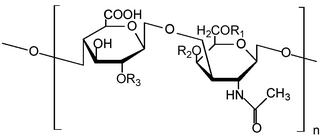
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) or mucopolysaccharides are long linear polysaccharides consisting of repeating disaccharide units. The repeating two-sugar unit consists of a uronic sugar and an amino sugar, with the exception of keratan, where in the place of the uronic sugar it has galactose. Because GAGs are highly polar and attract water, they are used in the body as a lubricant or shock absorber. Mucopolysaccharidoses are a group of metabolic disorders in which abnormal accumulations of glycosaminoglycans occur because of enzyme deficiencies.

Heparan sulfate (HS) is a linear polysaccharide found in all animal tissues. It occurs as a proteoglycan in which two or three HS chains are attached in close proximity to cell surface or extracellular matrix proteins. It is in this form that HS binds to a variety of protein ligands, including Wnt, and regulates a wide range of biological activities, including developmental processes, angiogenesis, blood coagulation, abolishing detachment activity by GrB, and tumour metastasis. HS has also been shown to serve as cellular receptor for a number of viruses, including the respiratory syncytial virus. One study suggests that cellular heparan sulfate has a role in SARS-CoV-2 Infection, particularly when the virus attaches with ACE2.

Exostosin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EXT1 gene.

Exostosin glycosyltransferase-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EXT2 gene.

Carbohydrate sulfotransferase 6 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CHST6 gene.

Carbohydrate sulfotransferase 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CHST4 gene.

Galactosylgalactosylxylosylprotein 3-beta-glucuronosyltransferase 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the B3GAT3 gene.

Bifunctional heparan sulfate N-deacetylase/N-sulfotransferase 1 is an enzyme. In humans, it is encoded by the NDST1 gene.

Exostosin-like 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EXTL3 gene.

Exostosin-like 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EXTL1 gene.

Heparan sulfate glucosamine 3-O-sulfotransferase 3A1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HS3ST3A1 gene.

Heparan-α-glucosaminide N-acetyltransferase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HGSNAT gene.

Bifunctional heparan sulfate N-deacetylase/N-sulfotransferase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NDST2 gene.

Heparan sulfate 2-O-sulfotransferase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HS2ST1 gene.

Heparan sulfate glucosamine 3-O-sulfotransferase 3B1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HS3ST3B1 gene. Heparan sulfate biosynthetic enzymes are key components in generating myriad distinct heparan sulfate fine structures that carry out multiple biologic activities. The enzyme encoded by this gene is a member of the heparan sulfate biosynthetic enzyme family. It is a type II integral membrane protein and possesses heparan sulfate glucosaminyl 3-O-sulfotransferase activity ( HS3ST3A1). The Sulfotransferase domain of this enzyme is highly similar to the same domain of heparan sulfate D-glucosaminyl 3-O-sulfotransferase 3A1 and these two enzymes sulfate an identical disaccharide. This gene is widely expressed, with the most abundant expression in liver and placenta.

D-glucuronyl C5-epimerase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GLCE gene.

Bifunctional heparan sulfate N-deacetylase/N-sulfotransferase 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NDST3 gene. It catalyses the reaction:
3'-phosphoadenylyl sulfate + α-D-glucosaminyl-[heparan sulfate](n) = adenosine 3',5'-bisphosphate + 2 H+ + N-sulfo-α-D-glucosaminyl-[heparan sulfate](n)

UDP-N-acetylglucosamine transferase subunit ALG13 homolog, also known as asparagine-linked glycosylation 13 homolog, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ALG13 gene.
Glucuronyl-galactosyl-proteoglycan 4-alpha-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine:beta-D-glucuronosyl-(1->3)-beta-D-galactosyl-(1->3)-beta-D-galactosyl-(1->4)-beta-D-xylosyl-proteoglycan 4IV-alpha-N-acetyl-D-glucosaminyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Glucuronosyl-N-acetylglucosaminyl-proteoglycan 4-alpha-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine:beta-D-glucuronosyl-(1->4)-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosaminyl-proteoglycan 4-alpha-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction


















