
In finance, a bond is a type of security under which the issuer (debtor) owes the holder (creditor) a debt, and is obliged – depending on the terms – to provide cash flow to the creditor. The timing and the amount of cash flow provided varies, depending on the economic value that is emphasized upon, thus giving rise to different types of bonds. The interest is usually payable at fixed intervals: semiannual, annual, and less often at other periods. Thus, a bond is a form of loan or IOU. Bonds provide the borrower with external funds to finance long-term investments or, in the case of government bonds, to finance current expenditure.
Investment is traditionally defined as the "commitment of resources to achieve later benefits". If an investment involves money, then it can be defined as a "commitment of money to receive more money later". From a broader viewpoint, an investment can be defined as "to tailor the pattern of expenditure and receipt of resources to optimise the desirable patterns of these flows". When expenditures and receipts are defined in terms of money, then the net monetary receipt in a time period is termed cash flow, while money received in a series of several time periods is termed cash flow stream.
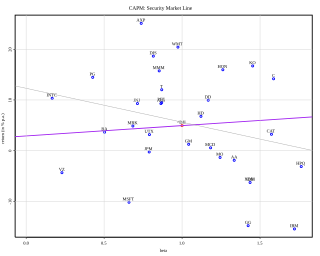
In finance, the capital asset pricing model (CAPM) is a model used to determine a theoretically appropriate required rate of return of an asset, to make decisions about adding assets to a well-diversified portfolio.
A hedge is an investment position intended to offset potential losses or gains that may be incurred by a companion investment. A hedge can be constructed from many types of financial instruments, including stocks, exchange-traded funds, insurance, forward contracts, swaps, options, gambles, many types of over-the-counter and derivative products, and futures contracts.
In finance, a convertible bond, convertible note, or convertible debt is a type of bond that the holder can convert into a specified number of shares of common stock in the issuing company or cash of equal value. It is a hybrid security with debt- and equity-like features. It originated in the mid-19th century, and was used by early speculators such as Jacob Little and Daniel Drew to counter market cornering.

A risk premium is a measure of excess return that is required by an individual to compensate being subjected to an increased level of risk. It is used widely in finance and economics, the general definition being the expected risky return less the risk-free return, as demonstrated by the formula below.
Stock valuation is the method of calculating theoretical values of companies and their stocks. The main use of these methods is to predict future market prices, or more generally, potential market prices, and thus to profit from price movement – stocks that are judged undervalued are bought, while stocks that are judged overvalued are sold, in the expectation that undervalued stocks will overall rise in value, while overvalued stocks will generally decrease in value. A target price is a price at which an analyst believes a stock to be fairly valued relative to its projected and historical earnings.
In economics and accounting, the cost of capital is the cost of a company's funds, or from an investor's point of view is "the required rate of return on a portfolio company's existing securities". It is used to evaluate new projects of a company. It is the minimum return that investors expect for providing capital to the company, thus setting a benchmark that a new project has to meet.
In finance, arbitrage pricing theory (APT) is a multi-factor model for asset pricing which relates various macro-economic (systematic) risk variables to the pricing of financial assets. Proposed by economist Stephen Ross in 1976, it is widely believed to be an improved alternative to its predecessor, the capital asset pricing model (CAPM). APT is founded upon the law of one price, which suggests that within an equilibrium market, rational investors will implement arbitrage such that the equilibrium price is eventually realised. As such, APT argues that when opportunities for arbitrage are exhausted in a given period, then the expected return of an asset is a linear function of various factors or theoretical market indices, where sensitivities of each factor is represented by a factor-specific beta coefficient or factor loading. Consequently, it provides traders with an indication of ‘true’ asset value and enables exploitation of market discrepancies via arbitrage. The linear factor model structure of the APT is used as the basis for evaluating asset allocation, the performance of managed funds as well as the calculation of cost of capital. Furthermore, the newer APT model is more dynamic being utilised in more theoretical application than the preceding CAPM model. A 1986 article written by Gregory Connor and Robert Korajczyk, utilised the APT framework and applied it to portfolio performance measurement suggesting that the Jensen coefficient is an acceptable measurement of portfolio performance.
In finance, the beta is a statistic that measures the expected increase or decrease of an individual stock price in proportion to movements of the stock market as a whole. Beta can be used to indicate the contribution of an individual asset to the market risk of a portfolio when it is added in small quantity. It refers to an asset's non-diversifiable risk, systematic risk, or market risk. Beta is not a measure of idiosyncratic risk.
The equity premium puzzle refers to the inability of an important class of economic models to explain the average equity risk premium (ERP) provided by a diversified portfolio of equities over that of government bonds, which has been observed for more than 100 years. There is a significant disparity between returns produced by stocks compared to returns produced by government treasury bills. The equity premium puzzle addresses the difficulty in understanding and explaining this disparity. This disparity is calculated using the equity risk premium:
Business valuation is a process and a set of procedures used to estimate the economic value of an owner's interest in a business. Here various valuation techniques are used by financial market participants to determine the price they are willing to pay or receive to effect a sale of the business. In addition to estimating the selling price of a business, the same valuation tools are often used by business appraisers to resolve disputes related to estate and gift taxation, divorce litigation, allocate business purchase price among business assets, establish a formula for estimating the value of partners' ownership interest for buy-sell agreements, and many other business and legal purposes such as in shareholders deadlock, divorce litigation and estate contest.

Asset allocation is the implementation of an investment strategy that attempts to balance risk versus reward by adjusting the percentage of each asset in an investment portfolio according to the investor's risk tolerance, goals and investment time frame. The focus is on the characteristics of the overall portfolio. Such a strategy contrasts with an approach that focuses on individual assets.
Financial risk is any of various types of risk associated with financing, including financial transactions that include company loans in risk of default. Often it is understood to include only downside risk, meaning the potential for financial loss and uncertainty about its extent.
In finance, an asset class is a group of financial instruments that have similar financial characteristics and behave similarly in the marketplace. We can often break these instruments into those having to do with real assets and those having to do with financial assets. Often, assets within the same asset class are subject to the same laws and regulations; however, this is not always true. For instance, futures on an asset are often considered part of the same asset class as the underlying instrument but are subject to different regulations than the underlying instrument.

The "Fed model", or "Fed Stock Valuation Model" (FSVM), is a disputed theory of equity valuation that compares the stock market's forward earnings yield to the nominal yield on long-term government bonds, and that the stock market – as a whole – is fairly valued, when the one-year forward-looking I/B/E/S earnings yield equals the 10-year nominal Treasury yield; deviations suggest over-or-under valuation.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to finance:
The risk–return spectrum is the relationship between the amount of return gained on an investment and the amount of risk undertaken in that investment. The more return sought, the more risk that must be undertaken.

Stocks for the Long Run is a book on investing by Jeremy Siegel. Its first edition was released in 1994. Its fifth edition was released on January 7, 2014. According to Pablo Galarza of Money, "His 1994 book Stocks for the Long Run sealed the conventional wisdom that most of us should be in the stock market." James K. Glassman, a financial columnist for The Washington Post, called it one of the 10 best investment books of all time.
Jeremy James Siegel is the Russell E. Palmer Professor of Finance at the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Siegel comments extensively on the economy and financial markets. He appears regularly on networks including CNN, CNBC and NPR, and writes regular columns for Kiplinger's Personal Finance and Yahoo! Finance. Siegel's paradox is named after him.






