Related Research Articles

The Russulales are an order of the Agaricomycetes,. According to the Dictionary of the Fungi, the order consists of 12 families, 80 genera, and 1767 species. According to Species Fungorum, the order contains 13 families, 117 genera, and 3,060 species.

The Cantharellales are an order of fungi in the class Agaricomycetes. The order includes not only the chanterelles (Cantharellaceae), but also some of the tooth fungi (Hydnaceae), clavarioid fungi, and corticioid fungi (Botryobasidiaceae). Species within the order are variously ectomycorrhizal, saprotrophic, associated with orchids, or facultative plant pathogens. Those of economic importance include edible and commercially collected Cantharellus, Craterellus, and Hydnum species as well as crop pathogens in the genera Ceratobasidium and Thanatephorus/Rhizoctonia.

The Agaricales are an order of fungi in the division Basidiomycota. As originally conceived, the order contained all the agarics, but subsequent research has shown that not all agarics are closely related and some belong in other orders, such as the Russulales and Boletales. Conversely, DNA research has also shown that many non-agarics, including some of the clavarioid fungi and gasteroid fungi belong within the Agaricales. The order has 46 extant families, more than 400 genera, and over 25,000 described species, along with six extinct genera known only from the fossil record. Species in the Agaricales range from the familiar Agaricus bisporus and the deadly Amanita virosa to the coral-like Clavaria zollingeri and bracket-like Fistulina hepatica.

The opisthokonts are a broad group of eukaryotes, including both the animal and fungus kingdoms. The opisthokonts, previously called the "Fungi/Metazoa group", are generally recognized as a clade. Opisthokonts together with Apusomonadida and Breviata comprise the larger clade Obazoa.

Eurotiomycetes is a large class of ascomycetes with cleistothecial ascocarps within the subphylum Pezizomycotina, currently containing around 3810 species according to the Catalogue of Life. It is the third largest lichenized class, with more than 1200 lichen species that are mostly bitunicate in the formation of asci. It contains most of the fungi previously known morphologically as "Plectomycetes".

The Ichthyosporea are a small group of Opisthokonta in Eukaryota, mostly parasites of fish and other animals.

The Mucorales is the largest and best-studied order of zygomycete fungi. Members of this order are sometimes called pin molds. The term mucormycosis is now preferred for infections caused by molds belonging to the order Mucorales.

The Leotiomycetes are a class of ascomycete fungi. Many of them cause serious plant diseases.
Archaeobiology, the study of the biology of ancient times through archaeological materials, is a subspecialty of archaeology. It can be seen as a blanket term for paleobotany, animal osteology, zooarchaeology, microbiology, and many other sub-disciplines. Specifically, plant and animal remains are also called ecofacts. Sometimes these ecofacts can be left by humans and sometimes they can be naturally occurring. Archaeobiology tends to focus on more recent finds, so the difference between archaeobiology and palaeontology is mainly one of date: archaeobiologists typically work with more recent, non-fossilised material found at archaeological sites. Only very rarely are archaeobiological excavations performed at sites with no sign of human presence.

Phycomycetes is an obsolete polyphyletic taxon for certain fungi with aseptate hyphae. It is used in the Engler system. Asexual reproduction takes place by zoospores (motile) or by Aplanospores (non-motile). These spores are endogenously produced in sporangium. A zygospore is formed by fusion of two gametes. These gametes are similar in morphology (isogamous) or dissimilar.
Dermocystida is an order of parasitic eukaryotes.

