Clifton Forge is a town in Alleghany County, Virginia, United States which is part of the greater Roanoke Region. The population was 3,555 at the 2020 census. The Jackson River flows through the town, which as a result was once known as Jackson's River Station.

Chesapeake is an independent city in the Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 census, the population was 249,422, it is the second-most populous independent city in Virginia, tenth-largest in the Mid-Atlantic, and the 90th most populous city in the United States.

Grundy is a town in Buchanan County, Virginia, United States, an area of the Appalachian Mountains. The population was 1,105 at the 2000 census and 1,021 at the 2010 census. It is the county seat of Buchanan County. The town has two higher educational institutions Appalachian School of Law and Appalachian College of Pharmacy.

Hampton Roads is the name of both a body of water that serves as a wide channel for the James, Nansemond and Elizabeth rivers between Old Point Comfort and Sewell's Point where the Chesapeake Bay flows into the Atlantic Ocean, and the surrounding metropolitan region located in the southeastern Virginia and northeastern North Carolina portions of the Tidewater region.

Suffolk is an independent city in the Commonwealth of Virginia, and as such has no county. As of the 2020 census, the population was 94,324. It is the 9th most populous city in Virginia and the largest city in Virginia by boundary land area as well as the 14th largest in the country.

The Monitor–Merrimac Memorial Bridge–Tunnel (MMMBT) is the 4.6 mile-long (7.4 km) Hampton Roads crossing for Interstate 664 in the southeastern portion of Virginia in the United States. It is a four-lane bridge–tunnel composed of bridges, trestles, man-made islands, and tunnels under a portion of the Hampton Roads harbor where the mouths of the James, Nansemond, and Elizabeth Rivers come together.

South Hampton Roads is a region located in the extreme southeastern portion of Virginia's Tidewater region in the United States with a total population of 1,191,937. It is part of the Virginia Beach-Norfolk-Newport News, VA-NC MSA, which itself has a population of 1,724,876.

The James River Bridge (JRB) is a four-lane divided highway lift bridge across the James River in the Commonwealth of Virginia. Owned and operated by the Virginia Department of Transportation, it carries U.S. Route 17 (US 17), US 258, and State Route 32 across the river near its mouth at Hampton Roads. The bridge connects Newport News on the Virginia Peninsula with Isle of Wight County in the South Hampton Roads region, and is the easternmost such crossing without a tunnel component.
Nansemond is an extinct jurisdiction that was located south of the James River in Virginia Colony and in the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States, from 1646 until 1974. It was known as Nansemond County until 1972. From 1972 to 1974, a period of eighteen months, it was the independent city of Nansemond. It is now part of the independent city of Suffolk.

State Route 10 is a primary state highway in the U.S. state of Virginia. The state highway runs 93.58 miles (150.60 km) from U.S. Route 360 in Richmond east to SR 337 in Suffolk. SR 10 is a major suburban highway through Chesterfield County between the Southside of Richmond and Hopewell. Between Hopewell and Smithfield, which is served by SR 10 Business, the state highway passes through rural Prince George, Surry, and Isle of Wight counties, following the route of an old stagecoach road through an area that features many of the preserved James River plantations. SR 10 runs concurrently with US 258 and SR 32 between Smithfield and Suffolk.
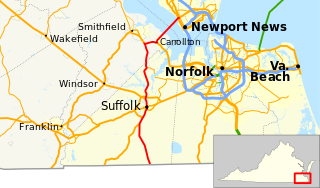
State Route 32 is a primary state highway in the U.S. state of Virginia. The state highway runs 38.89 miles (62.59 km) from the North Carolina state line in Suffolk north to U.S. Route 17, US 258, and SR 143 in Newport News. The southernmost part of SR 32 connects Suffolk with the Albemarle Region of North Carolina via North Carolina Highway 32. The remainder of SR 32 runs concurrently with at least one other state or U.S. Highway between Suffolk and Newport News, including US 13, SR 10, US 258, and US 17. The last two highways run together with SR 32 on the James River Bridge.
The state highway system of the U.S. state of Virginia is a network of roads maintained by the Virginia Department of Transportation (VDOT). As of 2006, the VDOT maintains 57,867 miles (93,128 km) of state highways, making it the third-largest system in the United States.

