| East-West Dedicated Freight Corridor | |
|---|---|
| Overview | |
| Status | Proposed |
| Owner | Indian Railways |
| Locale | West Bengal, Jharkhand, Odisha, Chhattisgarh, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra |
| Termini | |
| Service | |
| Type | Freight rail |
| Operator(s) | Indian Railways |
| Technical | |
| Line length | 2,000 km (1,200 mi) |
| Track gauge | 5 ft 6 in (1,676 mm) Indian broad gauge |
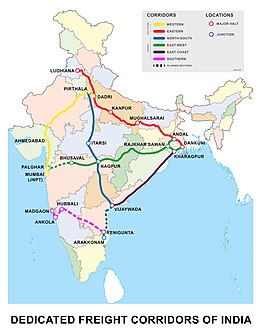
East-West Dedicated Freight Corridor or East-West DFC is a freight specific railway proposed from Eastern to Western India by Indian Railways. The corridor will run between Dankuni in West Bengal and Palghar in Maharashtra. [1] It was announced by then Railway Minister Suresh Prabhu, while presenting the Railway Budget of India in the fiscal year 2016-17. [2] The Government has indicated that they are likely to use foreign direct investment for funding the project. The project would be undertaken through Public Private Partnership (PPP) model. [3]
Notably, freight trains with a speed of maximum 100 km per hour will pass through the East-West DFC. [4]