Déjà vu is a French loanword for the phenomenon of feeling as though one has lived through the present situation before. It is an illusion of memory whereby — despite a strong sense of recollection — the time, place, and context of the "previous" experience are uncertain or impossible. Approximately two-thirds of surveyed populations report experiencing déjà vu at least one time in their lives. The phenomenon manifests occasionally as a symptom of pre-seizure auras, and some researchers have associated chronic/frequent "pathological" déjà vu with neurological or psychiatric illness. Experiencing déjà vu has been correlated with higher socioeconomic status, better educational attainment, and lower ages. People who travel often, frequently watch films, or frequently remember their dreams are also more likely to experience déjà vu than others.

Epilepsy is a group of non-communicable neurological disorders characterized by recurrent epileptic seizures. An epileptic seizure is the clinical manifestation of an abnormal, excessive, purposeless and synchronized electrical discharge in the brain cells called neurons. The occurrence of two or more unprovoked seizures defines epilepsy. The occurrence of just one seizure may warrant the definition in a more clinical usage where recurrence may be able to be prejudged. Epileptic seizures can vary from brief and nearly undetectable periods to long periods of vigorous shaking due to abnormal electrical activity in the brain. These episodes can result in physical injuries, either directly such as broken bones or through causing accidents. In epilepsy, seizures tend to recur and may have no immediate underlying cause. Isolated seizures that are provoked by a specific cause such as poisoning are not deemed to represent epilepsy. People with epilepsy may be treated differently in various areas of the world and experience varying degrees of social stigma due to the alarming nature of their symptoms.

An epileptic seizure, informally known as a seizure, is a period of symptoms due to abnormally excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. Outward effects vary from uncontrolled shaking movements involving much of the body with loss of consciousness, to shaking movements involving only part of the body with variable levels of consciousness, to a subtle momentary loss of awareness. Most of the time these episodes last less than two minutes and it takes some time to return to normal. Loss of bladder control may occur.

Hypergraphia is a behavioral condition characterized by the intense desire to write or draw. Forms of hypergraphia can vary in writing style and content. It is a symptom associated with temporal lobe changes in epilepsy and in Geschwind syndrome. Structures that may have an effect on hypergraphia when damaged due to temporal lobe epilepsy are the hippocampus and Wernicke's area. Aside from temporal lobe epilepsy, chemical causes may be responsible for inducing hypergraphia.

Lennox–Gastaut syndrome (LGS) is a complex, rare, and severe childhood-onset epilepsy. It is characterized by multiple and concurrent seizure types, cognitive dysfunction, and slow spike waves on electroencephalogram (EEG). Typically, it presents in children aged 3–5 years and can persist into adulthood. It has been associated with several gene mutations, perinatal injuries, congenital infections, brain tumors/malformations, and genetic disorders such as tuberous sclerosis and West syndrome. The prognosis for LGS is poor with a 5% mortality in childhood and persistent seizures into adulthood (80–90%).
Neurosteroids, also known as neuroactive steroids, are endogenous or exogenous steroids that rapidly alter neuronal excitability through interaction with ligand-gated ion channels and other cell surface receptors. The term neurosteroid was coined by the French physiologist Étienne-Émile Baulieu and refers to steroids synthesized in the brain. The term, neuroactive steroid refers to steroids that can be synthesized in the brain, or are synthesized by an endocrine gland, that then reach the brain through the bloodstream and have effects on brain function. The term neuroactive steroids was first coined in 1992 by Steven Paul and Robert Purdy. In addition to their actions on neuronal membrane receptors, some of these steroids may also exert effects on gene expression via nuclear steroid hormone receptors. Neurosteroids have a wide range of potential clinical applications from sedation to treatment of epilepsy and traumatic brain injury. Ganaxolone, a synthetic analog of the endogenous neurosteroid allopregnanolone, is under investigation for the treatment of epilepsy.
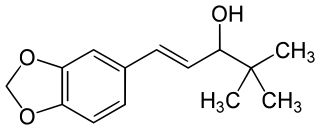
Stiripentol, sold under the brand name Diacomit, is an anticonvulsant medication used for the treatment of Dravet syndrome - a serious genetic brain disorder.