Amoebidiidae is a family of single-celled eukaryotes, previously thought to be zygomycete fungi belonging to the class Trichomycetes, but molecular phylogenetic analyses place the family with the opisthokont group Mesomycetozoea. The family was originally called Amoebidiaceae, and considered the sole family of the fungal order Amoebidiales that included two genera: Amoebidium and Paramoebidium. However, Amoebidiidae is now monogeneric as it was recently emended to include only Amoebidium. Species of Amoebidium are considered obligate symbionts of freshwater-dwelling arthropod hosts such as midge larvae and water fleas (Daphnia). However, because Amoebidium species attach to the exoskeleton (exterior) of the host and grow in axenic culture, at least some species may be facultative symbionts.
Stachylinoides is a fungal genus in the Harpellaceae family. The genus is monotypic, containing the single species Stachylinoides arctata, found in the gut of insect larvae in South America.
Smittium is a genus of fungi in the order Harpellales. It is the largest genus in the order. As of 2013, there were 81 described species. Many of these have been formally described only recently; in 1998 there were just 46. Several have been transferred to Smittium from other genera, such as Orphella, Rubetella, Genistella, and Typhella. In general, the genus has a cosmopolitan distribution, but some species are limited to small regions.
Howard C. Whisler (1931–2007) was an American mycologist. Born in Oakland, California, he attended Berkeley schools and then Palo Alto High School. Howard worked on his undergraduate degree at Oregon State College for two years and then went to the University of California, Berkeley, where he completed a Bachelor of Science degree in plant pathology in 1954. He joined the United States Air Force from 1954 to 1956 stationed in Italy. He returned to University of California, Berkeley after his military life and had finished his doctoral degree with Ralph Emerson in 1960. From 1960 to 1961 he held a post doctoral NATO-NSF Fellowship in France, at the Université de Montpellier. Howard was appointed assistant professor of Botany at McGill University in 1961. He was appointed to the faculty at the University of Washington on March 15, 1963 and worked until he died on September 16, 2007, at the age of 76.
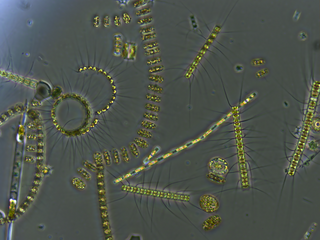
Mycoplankton are saprotrophic members of the plankton communities of marine and freshwater ecosystems. They are composed of filamentous free-living fungi and yeasts that are associated with planktonic particles or phytoplankton. Similar to bacterioplankton, these aquatic fungi play a significant role in heterotrophicmineralization and nutrient cycling. Mycoplankton can be up to 20 mm in diameter and over 50 mm in length.

Trichomycetes refers to a group of fungi in the division Zygomycota that grow in the guts of arthropods living in aquatic habitats. The name is obsolete, having not been validly published. Species formerly placed in the Trichomycetes are now placed in the orders Harpellales and Asellariales, both in the suborder subdivision Kickxellomycotina, while Amoebidiales and Eccrinales are included in Opisthokonta.
Robert W. Lichtwardt was a Brazilian-born American mycologist specializing in the study of arthropod-associated, gut-dwelling fungi (trichomycetes). He is known for his online monograph and interactive keys to trichomycete taxa.

Amoebidium is a genus of unicellular, symbiotic eukaryotes in the Opisthokont group Mesomycetozoea, family Amoebidiidae. Amoebidium species attach to the exoskeleton of freshwater aquatic arthropods such as midge larvae and water fleas (Daphnia). The type species is Amoebidium parasiticum, which is also one of the only species to be cultured axenically.

Paramoebidium is a genus of unicellular, symbiotic eukaryotes that inhabit the digestive tract of immature freshwater arthropod hosts. Paramoebidium is classified in the opisthokont class Mesomycetozoea, and is the sole genus in the family Paramoebidiidae. Prior to 2005, Paramoebidium species were tentatively placed with the fungal group Trichomycetes due to their habitation of arthropod guts, host overlap between various Paramoebidium and fungal trichomycete taxa, and similar vegetative growth form.
References
- ↑ M. Cafaro (2005). "Eccrinales (Trichomycetes) are not fungi, but a clade of protists at the early divergence of animals and fungi". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 35 (1): 21–24. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2004.12.019. PMID 15737579.