
Roman Britain was the territory that became the Roman province of Britannia after the Roman conquest of Britain, consisting of a large part of the island of Great Britain. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410.

Watling Street is a historic route in England, running from Dover and London in the southeast, via St Albans to Wroxeter. The road crosses the River Thames at London and was used in Classical Antiquity, Late Antiquity, and throughout the Middle Ages. It was used by the ancient Britons and paved as one of the main Roman roads in Britannia. The line of the road was later the southwestern border of the Danelaw with Wessex and Mercia, and Watling Street was numbered as one of the major highways of medieval England.

Camulodunum, the Ancient Roman name for what is now Colchester in Essex, was an important castrum and city in Roman Britain, and the first capital of the province. A temporary "strapline" in the 1960s identifying it as the "oldest recorded town in Britain" has become popular with residents and is still used on heritage roadsigns on trunk road approaches. Originally the site of the Brythonic-Celtic oppidum of Camulodunon, capital of the Trinovantes and later the Catuvellauni tribes, it was first mentioned by name on coinage minted by the chieftain Tasciovanus some time between 20 and 10 BC. The Roman town began life as a Roman legionary base constructed in the AD 40s on the site of the Brythonic-Celtic fortress following its conquest by the Emperor Claudius. After the early town was destroyed during the Iceni rebellion in AD 60/61, it was rebuilt, reaching its zenith in the 2nd and 3rd centuries. During this time it was known by its official name Colonia Claudia Victricensis, often shortened to Colonia Victricensis, and as Camulodunum, a Latinised version of its original Brythonic name. The town was home to a large classical temple, two theatres, several Romano-British temples, Britain's only known chariot circus, Britain's first town walls, several large cemeteries and over 50 known mosaics and tessellated pavements. It may have reached a population of 30,000 at its height.
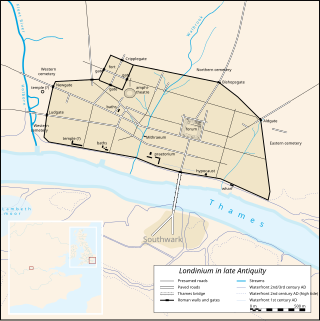
Londinium, also known as Roman London, was the capital of Roman Britain during most of the period of Roman rule. Most twenty-first century historians think that it was originally a settlement established shortly after the Claudian invasion of Britain, on the current site of the City of London around 47–50 AD, but some defend an older view that the city originated in a defensive enclosure constructed during the Claudian invasion in 43 AD. Its earliest securely-dated structure is a timber drain of 47 AD. It sat at a key ford at the River Thames which turned the city into a road nexus and major port, serving as a major commercial centre in Roman Britain until its abandonment during the 5th century.

The Iceni or Eceni were an ancient tribe of eastern Britain during the Iron Age and early Roman era. Their territory included present-day Norfolk and parts of Suffolk and Cambridgeshire, and bordered the area of the Corieltauvi to the west, and the Catuvellauni and Trinovantes to the south. In the Roman period, their capital was Venta Icenorum at modern-day Caistor St Edmund.

Letocetum is the ancient remains of a Roman settlement. It was an important military staging post and posting station near the junction of Watling Street, the Roman military road to north Wales, and Icknield Street. The site is now within the parish of Wall, Staffordshire, England. It is owned and run by the National Trust, under the name Letocetum Roman Baths Site & Museum. The site is in the guardianship of English Heritage as Wall Roman Site.

Eboracum was a fort and later a city in the Roman province of Britannia. In its prime it was the largest town in northern Britain and a provincial capital. The site remained occupied after the decline of the Western Roman Empire and ultimately developed into the present-day city of York, in North Yorkshire, England.

Durnovaria is a suggested spelling for the Latin form of the name of the Roman town of Dorchester in the modern English county of Dorset, amended from the actually observed Durnonovaria. Upon the assumption that the name was originally Brythonic, it is suggested that the first element in the name, *durno- may mean "fist" like and the second may be related to Old Irish fáir ~ fóir denoting a confined area or den. A simpler amendment would lead to *Duronovaria, making this place one of up to 18 ancient British names that contain Duro- and mostly occur at river crossings, while -novaria has two possible ancient parallels in Britain associated with river junctions. That analysis would perfectly fit the geographical situation of Dorchester.