Transportation in the Commonwealth of Virginia is by land, sea and air. Virginia's extensive network of highways and railroads were developed and built over a period almost 400 years, beginning almost immediately after the founding of Jamestown in 1607, and often incorporating old established trails of the Native Americans.
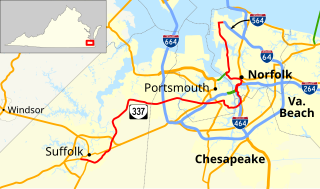
State Route 337 is a primary state highway in the South Hampton Roads area of the U.S. state of Virginia. It runs east from Suffolk to Portsmouth, where it crosses Jordan Bridge. It continues on the east side of the Southern Branch Elizabeth River in the South Norfolk neighborhood of Chesapeake. There it turns north, through Norfolk, crossing the Berkley Bridge into downtown, and ending at the Naval Station Norfolk at Sewell's Point. Most of its length was formed when other highways were rerouted: U.S. Route 460 from Suffolk to South Norfolk, SR 170 from South Norfolk to downtown Norfolk, and US 17 from downtown Norfolk to Sewell's Point. SR 337 is the only numbered highway to cross all three Branches of the Elizabeth River. It crosses the Western Branch as Portsmouth Boulevard at the Hodges Ferry Bridge, the Southern Branch on the Jordan Bridge, and the Eastern Branch on the Berkley Bridge. The Berkley Bridge is a drawbridge. SR 337 also crosses the Lafayette River in the city of Norfolk.
U.S. Route 13 is a north–south U.S. highway established in 1926 that runs for 517 miles (832 km) from Interstate 95 just north of Fayetteville, North Carolina to U.S. Route 1 in Morrisville, Pennsylvania, a northeastern suburb of Philadelphia. In the U.S. state of Virginia, US 13 runs north–south through the Hampton Roads and Eastern Shore regions of the state, using the Chesapeake Bay Bridge–Tunnel to get between the two. In the Hampton Roads area, it uses Military Highway to bypass the city centers. It is most usually a four-lane highway, sometimes up to freeway or expressway standards with controlled access.
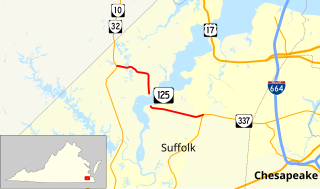
State Route 125 is a primary state highway in the U.S. state of Virginia. Known as Kings Highway, the state highway has two sections that run a total of 5.73 miles (9.22 km) from SR 10 and SR 32 at Chuckatuck east to SR 337 at Driver within the independent city of Suffolk. SR 125 consists of a 2.69-mile (4.33 km) western section and a 3.04-mile (4.89 km) eastern section separated by a gap at the Nansemond River. This gap arose when the Kings Highway Bridge across the river was removed in 2008.

Kings Highway Bridge was located on the Nansemond River in the independent city of Suffolk, Virginia, United States. Built in 1928, it carried traffic on the Kings Highway, also known as State Route 125, for over 75 years.

The Byrd Road Act was an Act of Assembly passed in February 1932 by the Virginia General Assembly. Named for former Governor Harry F. Byrd, the legislation was originally presented as measure to relieve the financial pressures of the Great Depression upon the counties, as the state offered to take over responsibility and control of most county roads, creating the Virginia Secondary Roads System.
Whaleyville is a neighborhood of Suffolk, Virginia, United States. It was formerly an incorporated town located in southern Nansemond County, Virginia. Whaleyville is located midway between the former county seat at downtown Suffolk and the North Carolina border along U.S. Route 13.