The European Central Bank (ECB) is the central component of the Eurosystem and the European System of Central Banks (ESCB) as well as one of seven institutions of the European Union. It is one of the world's most important central banks with a balance sheet total of around 7 trillion.

The euro area, commonly called the eurozone (EZ), is a currency union of 20 member states of the European Union (EU) that have adopted the euro (€) as their primary currency and sole legal tender, and have thus fully implemented EMU policies.

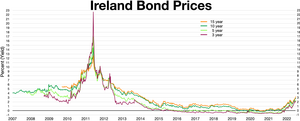
The post-2008 Irish banking crisis was when a number of Irish financial institutions faced almost imminent collapse due to insolvency during the Great Recession. In response, the Irish government instigated a €64 billion bank bailout. This then led to a number of unexpected revelations about the business affairs of some banks and business people. Ultimately, added onto the deepening recession in the country, the banks' bailout was the primary reason for the Irish government requiring IMF assistance and a total restructuring of the government occurred as result.

The European debt crisis, often also referred to as the eurozone crisis or the European sovereign debt crisis, was a multi-year debt crisis that took place in the European Union (EU) from 2009 until the mid to late 2010s. Several eurozone member states were unable to repay or refinance their government debt or to bail out over-indebted banks under their national supervision without the assistance of other eurozone countries, the European Central Bank (ECB), or the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
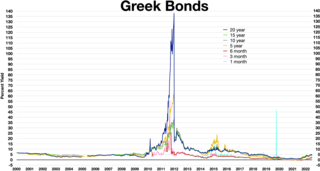
Greece faced a sovereign debt crisis in the aftermath of the 2007–2008 financial crisis. Widely known in the country as The Crisis, it reached the populace as a series of sudden reforms and austerity measures that led to impoverishment and loss of income and property, as well as a humanitarian crisis. In all, the Greek economy suffered the longest recession of any advanced mixed economy to date and became the first developed country whose stock market was downgraded to that of an emerging market in 2013. As a result, the Greek political system was upended, social exclusion increased, and hundreds of thousands of well-educated Greeks left the country.

The European Financial Stability Facility (EFSF) is a special purpose vehicle financed by members of the eurozone to address the European sovereign-debt crisis. It was agreed by the Council of the European Union on 9 May 2010, with the objective of preserving financial stability in Europe by providing financial assistance to eurozone states in economic difficulty. The Facility's headquarters are in Luxembourg City, as are those of the European Stability Mechanism. Treasury management services and administrative support are provided to the Facility by the European Investment Bank through a service level contract. Since the establishment of the European Stability Mechanism, the activities of the EFSF are carried out by the ESM.

From late 2009, fears of a sovereign debt crisis in some European states developed, with the situation becoming particularly tense in early 2010. Greece was most acutely affected, but fellow Eurozone members Cyprus, Ireland, Italy, Portugal, and Spain were also significantly affected. In the EU, especially in countries where sovereign debt has increased sharply due to bank bailouts, a crisis of confidence has emerged with the widening of bond yield spreads and risk insurance on credit default swaps between these countries and other EU members, most importantly Germany.

The European Financial Stabilisation Mechanism (EFSM) is an emergency funding programme reliant upon funds raised on the financial markets and guaranteed by the European Commission using the budget of the European Union as collateral. It runs under the supervision of the Commission and aims at preserving financial stability in Europe by providing financial assistance to member states of the European Union in economic difficulty.

The European Stability Mechanism (ESM) is an intergovernmental organization located in Luxembourg City, which operates under public international law for all eurozone member states having ratified a special ESM intergovernmental treaty. It was established on 27 September 2012 as a permanent firewall for the eurozone, to safeguard and provide instant access to financial assistance programmes for member states of the eurozone in financial difficulty, with a maximum lending capacity of €500 billion. It has replaced two earlier temporary EU funding programmes: the European Financial Stability Facility (EFSF) and the European Financial Stabilisation Mechanism (EFSM).