An aura is a perceptual disturbance experienced by some with epilepsy or migraine. An epileptic aura is a seizure.
Psychogenic non-epileptic seizures (PNES) are events resembling an epileptic seizure, but without the characteristic electrical discharges associated with epilepsy. PNES fall under the category of disorders known as functional neurological disorders (FND), also known as conversion disorders. A more recent term to describe these events is dissociative non-epileptic seizures. These are typically treated by psychologists or psychiatrists. PNES has previously been called pseudoseizures, psychogenic seizures, and hysterical seizures, but these terms have fallen out of favor.

Temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) is a chronic disorder of the nervous system which is characterized by recurrent, unprovoked focal seizures that originate in the temporal lobe of the brain and last about one or two minutes. TLE is the most common form of epilepsy with focal seizures. A focal seizure in the temporal lobe may spread to other areas in the brain when it may become a focal to bilateral seizure.
Frontal lobe epilepsy (FLE) is a neurological disorder that is characterized by brief, recurring seizures arising in the frontal lobes of the brain, that often occur during sleep. It is the second most common type of epilepsy after temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE), and is related to the temporal form in that both forms are characterized by partial (focal) seizures.

Epilepsy Currents is a bimonthly peer-reviewed open-access medical journal that was established in 2001 by the American Epilepsy Society. It publishes commentary articles, written by a board of contributing editors, and brief topical reviews. While commentary articles are solicited from members of the board of contributing editors, the editors entertain suggestions regarding topics for review articles. Content is available on the society's web site and on PubMed Central. The journal began to be self-published by the society in collaboration with Allen Press in 2011; prior to that time the journal was published on behalf of the society by Wiley-Blackwell.
The Archives of Sexual Behavior is a peer-reviewed academic journal in sexology. It is the official publication of the International Academy of Sex Research.
Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy (JME), also known as Janz syndrome, is a form of genetic generalized epilepsy, representing 5–10% of all epilepsy cases. Typically it first presents between the ages of 12 and 18 with myoclonic seizures. These events typically occur after awakening from sleep, during the evening or when sleep deprived. JME is also characterized by generalized tonic–clonic seizures, and a minority of patients have absence seizures. The genetics of JME are complex and rapidly evolving as over 20 chromosomal loci and multiple genes have been identified. Given the genetic and clinical heterogeneity of JME some authors have suggested that it should be thought of as a spectrum disorder.
Geschwind syndrome, also known as Gastaut-Geschwind, is a group of behavioral phenomena evident in some people with temporal lobe epilepsy. It is named for one of the first individuals to categorize the symptoms, Norman Geschwind, who published prolifically on the topic from 1973 to 1984. There is controversy surrounding whether it is a true neuropsychiatric disorder. Temporal lobe epilepsy causes chronic, mild, interictal changes in personality, which slowly intensify over time. Geschwind syndrome includes five primary changes; hypergraphia, hyperreligiosity, atypical sexuality, circumstantiality, and intensified mental life. Not all symptoms must be present for a diagnosis. Only some people with epilepsy or temporal lobe epilepsy show features of Geschwind syndrome.
Genes, Brain and Behavior is a peer-reviewed online-only scientific journal covering research in the fields of behavioral, neural, and psychiatric genetics. It is published by Wiley-Blackwell on behalf of the International Behavioural and Neural Genetics Society. The journal was established in 2002 as a quarterly and is currently published monthly. G2B is a hybrid open access journal, but two years after publication all content is available for free online.

Epileptic Disorders is a peer-reviewed medical journal focusing on quality scientific and educational content related to all aspects of epilepsy including its diagnosis, natural history, and management. The current editor-in-chief is Sandor Beniczky and it is published by John Libbey Eurotext. As of 2021, the impact factor of the journal is 2.333. In 2013, Epileptic Disorders became the official educational journal of the International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE).
Epilepsia is a peer-reviewed medical journal focusing on all aspects of epilepsy. The journal was established in 1909. It is the official journal of the International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE),
Epilepsy-intellectual disability in females also known as PCDH19 gene-related epilepsy or epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, 9 (EIEE9), is a rare type of epilepsy that affects predominately females and is characterized by clusters of brief seizures, which start in infancy or early childhood, and is occasionally accompanied by varying degrees of cognitive impairment. The striking pattern of onset seizures at a young age, genetic testing and laboratory results, potential developmental delays or developmental regression and associated disorders, eases diagnosis.

Seizure: European Journal of Epilepsy is a peer-reviewed medical journal covering epilepsy established in 1992. The editor-in-chief is Markus Reuber. It is the official journal of Epilepsy Action. It is published ten times a year by Elsevier.







