Related Research Articles

The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), also called the Law of the Sea Convention or the Law of the Sea Treaty, is an international agreement that establishes a legal framework for all marine and maritime activities. As of June 2016, 167 countries and the European Union are parties.

The Strait of Juan de Fuca is a body of water about 96 miles long that is the Salish Sea's main outlet to the Pacific Ocean. The international boundary between Canada and the United States runs down the centre of the Strait.

The Beaufort Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located north of the Northwest Territories, the Yukon, and Alaska, and west of Canada's Arctic islands. The sea is named after Sir Francis Beaufort, a hydrographer. The Mackenzie River, the longest in Canada, empties into the Canadian part of the Beaufort Sea west of Tuktoyaktuk, which is one of the few permanent settlements on the sea's shores.

The term territorial waters is sometimes used informally to refer to any area of water over which a sovereign state has jurisdiction, including internal waters, the territorial sea, the contiguous zone, the exclusive economic zone, and potentially the extended continental shelf. In a narrower sense, the term is used as a synonym for the territorial sea.

Law of the sea is a body of international law governing the rights and duties of states in maritime environments. It concerns matters such as navigational rights, sea mineral claims, and coastal waters jurisdiction.

An exclusive economic zone (EEZ), as prescribed by the 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, is an area of the sea in which a sovereign state has special rights regarding the exploration and use of marine resources, including energy production from water and wind. It stretches from the outer limit of the territorial sea out to 200 nautical miles (nmi) from the coast of the state in question. It is also referred to as a maritime continental margin and, in colloquial usage, may include the continental shelf. The term does not include either the territorial sea or the continental shelf beyond the 200 nautical mile limit. The difference between the territorial sea and the exclusive economic zone is that the first confers full sovereignty over the waters, whereas the second is merely a "sovereign right" which refers to the coastal state's rights below the surface of the sea. The surface waters, as can be seen in the map, are international waters.
The natural prolongation principle or principle of natural prolongation is a legal concept introduced in maritime claims submitted to the United Nations.
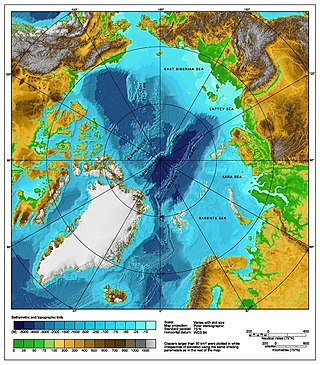
The Arctic consists of land, internal waters, territorial seas, exclusive economic zones (EEZs) and international waters above the Arctic Circle. All land, internal waters, territorial seas and EEZs in the Arctic are under the jurisdiction of one of the eight Arctic coastal states: Canada, Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia, Sweden and the United States. International law regulates this area as with other portions of Earth.

The Indonesia–Malaysia border consists of a 1,881 km land border that divides the territory of Indonesia and Malaysia on the island of Borneo. It also includes maritime boundaries along the length of the Straits of Malacca, in the South China Sea and in the Celebes Sea.
Malaysia and Vietnam are two Southeast Asian countries with maritime boundaries which meet in the Gulf of Thailand and South China Sea. The two countries have overlapping claims over the continental shelf in the Gulf of Thailand. Both countries have, however, come to an agreement to jointly exploit the natural resources in the disputed area pending resolution of the dispute over sovereignty.