In the context of sovereign debt crisis, private sector involvement (PSI) refers, broadly speaking, to the forced contribution of private sector creditors to a financial crisis resolution process, and, specifically, to the private sector incurring outright reductions ("haircuts") on the value of its debt holdings.

The European debt crisis, often also referred to as the eurozone crisis or the European sovereign debt crisis, was a multi-year debt crisis that took place in the European Union (EU) from 2009 until the mid to late 2010s. Several eurozone member states were unable to repay or refinance their government debt or to bail out over-indebted banks under their national supervision without the assistance of other eurozone countries, the European Central Bank (ECB), or the International Monetary Fund (IMF).

The First Economic Adjustment Programme for Greece, initially called the Economic Adjustment Programme for Greece and usually referred to as the first bailout package or the first memorandum, is a memorandum of understanding on financial assistance to the Hellenic Republic in order to cope with the Greek government-debt crisis.
The Second Economic Adjustment Programme for Greece, usually referred to as the second bailout package or the second memorandum, is a memorandum of understanding on financial assistance to the Hellenic Republic in order to cope with the Greek government-debt crisis.
The Third Economic Adjustment Programme for Greece, usually referred to as the third bailout package or the third memorandum, is a memorandum of understanding on financial assistance to the Hellenic Republic in order to cope with the Greek government-debt crisis.
The Economic Adjustment Programme for Cyprus, usually referred to as the Bailout programme, is a memorandum of understanding on financial assistance to the Republic of Cyprus in order to cope with the 2012–13 Cypriot financial crisis.
The Economic Adjustment Programme for Portugal, usually referred to as the Bailout programme, is a Memorandum of understanding on financial assistance to the Portuguese Republic in order to cope with the 2010–14 Portuguese financial crisis.
The Troika is a term used to refer to the single decision group created by three entities, the European Commission (EC), the European Central Bank (ECB) and the International Monetary Fund (IMF). It was formed due to the European debt crisis as an ad hoc authority with a mandate to manage the bailouts of Cyprus, Greece, Ireland and Portugal, in the aftermath of their prospective insolvency caused by the world financial crisis of 2007–2008.
Greece is one of the original members of the International Monetary Fund, joining it on December 27, 1945. It has a quota of 2,428.90 million SDRs and 25,754 votes, 0.51% of the total IMF quota and votes. Greece has been represented on the IMF Board of Governors by Minister of Finance Christos Staikouras since 2019. Greece elects an Executive Director on the fund's Executive Board with Albania, Italy, Malta, Portugal and San Marino. Michail Psalidopoulos is the elected alternate director. Greece has signed two loan agreements with the IMF: a Stand-By Arrangement from 2010 to 2012 and an agreement under the Extended Fund Facility from 2012 to 2016, borrowing a total of 27,766.3 million SDR. Greece owes the IMF 6,735.64 million SDR, and is the fund's third-largest borrower. In 2018, the fund began conducting annual post-program monitoring of Greece in addition to its annual Article IV consultation.
In 2009–2010, due to substantial public and private sector debt, and "the intimate sovereign-bank linkages" the eurozone crisis impacted periphery countries. This resulted in significant financial sector instability in Europe; banks' solvency risks grew, which had direct implications for their funding liquidity. The European central bank (ECB), as the monetary union's central bank, responded to the sovereign debt crisis with a series of conventional and unconventional measures, including a decrease in the key policy interest rate, and three-year long-term refinancing operation (LTRO) liquidity injections in December 2011 and February 2012, and the announcement of the outright monetary transactions (OMT) program in the summer of 2012. The ECB acted as a de facto lender-of-last-resort (LOLR) to the euro area banking system, providing banks with cash flow in exchange for collateral, as well as a buyer of last resort (BOLR), purchasing eurozone sovereign bonds. However, the ECB's policies have been criticised for their economic repercussions as well as its political agenda.