Via Devana is the name given to a Roman Road in England that ran from Colchester in the south-east, through Cambridge in the interior, and on to Chester in the north-west. These were important Roman military centres and it is conjectured that the main reason the road was constructed was military rather than civilian. The Latin name for Chester is Deva and 'Via Devana' is thus 'The Chester Road'. Colchester was Colonia Victricensis, 'the City of Victory', and lays claim to be the oldest Roman city in Britain. The Via Devana had little civilian rationale and the road eventually fell into disuse as it was not possible to maintain extensive public works following withdrawal of the last Roman legion from Britain in 407. As a result, its route is difficult to find today, especially in its more northern reaches. It is omitted from some historians' maps for this reason but most nowadays accept its existence. The undocumented name Via Devana was coined by Charles Mason, D.D., of Trinity College, Cambridge, who was also rector of Orwell, Cambridgeshire, and Woodwardian Professor of Fossils at Cambridge University from 1734. During his life, Mason compiled a complete map of Cambridgeshire which was later published in 1808, long after his death.

High Cross is the name given to the crossroads of the Roman roads of Watling Street and Fosse Way on the border between Leicestershire and Warwickshire, England. A naturally strategic high point, High Cross was "the central cross roads" of Anglo-Saxon and Roman Britain. It was the site of a Romano-British settlement known as Venonae or Venonis, with an accompanying fort.

Isca Dumnoniorum, also known simply as Isca, was originally a Roman legionary fortress for the Second Augustan Legion in the Roman province of Britannia at the site of present-day Exeter in Devon.

Castle Hill in Cambridge, England, is located in the Castle ward of the city. Cambridgeshire County Council's former headquarters, Shire Hall, are located directly adjacent to Castle Hill.

Venta Belgarum, or Venta Bulgarum, was a town in the Roman province of Britannia Superior, the civitas capital of the local tribe, the Belgae, and which later became the city of Winchester.
Luguvalium was an ancient Roman city in northern Britain located within present-day Carlisle, Cumbria, and may have been the capital of the 4th-century province of Valentia. It was the northernmost city of the Roman Empire.

Lindinis or Lendiniae was a small town in the Roman province of Britannia. Today it is known as Ilchester, located in the English county of Somerset in the United Kingdom.

Corinium Dobunnorum was the Romano-British settlement at Cirencester in the present-day English county of Gloucestershire. Its 2nd-century walls enclosed the second-largest area of a city in Roman Britain. It was the tribal capital of the Dobunni and is usually thought to have been the capital of the Diocletian-era province of Britannia Prima.
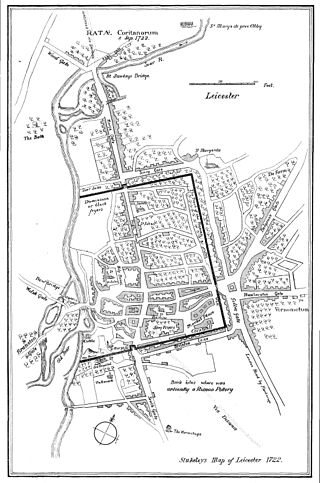
Ratae Corieltauvorum or simply Ratae was a town in the Roman province of Britannia. Today it is known as Leicester, located in the English county of Leicestershire.
Lactodurum was a town in the Roman province of Britannia. Today it is known as Towcester, located in the English county of Northamptonshire.

The Caersws Roman Forts are two Roman military camps at Caersws, Powys in Mid Wales. They were garrisoned during the occupation of Great Britain between the 1st and 5th centuries when this part of Wales was part of the Roman province of Britannia Superior. A surviving section of Roman road lies to the west of the encampments.

Lancaster Roman Fort, also known as Wery Wall or Galacum, is the modern name given to ruined former Roman fort atop Castle Hill in Lancaster in North West England. The first castra was founded c. 80 AD within the Roman province of Britannia.


