The Australia–Indonesia border is a maritime boundary running west from the two countries' tripoint maritime boundary with Papua New Guinea in the western entrance to the Torres Straits, through the Arafura Sea and Timor Sea, and terminating in the Indian Ocean. The boundary is, however, broken by the Timor Gap, where Australian and East Timorese territorial waters meet and where the two countries have overlapping claims to the seabed.
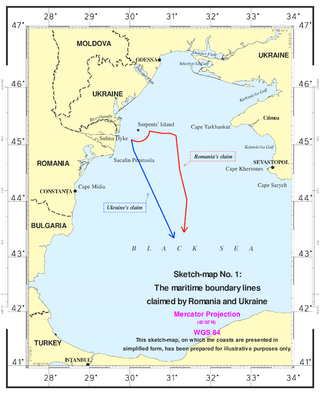
The Case concerning maritime delimitation in the Black Sea (Romania v Ukraine) [2009] ICJ 3 was a decision of the International Court of Justice (ICJ). On September 16, 2004, Romania brought its case to the court after unsuccessful bilateral negotiations. On February 3, 2009, the court handed down its verdict, establishing a maritime boundary including the continental shelf and exclusive economic zones for Romania and Ukraine.
Daniel J. Dzurek is an American academic geographer, author and government official. He was formerly the Chief of the Spatial, Environmental and Boundary Analysis Division of the United States Department of State.

A maritime boundary is a conceptual division of the Earth's water surface areas using physiographic or geopolitical criteria. As such, it usually bounds areas of exclusive national rights over mineral and biological resources, encompassing maritime features, limits and zones. Generally, a maritime boundary is delineated at a particular distance from a jurisdiction's coastline. Although in some countries the term maritime boundary represents borders of a maritime nation that are recognized by the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, maritime borders usually serve to identify the edge of international waters.

Germany v Denmark and the Netherlands [1969] ICJ 1 were a series of disputes that came to the International Court of Justice in 1969. They involved agreements among Denmark, Germany, and the Netherlands regarding the "delimitation" of areas—rich in oil and gas—of the continental shelf in the North Sea.

There are disputes between China, Japan, Taiwan and South Korea over the extent of their respective exclusive economic zones (EEZs) in the East China Sea.

The Chukchi Plateau or Chukchi Cap is a large subsea formation extending north from the Alaskan margin into the Arctic Ocean. The ridge is normally covered by ice year-round, and reaches an approximate bathymetric prominence of 3,400 m with its highest point at 246 m below sea level. As a subsea ridge extending from the continental shelf of the United States north of Alaska, the Chukchi Plateau is an important feature in maritime law of the Arctic Ocean and has been the subject of significant geographic research. The ridge has been extensively mapped by the USCGC Healy, and by the Canadian icebreaker CCGS Louis S. St-Laurent in 2011 and RV Marcus Langseth, a National Science Foundation vessel operated by the Lamont–Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University.
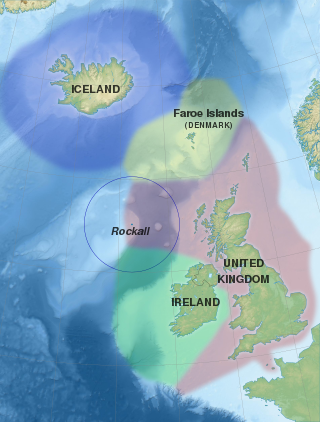
Several states have claimed interests over the sea bed adjoining Rockall, an uninhabitable granite islet which is located within the exclusive economic zone (EEZ) of the United Kingdom. Ireland, Denmark, Iceland, and the United Kingdom have all made submissions to the commission set up under the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS).

The exclusive economic zone of North Korea stretches 200 nautical miles from its basepoints in both the Yellow Sea and the Sea of Japan. The exclusive economic zone (EEZ) was declared in 1977 after North Korea had contested the validity of the Northern Limit Lines (NLL) set up after the Korean War as maritime borders. The EEZ has not been codified in law and North Korea has never specified its coordinates, making it difficult to determine its specific scope.
The borders of Indonesia include land and maritime borders with Malaysia, Papua New Guinea, and Timor Leste, as well as shared maritime boundaries with Australia, India, Palau, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam.
References
- 1 2 "Federal Outer Continental Shelf (OCS) Administrative Boundaries Extending from the Submerged Lands Act Boundary seaward to the Limit of the United States Outer Continental Shelf," Federal Register, January 3, 2006 (Volume 71, Number 1) pp. 127–131.
- ↑ Dorinda G. Dallmeyer et al. (1989). Rights to Oceanic Resources: Deciding and Drawing Maritime Boundaries, pp. 34, 158. , p. 34, at Google Books