Financial economics is the branch of economics characterized by a "concentration on monetary activities", in which "money of one type or another is likely to appear on both sides of a trade". Its concern is thus the interrelation of financial variables, such as share prices, interest rates and exchange rates, as opposed to those concerning the real economy. It has two main areas of focus: asset pricing and corporate finance; the first being the perspective of providers of capital, i.e. investors, and the second of users of capital. It thus provides the theoretical underpinning for much of finance.
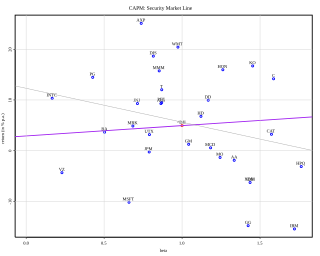
In finance, the capital asset pricing model (CAPM) is a model used to determine a theoretically appropriate required rate of return of an asset, to make decisions about adding assets to a well-diversified portfolio.

The efficient-market hypothesis (EMH) is a hypothesis in financial economics that states that asset prices reflect all available information. A direct implication is that it is impossible to "beat the market" consistently on a risk-adjusted basis since market prices should only react to new information.
Rational pricing is the assumption in financial economics that asset prices – and hence asset pricing models – will reflect the arbitrage-free price of the asset as any deviation from this price will be "arbitraged away". This assumption is useful in pricing fixed income securities, particularly bonds, and is fundamental to the pricing of derivative instruments.
Modern portfolio theory (MPT), or mean-variance analysis, is a mathematical framework for assembling a portfolio of assets such that the expected return is maximized for a given level of risk. It is a formalization and extension of diversification in investing, the idea that owning different kinds of financial assets is less risky than owning only one type. Its key insight is that an asset's risk and return should not be assessed by itself, but by how it contributes to a portfolio's overall risk and return. It uses the past variance of asset prices as a proxy for future risk.
In finance, the beta is a statistic that measures the expected increase or decrease of an individual stock price in proportion to movements of the Stock market as a whole. Beta can be used to indicate the contribution of an individual asset to the market risk of a portfolio when it is added in small quantity. It is referred to as an asset's non-diversifiable risk, systematic risk, or market risk. Beta is not a measure of idiosyncratic risk.
In finance, Jensen's alpha is used to determine the abnormal return of a security or portfolio of securities over the theoretical expected return. It is a version of the standard alpha based on a theoretical performance instead of a market index.
Alpha is a measure of the active return on an investment, the performance of that investment compared with a suitable market index. An alpha of 1% means the investment's return on investment over a selected period of time was 1% better than the market during that same period; a negative alpha means the investment underperformed the market. Alpha, along with beta, is one of two key coefficients in the capital asset pricing model used in modern portfolio theory and is closely related to other important quantities such as standard deviation, R-squared and the Sharpe ratio.
A market anomaly in a financial market is predictability that seems to be inconsistent with theories of asset prices. Standard theories include the capital asset pricing model and the Fama-French Three Factor Model, but a lack of agreement among academics about the proper theory leads many to refer to anomalies without a reference to a benchmark theory. Indeed, many academics simply refer to anomalies as "return predictors", avoiding the problem of defining a benchmark theory.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to finance:
The single-index model (SIM) is a simple asset pricing model to measure both the risk and the return of a stock. The model has been developed by William Sharpe in 1963 and is commonly used in the finance industry. Mathematically the SIM is expressed as:
The consumption-based capital asset pricing model (CCAPM) is a model of the determination of expected return on an investment. The foundations of this concept were laid by the research of Robert Lucas (1978) and Douglas Breeden (1979).
Roll's critique is a famous analysis of the validity of empirical tests of the capital asset pricing model (CAPM) by Richard Roll. It concerns methods to formally test the statement of the CAPM, the equation
In asset pricing and portfolio management the Fama–French three-factor model is a statistical model designed in 1992 by Eugene Fama and Kenneth French to describe stock returns. Fama and French were colleagues at the University of Chicago Booth School of Business, where Fama still works. In 2013, Fama shared the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for his empirical analysis of asset prices. The three factors are (1) market excess return, (2) the outperformance of small versus big companies, and (3) the outperformance of high book/market versus low book/market companies. There is academic debate about the last two factors.
A portfolio manager (PM) is a professional responsible for making investment decisions and carrying out investment activities on behalf of vested individuals or institutions. Clients invest their money into the PM's investment policy for future growth, such as a retirement fund, endowment fund, or education fund. PMs work with a team of analysts and researchers and are responsible for establishing an investment strategy, selecting appropriate investments, and allocating each investment properly towards an investment fund or asset management vehicle.
In Finance the Treynor–Black model is a mathematical model for security selection published by Fischer Black and Jack Treynor in 1973. The model assumes an investor who considers that most securities are priced efficiently, but who believes they have information that can be used to predict the abnormal performance (Alpha) of a few of them; the model finds the optimum portfolio to hold under such conditions.

In investing and finance, the low-volatility anomaly is the observation that low-volatility stocks have higher returns than high-volatility stocks in most markets studied. This is an example of a stock market anomaly since it contradicts the central prediction of many financial theories that taking higher risk must be compensated with higher returns.
Returns-based style analysis is a statistical technique used in finance to deconstruct the returns of investment strategies using a variety of explanatory variables. The model results in a strategy's exposures to asset classes or other factors, interpreted as a measure of a fund or portfolio manager's investment style. While the model is most frequently used to show an equity mutual fund’s style with reference to common style axes, recent applications have extended the model’s utility to model more complex strategies, such as those employed by hedge funds.
In portfolio management, the Carhart four-factor model is an extra factor addition in the Fama–French three-factor model, proposed by Mark Carhart. The Fama-French model, developed in the 1990, argued most stock market returns are explained by three factors: risk, price and company size. Carhart added a momentum factor for asset pricing of stocks. The Four Factor Model is also known in the industry as the Monthly Momentum Factor (MOM). Momentum is the speed or velocity of price changes in a stock, security, or tradable instrument.
Nontraded assets are assets that are not traded on the market. Human capital is the most important nontraded assets. Other important nontraded asset classes are private businesses, claims to government transfer payments and claims on trust income.






















