
Coca is any of the four cultivated plants in the family Erythroxylaceae, native to western South America. Coca is known for its psychoactive alkaloid, cocaine.

Sorghum is a genus of about 25 species of flowering plants in the grass family Poaceae. Some of these species have grown as cereals for human consumption and some in pastures for animals. One species, Sorghum bicolor, was originally domesticated in Africa and has since spread throughout the globe. Seventeen of the 25 species are native to Australia, with the range of some extending to Africa, Asia, Mesoamerica, and certain islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. One species is grown for grain, while many others are used as fodder plants, either cultivated in warm climates worldwide or naturalized in pasture lands. Sorghum is in the subfamily Panicoideae and the tribe Andropogoneae.

Erythroxylum coca is one of two species of cultivated coca.

Rosewood refers to any of a number of richly hued timbers, often brownish with darker veining, but found in many different hues.
The name Catuaba is used for the infusions of the bark of a number of trees native to Brazil. The most widely used barks are derived from the trees Trichilia catigua and Erythroxylum vaccinifolium. Other catuaba preparations use the bark of trees from the following genera or families: Anemopaegma, Ilex, Micropholis, Phyllanthus, Secondatia, Tetragastris and species from the Myrtaceae.

Erythroxylum (Erythroxylon) is a genus of tropical flowering plants in the family Erythroxylaceae. Many of the approximately 200 species contain the drug cocaine; Erythroxylum coca, a native of South America, is the main commercial source of cocaine and of the mild stimulant coca tea. Another species, Erythroxylum vaccinifolium is used as an aphrodisiac in Brazilian drinks and herbal medicine.

Erythroxylaceae is a family of flowering trees and shrubs consisting of 4 genera and 271 species. The four genera are AneulophusBenth., ErythroxylumP.Browne, NectaropetalumEngl., and PinacopodiumExell & Mendonça. The best-known species are the coca plants, including the species Erythroxylum coca, the source of the drug cocaine.

Erythroxylum australe is a shrub or small tree in the Malpighiales, endemic to northern Australia. The plant is known by a variety of names including Brigalow erythroxylon shrub and dogwood.
Erythroxylum ellipticum is a Northern Australian species of Erythroxylum. It grows as a shrub or tree.

Catuabines are a group of tropane alkaloids, isolated from Erythroxylum vaccinifolium, which are used in the preparation of the drug Catuaba. While catuabine A, B and C were isolated and characterized by Graf and Lude, catuabine D was recently isolated by Zanolari et al. The catuabines are not known to have any physiological effects, this is in contrast to cocaine, which is an active constituent of another species, Erythroxylum coca.
Erythroxylum pacificum is a species of plant in the Erythroxylaceae family. It is endemic to Peru.
Erythroxylum sechellarum is a species of plant in the Erythroxylaceae family. It is endemic to Seychelles.
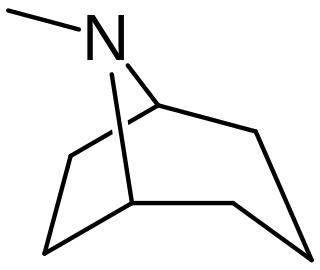
Tropane alkaloids are a class of bicyclic [3.2.1] alkaloids and secondary metabolites that contain a tropane ring in their chemical structure. Tropane alkaloids occur naturally in many members of the plant family Solanaceae. Some tropane alkaloids have pharmacological properties and can act as anticholinergics or stimulants.

Erythroxylum novogranatense is a neotropical species of Erythroxylum (Erythroxylaceae). Cocaine is produced from the leaves.

Ombuin is an O-methylated flavonol, a type of flavonoid. It is the 4',7-O-methyl derivative of quercetin.
Coca alkaloids are the alkaloids found in the coca plant, Erythroxylum coca. They are predominantly of either the pyrrolidine or the tropane types.

Erythroxylum vaccinifolium is a flowering plant species in the genus Erythroxylum.
Erythroxylum rufum, the rufous false coca, is a flowering plant species in the genus Erythroxylum.
Erythroxylum zeylanicum is a species of plant in the Erythroxylaceae family. It is endemic to Sri Lanka.

Erythroxylum monogynum, the bastard sandal or red cedar, is a tropical tree in the family Erythroxylaceae. It is native to Peninsular India and Sri Lanka. It is a small, evergreen bushy tree reaching 7 m (23 ft). The leaves are simple, alternate. Small white flowers are bisexual with 5–6 sepals. borne March through June; Fruit is a one-seeded drupe. Flowering and fruiting occur throughout the year. The plant is known to have high medicinal value. It is taken to cure many diseases such as Stomachic, Dyspepsia, Fever, and Dropsy in ayurvedic medicine.











