Transport in Egypt is centered in Cairo and largely follows the pattern of settlement along the Nile. The Ministry of Transportation and other government bodies are responsible for transportation in Egypt, whether by sea, river, land or air.
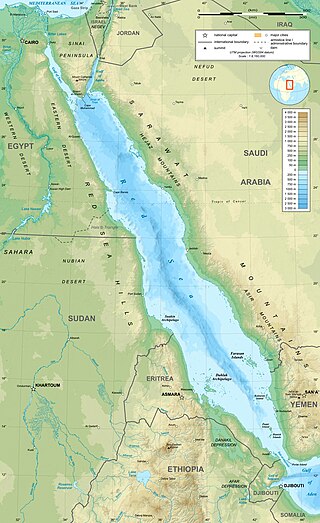
The Red Sea is a sea inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab-el-Mandeb strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and the Gulf of Suez—leading to the Suez Canal. It is underlain by the Red Sea Rift, which is part of the Great Rift Valley.

Transport in Saudi Arabia is facilitated through a relatively young system of roads, railways and seaways. Most of the network started construction after the discovery of oil in the Eastern Province in 1952, with the notable exception of Highway 40, which was built to connect the capital Riyadh to the economically productive Eastern Province, and later to the Islamic holy city of Mecca and the port city of Jeddah. With the economic growth of the 1970s, the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia has initiated many infrastructure development projects across the country, and the extensive development of the transportation network has followed suit in support of various economic developments.

The Straits of Tiran are the narrow sea passages between the Sinai and Arabian peninsulas that connect the Gulf of Aqaba and the Red Sea. The distance between the two peninsulas is about 13 km. The Multinational Force and Observers monitors the compliance of Egypt in maintaining freedom of navigation of the straits, as provided under the Egypt–Israel peace treaty.

Jeddah, alternatively transliterated as Jedda, Jiddah or Jidda, is a port city in Makkah Province, Saudi Arabia, located along the Red Sea coast in the Hejaz region. Jeddah is the commercial center of the country. It is not known when Jeddah was founded, but Jeddah's prominence grew in 647 when the Caliph Uthman made it a travel hub serving Muslim travelers going to the holy city of Mecca for Islamic pilgrimage. Since those times, Jeddah has served as the gateway for millions of pilgrims who have arrived in Saudi Arabia, traditionally by sea and recently by air.

King Abdulaziz International Airport, is a major international airport serving the cities of Jeddah and Mecca in Saudi Arabia, located 19 kilometres (12 mi) north of Jeddah and covering an area of 105 square kilometres (41 sq mi). The airport is the busiest in the kingdom and the third-largest by land area. It is also one of the busiest airports in the Middle East. Opened in 1981, it was built to replace the now-demolished Kandara Airport and is named after the founder of Saudi Arabia, King Abdulaziz.

The Egyptian Navy, also known as the Egyptian Naval Force, is the maritime branch of the Egyptian Armed Forces. It is the largest navy in the Middle East as well as Africa, and is the twelfth largest navy in the world. The navy protects more than 2,000 kilometers of coastline of the Mediterranean Sea and the Red Sea, defense of approaches to the Suez Canal, and it also supports for army operations. The majority of the modern Egyptian Navy was created with the help of the Soviet Union in the 1960s. The navy received ships in the 1980s from China and Western sources. In 1989, the Egyptian Navy had 18,000 personnel as well as 2,000 personnel in the Coast Guard. The navy received ships from the US in 1990. US shipbuilder Swiftships has built around 30 boats for the Egyptian Navy including mine hunters, survey vessels, and both steel and aluminium patrol boats.

Duba is a small city on the northern Red Sea coast, of Saudi Arabia. It is in Tabuk Province. Local citizens describe it as The Pearl of the Red Sea. The population of Duba is about 39,000.

The MS al-Salam Boccaccio 98 was an Egyptian Ro/Ro passenger ferry, operated by El Salam Maritime Transport, that sank on 3 February 2006 in the Red Sea en route from Duba, Saudi Arabia, to Safaga in southern Egypt.

The free surface effect is a mechanism which can cause a watercraft to become unstable and capsize.

The Saudi Railways Organization (SRO) was a state-owned railway company that operated part of Saudi Arabia's rail network, along with the Saudi Railway Company. The SRO operated a network of railways with a total length of approximately 1,380 kilometers. The network consisted of two main lines. A 449 km passenger line that links Dammam with Riyadh, and a 556 km freight line that connects the King Abdul Aziz Port in Dammam with Riyadh.

Jeddah Islamic Port is a Saudi Arabian port, located in Jeddah on the Red Sea, at the middle of an international shipping route between the east and west via the Suez Canal. It is the second-largest and second-busiest port in the Arab world. The city of Jeddah is the second-largest city in Saudi Arabia, and is Saudi Arabia's commercial capital.

Rabigh is a city and governorate in the Province of Makkah of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, situated on the coast of the Red Sea, around 208 km (129 mi) northwest of Mecca in the historic Hejazi region. The city had an estimated population of 180,352 in 2014 and is situated at an elevation of 13 m (43 ft) above sea level, close to the border with the Madinah Province. The city dates back to the era before the advent of Islam in the 7th century C.E., and up to the 17th century, was known as Al-Juhfah, or Al-Johfah.
Operation Hajji Baba was a humanitarian airlift operation performed by the United States Air Force between 25 and 29 August 1952. The mission of the operation was to airlift Hajj pilgrims stranded in Beirut, Lebanon to Jeddah, Saudi Arabia before the closing of the gates to Mecca.
A fixed link or fixed crossing is a permanent, unbroken road or rail connection across water that uses some combination of bridges, tunnels, and causeways and does not involve intermittent connections such as drawbridges or ferries. A bridge–tunnel combination is commonly used for major fixed links.

The Salem Express was a passenger ship that sank in the Red Sea. It is notable due to the heavy loss of life which occurred when she sank shortly after striking a reef at around 11:13pm on Saturday December 14, 1991.

The Saudi–Egypt Causeway is a proposal to link Egypt and Saudi Arabia with a causeway and bridge.

MV Free Enterprise III was a Ro-Pax vessel built in 1966 as a cross-channel ferry, operated by Townsend Thoresen mainly on the Calais and Zeebrugge routes from Dover. She was sold to Egyptian owners in 1986 and wrecked in the Red Sea in 2004.

El Arish International Airport is an airport south of El Arish, Egypt.

The Red Sea International Film Festival is a film festival launched in 2019 and held in Jeddah, western Saudi Arabia. The festival mainly focuses on new storytelling trends, as well as emerging talents from Saudi Arabia, the Arab world and the rest of the Global South. The festival looks at establishing a solid foundation for the film industry in Saudi Arabia that may contribute to diversifying the income of the country. The first edition of the festival was held in the old town of Jeddah from the 6 December to 15 December 2021. The second edition of the festival was held between the 1st and the 10th of Dec 2022, and featured the best films from Saudi Arabia, the region and a curated selection of titles from around the world.

















