
At 824,292 km2 (318,261 sq mi), Namibia is the world's thirty-fourth largest country. After Mongolia, Namibia is the second least densely populated country in the world. Namibia got its name from the Namib desert that stretches along the coast of the Atlantic. It is also known for its wildlife.

The Himba are an ethnic group with an estimated population of about 50,000 people living in northern Namibia, in the Kunene Region and on the other side of the Kunene River in southern Angola. There are also a few groups left of the OvaTwa, who the OvaHimba consider to be part of their tribe, but are hunter-gatherers. Culturally distinguishable from the Herero people, the OvaHimba are a semi-nomadic, pastoralist people and speak OtjiHimba, a variety of Herero, which belongs to the Bantu family within Niger–Congo. The OvaHimba are semi-nomadic as they have base homesteads where crops are cultivated, but may have to move within the year depending on rainfall and where there is access to water.

Etosha National Park is a national park in northwestern Namibia and one of the largest national parks in Africa. It was proclaimed a game reserve in March 1907 in Ordinance 88 by the Governor of German South West Africa, Friedrich von Lindequist. It was designated as Wildschutzgebiet in 1958, and was awarded the status of national park in 1967, by an act of parliament of the Republic of South Africa. It spans an area of 22,270 km2 (8,600 sq mi) and was named after the large Etosha pan which is almost entirely within the park. With an area of 4,760 km2 (1,840 sq mi), the Etosha pan covers 23% of the total area of the national park. The area is home to hundreds of species of mammals, birds and reptiles, including several threatened and endangered species such as the black rhinoceros. Sixty-one black rhinoceros were killed during poaching in Namibia during 2022, 46 of which were killed in Etosha.

Omusati is one of the fourteen regions of Namibia, its capital is Outapi. The towns of Okahao, Oshikuku and Ruacana as well as the self-governed village Tsandi are situated in this region. As of 2020, Omusati had 148,834 registered voters.

Kunene is one of the fourteen regions of Namibia. Its capital is Opuwo, its governor is Marius Sheya. The region's name comes from the Kunene River which forms the northern border with Angola. Besides the capital Opuwo, the region contains the municipality of Outjo, the town Khorixas and the self-governed village Kamanjab. Kunene is home to the Himba people, a subtribe of the Herero, as well as to Damara people and Nama people. As of 2020, Kunene had 58,548 registered voters.

The Cunene or Kunene is a river in Southern Africa. It flows from the Angola highlands southwards to the border with Namibia. It then flows in a westerly direction along the border until it reaches the Atlantic Ocean.
Kaokoland was an administrative unit and a bantustan in northern South West Africa. Established in 1980 during the apartheid era, it was intended to be a self-governing homeland of the Ovahimba, but an actual government was never established, and the territory was administered by the leaders of Hereroland. Like other homelands in South West Africa, the Kaokoland bantustan was abolished in May 1989, at the beginning of the transition of Namibia towards independence.
Articles related to Namibia include:

Sioma Ngwezi National Park is a 5,000-square-kilometre park in the south west corner of Zambia. It is undeveloped and rarely visited, lacking roads and being off the usual tourist tracks, but this may change in the future.

Calueque is a town next to a dam and pumping station of the same name on the Kunene River in the Kunene Province of southern Angola. The water project is linked to Ruacana, 20 km (12 mi) away in Namibia, where the Ruacana Power Station is. This dam is one of the last landmarks along the Kunene River, prior to the Kunene becoming a border feature between Angola and Namibia. A 300 km (190 mi) pipeline and canal extends across the border into Namibia, supplying towns as far away as Oshakati in Ovamboland with water. The dam was completed in 1976. However, due to the onset of the Angolan civil war following independence, the full master plan for the scheme was not realised by the South African and Portuguese governments.

Angola is located on the western Atlantic Coast of Southern Africa between Namibia and the Republic of the Congo. It also is bordered by the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Zambia to the east. The country consists of a sparsely watered and somewhat sterile coastal plain extending inland for a distance varying from 50 to 160 km. Slightly inland and parallel to the coast is a belt of hills and mountains and behind those a large plateau. The total land size is 1,246,700 km2 (481,400 sq mi). It has an Exclusive Economic Zone of 518,433 km2 (200,168 sq mi).
The Calueque Dam, is an operational multipurpose dam across the Kunene River, in Kunene Province, in southwestern Angola. The dam stores water for the 347 MW (465,000 hp) Ruacana Hydroelectric Power Station, in neighboring Namibia. Its waters are also used for the irrigation of farmland, both in Angola and Namibia.

Angolan mopane woodlands are situated in southwestern Angola, extending into northern Namibia. This ecosystem surrounds Etosha Pan, which is considered a separate ecoregion. The mopane trees are the main type of vegetation.

The Ruacana Hydroelectric Power Station is a hydroelectric power plant across the Kunene River near Ruacana in northwest Namibia, close to the Angolan border. Commissioned in 1978, it is by far the largest power station in Namibia. Its operator is NamPower, the Namibian national electric power utility company.

Ruacana Constituency is an electoral constituency in the Omusati Region of Namibia on the border to Angola. It had 10,722 inhabitants in 2004 and 9,285 registered voters in 2020. Its district capital is the town of Ruacana.

Swartbooisdrift is a small settlement in the Kunene Region in the north of Namibia. It is situated on the banks of the Kunene River, at the Angolan border on the minor road D3700 and falls within the Epupa electoral constituency. Swartbooisdrift is populated by 150 - 300 semi-nomadic people of Himba and Herero descent, depending on the season.

The Minyon Falls is a plunge waterfall on Repentance Creek in the Northern Rivers region of New South Wales, Australia. The waterfall descends more than 100 metres (330 ft) over the huge rhyolite cliffs which were once part of the Tweed Volcano. The water flow eroded the rocks to create the waterfall.

The Zembapeople are a Bantu ethnic group residing in the border regions of Namibia and Angola. In Namibia, they are predominantly found in the Kunene region, most notably in the Opuwa area. They speak the Zemba language, also known as OtjiZemba or Dhimba. The Zemba are well-known for their distinctive hairstyles, intricate iron and copper jewelry, as well as traditional clothing that often incorporates animal hides. Additionally, they decorate themselves with a blend of ash, ochre paste, and rancid butter to enhance their appearance.

Bwabwata National Park is a protected area in northeastern Namibia that was established in 2007 and covers 6,274 km2 (2,422 sq mi). It was created by merging Namibia's Caprivi Game Park and Mahango Game Park. It is situated in the Zambezi and Kavango East regions, extending along the Caprivi Strip. It is bounded by the Okavango River to the west and the Kwando River to the east. Angola lies to the north and Botswana to the south.
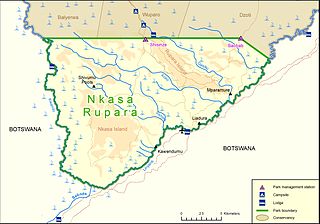
Nkasa Rupara National Park, also Nkasa Lupala National Park, formerly Mamili National Park, is a national park in Namibia. It is centered on the Nkasa and Rupara islands on the Kwando/Linyanti River in the south-western corner of East Caprivi. Botswana lies to the west, south and east, and Sangwali village to the north. It is Namibia's largest formally protected wetland area. It is one of Namibia’s protected areas that benefits local communities surrounding parks. The unfenced park forms a trans-boundary link for wildlife migration between Angola, Botswana, Namibia and Zambia. Nkasa Rupara is part of the Kavango Zambezi Transfrontier Conservation Area.


















