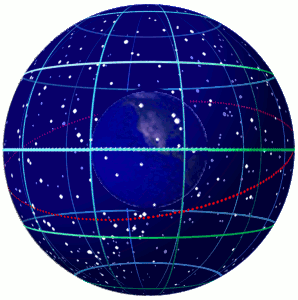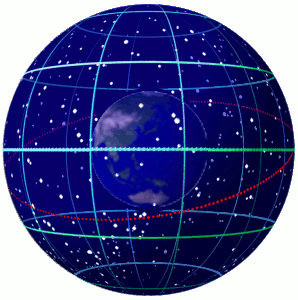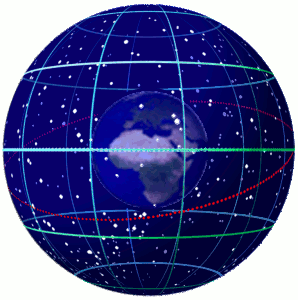
In astronomy and navigation,the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere,which may be centered on Earth or the observer. If centered on the observer,half of the sphere would resemble a hemispherical screen over the observing location.

Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics,physics,and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets,moons,stars,nebulae,galaxies,meteoroids,asteroids,and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions,gamma ray bursts,quasars,blazars,pulsars,and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally,astronomy studies everything that originates beyond Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole.
In astronomy and celestial navigation,an ephemeris is a book with tables that gives the trajectory of naturally occurring astronomical objects as well as artificial satellites in the sky,i.e.,the position over time. Historically,positions were given as printed tables of values,given at regular intervals of date and time. The calculation of these tables was one of the first applications of mechanical computers. Modern ephemerides are often provided in electronic form. However,printed ephemerides are still produced,as they are useful when computational devices are not available.

An armillary sphere is a model of objects in the sky,consisting of a spherical framework of rings,centered on Earth or the Sun,that represent lines of celestial longitude and latitude and other astronomically important features,such as the ecliptic. As such,it differs from a celestial globe,which is a smooth sphere whose principal purpose is to map the constellations. It was invented separately,in ancient China possibly as early as the 4th century BC and ancient Greece during the 3rd century BC,with later uses in the Islamic world and Medieval Europe.

An astronomical object,celestial object,stellar object or heavenly body is a naturally occurring physical entity,association,or structure that exists within the observable universe. In astronomy,the terms object and body are often used interchangeably. However,an astronomical body or celestial body is a single,tightly bound,contiguous entity,while an astronomical or celestial object is a complex,less cohesively bound structure,which may consist of multiple bodies or even other objects with substructures.
Dirk Brouwer was a Dutch-American astronomer.

Astronomy in China has a long history stretching from the Shang dynasty,being refined over a period of more than 3,000 years. The ancient Chinese people have identified stars from 1300 BCE,as Chinese star names later categorized in the twenty-eight mansions have been found on oracle bones unearthed at Anyang,dating back to the mid-Shang dynasty. The core of the "mansion" system also took shape around this period,by the time of King Wu Ding.

Sidewalk astronomy or street corner astronomy refers to the activity of setting up a telescope in an urban place on a for-profit or non-profit basis as entertainment and/or for public education.

A star chart is a celestial map of the night sky with astronomical objects laid out on a grid system. They are used to identify and locate constellations,stars,nebulae,galaxies,and planets. They have been used for human navigation since time immemorial. Note that a star chart differs from an astronomical catalog,which is a listing or tabulation of astronomical objects for a particular purpose. Tools using a star chart include the astrolabe and planisphere.

Peter Goldreich is an American astrophysicist whose research focuses on celestial mechanics,planetary rings,helioseismology and neutron stars. He is the Lee DuBridge Professor of Astrophysics and Planetary Physics at California Institute of Technology. Since 2005 he has also been a professor at the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton,New Jersey. Asteroid 3805 Goldreich is named after him.

Babylonian astronomy was the study or recording of celestial objects during the early history of Mesopotamia.
Astronomical chronology,or astronomical dating,is a technical method of dating events or artifacts that are associated with astronomical phenomena. Written records of historical events that include descriptions of astronomical phenomena have done much to clarify the chronology of the Ancient Near East;works of art which depict the configuration of the stars and planets and buildings which are oriented to the rising and setting of celestial bodies at a particular time have all been dated through astronomical calculations.
Clifford J. Cunningham is a Canadian-Scottish professional astronomer and author of numerous books on asteroids.

