Related Research Articles

Opera buffa is a genre of opera. It was first used as an informal description of Italian comic operas variously classified by their authors as commedia in musica, commedia per musica, dramma bernesco, dramma comico, divertimento giocoso.

Joseph Weigl was an Austrian composer and conductor, born in Eisenstadt, Hungary, Austrian Empire.

Florian Leopold Gassmann was a German-speaking Bohemian opera composer of the transitional period between the baroque and classical eras. He was one of the principal composers of dramma giocoso immediately before Mozart. He was one of Antonio Salieri’s teachers.

Giuseppe Nicolini was an Italian composer who wrote at least 45 operas. From 1819 onwards, he devoted himself primarily to religious music. He was born and died at Piacenza.
Giuseppe Farinelli was an Italian composer active at the end of the 18th century and the beginning of the 19th century who excelled in writing opera buffas. Considered the successor and most successful imitator of Domenico Cimarosa, the greatest of his roughly 60 operas include I riti d'Efeso, La contadina bizzarra and Ginevra degli Almieri. More than 2/3 of his operas were produced between 1800-1810 at the height of his popularity. With the arrival of Gioachino Rossini his operas became less desirable with the public, and by 1817 his operas were no longer performed. His other compositions include 3 piano forte sonatas, 3 oratorios, 11 cantatas, 5 masses, 2 Te Deums, a Stabat mater, a Salve regina, a Tantum ergo, numerous motets, and several other sacred works.
Farsa is a genre of opera, associated with Venice in the late 18th and early 19th centuries. It is also sometimes called farsetta.

Fra i due litiganti il terzo gode is a dramma giocoso in two acts by Giuseppe Sarti. The libretto was after Carlo Goldoni's Le nozze.
A dramma per musica is a libretto. The term was used by dramatists in Italy and elsewhere between the mid-17th and mid-19th centuries. In modern times the same meaning of drama for music was conveyed through the Italian Greek-rooted word melodramma. Dramma per musica never meant "drama through music", let alone music drama.
Vincenzo Fabrizi was an Italian composer of opera buffa.
Gennaro Astarita was an Italian composer, mainly of operas. The place of his birth is unknown, although he was active in Naples for many years. He began his operatic career in 1765, collaborating with Niccolò Piccinni in the writing of the opera L'orfana insidiata. He became the maestro di cappella in Naples in 1770.
The Mistress of the Inn, also translated as The Innkeeper Woman or Mirandolina, is a 1753 three-act comedy by the Italian playwright Carlo Goldoni about a coquette. The play has been regarded as his masterpiece. Frederick Davies describes it as Goldoni's Much Ado About Nothing.

Rinaldo di (da) Capua was an Italian composer. Little is known of him with any certainty, including his name, although he was known to Charles Burney. He may have been the father of composer Marcello Bernardini.
Marcello Bernardini was an Italian composer and librettist. Little is known of him, save that he wrote 37 operas in his career. His father was most likely the composer Rinaldo di Capua.
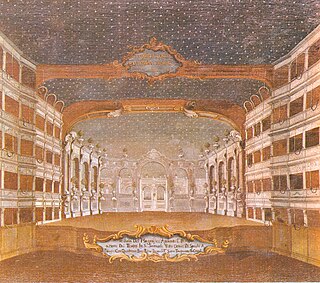
Teatro San Samuele was an opera house and theatre located at the Rio del Duca, between Campo San Samuele and Campo Santo Stefano, in Venice. One of several important theatres built in that city by the Grimani family, the theatre opened in 1656 and operated continuously until a fire destroyed the theatre in 1747. A new structure was built and opened in 1748, but financial difficulties forced the theatre to close and be sold in 1770. The theatre remained active until 1807 when it was shut down by Napoleonic decree. It reopened in 1815 and was later acquired by impresario Giuseppe Camploy in 1819. In 1853 the theatre was renamed the Teatro Camploy. Upon Camploy's death in 1889, the theatre was bequeathed to the City of Verona. The Venice City Council in turn bought the theatre and demolished it in 1894.

Il filosofo di campagna is a dramma giocoso per musica in 3 acts by composer Baldassare Galuppi. The opera uses an Italian language libretto by Carlo Goldoni. The work premiered at the Teatro San Samuele in Venice on 26 October 1754.

Il mondo della luna is an opera in 3 acts by Baldassare Galuppi. The Italian-language libretto was by Carlo Goldoni. It premiered on 29 January 1750 at the Teatro San Moisè, Venice.
Antonio Boroni was an Italian composer.

The Teatro Re was a theatre in Milan, located near the Piazza del Duomo and named for its proprietor, Carlo Re. It functioned as both a prose theatre and an opera house and saw the world premieres of numerous operas, including four by Giovanni Pacini. Designed by Luigi Canonica, the theatre was inaugurated in 1813, closed in 1872, and demolished in 1879.
References
- Stone, John (1990), HC Robbins Landon (ed.), "Mozart's Opinions and Outlook: Opera", The Mozart Compendium, London: Thames and Hudson, pp. 154–157
- Thiel, Eberhard (1984), Sachwörterbuch der Musik (in German) (4 ed.), Stuttgart: Kröner, ISBN 3520210045, OCLC 901925536
- Warrack, John; West, Ewan (1992), The Oxford Dictionary of Opera, Oxford University Press, p. 205, ISBN 0-19-869164-5