
Ctenosaura is a lizard genus commonly known as spinytail iguanas or Ctenosaurs. The genus is part of the large lizard family, Iguanidae and is native to Mexico and Central America. The name is derived from two Greek words: ctenos (κτενός), meaning "comb", and saura (σαύρα), meaning "lizard".

The long-billed pipit or brown rock pipit is a passerine bird which has a wide distribution. A number of subspecies have been created for the populations in Africa, through the Arabian peninsula and South Asia. The systematics of this complex is yet to be clarified. Most birds are residents or short distance migrants.
In ancient Celtic religion, Sulevia was a goddess worshipped in Gaul, Britain, and Galicia, very often in the plural forms Suleviae or (dative) Sule(v)is. Dedications to Sulevia(e) are attested in about forty inscriptions, distributed quite widely in the Celtic world, but with particular concentrations in Noricum, among the Helvetii, along the Rhine, and also in Rome. Jufer and Luginbühl distinguish the Suleviae from another group of plural Celtic goddesses, the Matres, and interpret the name Suleviae as meaning "those who govern well". The Suleviae have been identified in one inscription with the Junones, but mostly with the Matres, for example on an inscription from Roman Colchester, as well as on most of the inscriptions from Rome. The Colchester inscription reads:
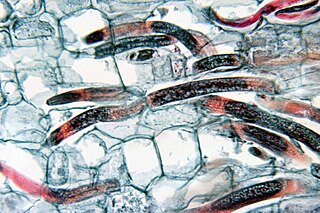
Radopholus similis is a species of nematode known commonly as the burrowing nematode. It is a parasite of plants, and it is a pest of many agricultural crops. It is an especially important pest of bananas and citrus, and it can be found on coconut, avocado, coffee, sugarcane, other grasses, and ornamentals. It is a migratory endoparasite of roots, causing lesions that form cankers. Infected plants experience malnutrition.

The social flycatcher is a passerine bird from the Americas, a member of the large tyrant flycatcher family (Tyrannidae).

Anadara is a genus of saltwater bivalves, ark clams, in the family Arcidae. It is also called Scapharca.

Ctenosaura similis, commonly known as the black spiny-tailed iguana, black iguana, or black ctenosaur, is a lizard native to Mexico and Central America that has been introduced to the United States in the state of Florida. It is the largest species in the genus Ctenosaura and has been recorded as the fastest-running species of lizard.
Callinectes similis, sometimes called the lesser blue crab or dwarf crab, is a West Atlantic species of blue crab. It was described by Austin B. Williams in 1966.
Similodonta is an extinct genus of early bivalve in the extinct family Praenuculidae. The genus is one of eleven genera in the subfamily Praenuculinae. Similodonta is known from Middle Ordovician through Middle Silurian fossils found in Europe and North America. The genus currently contains eight accepted species, Similodonta ceryx, Similodonta collina, Similodonta djupvikensis, Similodonta magna, Similodonta recurva, Similodonta spjeldnaesi, Similodonta wahli and the type species Similodonta similis.

Mylothris similis is a butterfly in the family Pieridae. It is found in Tanzania, Malawi, Zambia, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Uganda and Rwanda. The habitat consists of submontane and montane forests.

Pteropliini is a tribe of longhorn beetles of the Lamiinae subfamily.
Epectasis is a genus of longhorn beetles of the subfamily Lamiinae, containing the following species:

The Simili Tour was the eighth concert tour by Italian recording artist, Laura Pausini. Launched in the spring of 2016, the tour promoted her twelfth studio album Simili (2015). Over the course of five months, the tour visited Europe and the Americas.

Simili is an Italian-language studio album released by Laura Pausini on November 6, 2015, this is her twelfth studio album. Pausini also made a Spanish version of the album Similares, released on November 13, 2015. The first single was released on September 25, 2015 in two versions; in Italian "Lato Destro del Cuore", and the Spanish version "Lado Derecho del Corazón". The Spanish-language version of the album received a nomination for a Grammy Award for Best Latin Pop Album.
Epectasis hiekei is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Stephan von Breuning in 1974. It is known from Honduras and Mexico.
Epectasis juncea is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae, and the type species of its genus. It was described by Newman in 1840, originally under the genus Saperda. It has a wide distribution between Central and South America.
Epectasis junceoides is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Stephan von Breuning in 1961. It is known from Brazil.
Epectasis mexicana is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Stephan von Breuning in 1954. It is known from Mexico.
Epectasis panamensis is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Stephan von Breuning in 1974. It is known from Panama.
Epectasis rotundipennis is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Stephan von Breuning in 1943. It is known from Brazil.