Forensic astronomy is the use of astronomy,the scientific study of celestial objects,to determine the appearance of the sky at specific times in the past. This has been used,if relatively rarely,in forensic science and for resolving historical problems more generally,notably issues in art history.

Historical models of the Solar System began during prehistoric periods and are updated to this day. The models of the Solar System throughout history were first represented in the early form of cave markings and drawings,calendars and astronomical symbols. Then books and written records became the main source of information that expressed the way the people of the time thought of the Solar System.
References
- ↑ Blaschke, Jayme; University, Texas State. "'Celestial sleuth' sheds new light on Vermeer's masterpiece 'View of Delft'". phys.org. Retrieved 2022-06-09.
- ↑ "Department Faculty". www.txst.edu. 2022-08-25. Retrieved 2022-10-15.
- 1 2 3 "Don Olson Named as Recipient of 2014 Klopsteg Memorial Lecture Award". www.aapt.org. Retrieved 2022-10-15.
- ↑ Magazine, Smithsonian. "Forensic Astronomer Solves Fine Arts Puzzles". Smithsonian Magazine. Retrieved 2022-06-09.
- ↑ Mike Wall (2019-06-06). "How Astronomy Helped Turn the Tide for the Allies on D-Day". Space.com. Retrieved 2022-06-09.
- ↑ Peplow, Mark (2004-07-19). "Battle of Marathon date revised" . Nature: news040719–1. doi:10.1038/news040719-1. ISSN 0028-0836.
- ↑ "Scientists turn up the heat on Marathon's lunar mystery". the Guardian. 2004-07-19. Retrieved 2022-06-09.
- ↑ "New Date for Caesar's British Invasion". Sky & Telescope. 2008-06-25. Retrieved 2022-06-09.
- ↑ Blaschke, Jayme; University, Texas State. "Frankenstein's moon: Astronomers vindicate account of masterwork". phys.org. Retrieved 2022-10-15.
- ↑ "Did the Moon Contribute to the Sinking of the Titanic?". Solar System Exploration Research Virtual Institute. Retrieved 2022-06-17.
- ↑ Blaschke, Jayme; University, Texas State. "The iceberg's accomplice: Did the moon sink the Titanic?". phys.org. Retrieved 2022-06-17.
- 1 2 Ouellette, Jennifer. "Forensic Astronomer Cracks the Case of Historic Meteor Procession". Scientific American Blog Network. Retrieved 2022-06-09.
- ↑ Megan Gannon (2014-09-16). "Astronomy Detectives Reveal Origin of Monet's 'Impression' Painting". Space.com. Retrieved 2022-06-09.
- ↑ Ash, Summer. ""Forensic Astronomy" Reveals the Secrets of an Iconic Ansel Adams Photo". Scientific American. Retrieved 2022-06-09.
- ↑ Simons, Paul. "Astronomers can shed light on when a picture was painted". The Times . ISSN 0140-0460 . Retrieved 2022-06-09.
- ↑ Magazine, Smithsonian; Katz, Brigit. "Is Jupiter the "Star" in Lord Byron's Famous Poem?". Smithsonian Magazine. Retrieved 2022-06-09.
- ↑ Altschuler, Eric L. (2014-03-14). "Reading Clues in the Sky Celestial Sleuth Using Astronomy to Solve Mysteries in Art, History and Literature by Donald W. Olson Springer, New York, 2014. 373 pp. Paper, 39.99. ISBN 9781461484028. Springer-Praxis Books in Popular Astronomy" . Science. 343 (6176): 1202. doi:10.1126/science.1252465. ISSN 0036-8075. S2CID 51599372.
- ↑ Ouellette, Jennifer (2018-11-16). ""Wolf's jaw" star cluster may have inspired parts of Ragnarök myth". Ars Technica. Retrieved 2022-06-09.
- ↑ Olson, Donald W. (2022). Investigating Art, History, and Literature with Astronomy. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-95554-0. ISBN 978-3-030-95553-3. S2CID 247544237.