Related Research Articles

Bishkek, formerly Pishpek and Frunze, is the capital and largest city of Kyrgyzstan. Bishkek is also the administrative centre of the Chuy Region. The region surrounds the city, although the city itself is not part of the region but rather a region-level unit of Kyrgyzstan. It is also near the Kazakhstan–Kyrgyzstan border. Its population was 1,074,075 in 2021.

Kaliningrad Oblast is the westernmost federal subject of Russia. It is a semi-exclave, and is situated on the Baltic coast. The oblast's largest city and administrative centre is the city of Kaliningrad, formerly known as Königsberg. The oblast's port city of Baltiysk is Russia's only port on the Baltic Sea that remains ice-free in winter. The oblast had a population of roughly 1 million in the Russian Census of 2010.

Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, covering over 17,125,191 square kilometres (6,612,073 sq mi), and encompassing one-eighth of Earth's inhabitable landmass. Russia extends across eleven time zones, and has the most borders of any country in the world, with sixteen sovereign nations. It has a population of 146.2 million; and is the most populous country in Europe, and the ninth-most populous country in the world. Moscow, the capital, is the largest city in Europe; while Saint Petersburg is the second-largest city and cultural centre. Russians are the largest Slavic and European nation; they speak Russian, the most spoken Slavic language, and the most spoken native language in Europe.

Russian is an East Slavic language native to Russia in Eastern Europe. It is a part of the Indo-European language family, and is one of four living East Slavic languages, and also part of the larger Balto-Slavic branch. Russian is an official language in Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan, and is used widely as a lingua franca throughout Ukraine, the Caucasus, Central Asia, and to some extent in the Baltic states. It was the de facto language of the Soviet Union until its dissolution, and continues to be used in public life with varying proficiency in all of the post-Soviet states.

Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin is a Russian politician and former intelligence officer who is serving as the current president of Russia. He has been serving in this position since 2012, and he previously held this office from 1999 until 2008. He was also the prime minister from 1999 to 2000, and again from 2008 to 2012. Putin is the second-longest serving European president in modern history.

The East Slavs are the most populous subgroup of the Slavs. They speak the East Slavic languages, and formed the majority of the population of the medieval state Kievan Rus', which all three independent East Slavic states claim as their cultural ancestor. By the seventeenth-century, the East Slavs eventually evolved into the Belarusians, the Russians, the Rusyns, and the Ukrainians.

Ukrainian, historically also called Ruthenian, is an East Slavic language of the Indo-European language family, and is one of Slavic languages, which are part of a larger Balto-Slavic branch. It is the native language of Ukrainians and the official state language of Ukraine. Written Ukrainian uses a variant of the Cyrillic script.

The Bering Strait is a strait between the Pacific and Arctic oceans, separating the Chukchi Peninsula of the Russian Far East from the Seward Peninsula of Alaska. The present Russia-United States maritime boundary is at 168° 58' 37" W longitude, slightly south of the Arctic Circle at about 65° 40' N latitude. The Strait is named after Vitus Bering, a Danish explorer in the service of the Russian Empire.

Sakha, also known as Yakutia or Yakutiya, is a republic of Russia. It is situated in the Russian Far East, along the Arctic Ocean, with a population of roughly 1 million. Sakha comprises half of the area of its governing Far Eastern Federal District, and is the world's largest country subdivision, covering over 3,083,523 square kilometers (1,190,555 sq mi). Yakutsk, which is the world's coldest large city, is its capital and largest city. The republic has a reputation for an extreme and severe climate, with the lowest temperatures in the Northern Hemisphere being recorded in Verkhoyansk and Oymyakon, and regular winter averages commonly dipping below −35 °C (−31 °F) in Yakutsk. The hypercontinental tendencies also result in warm summers for much of the republic.

The Russians are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Eastern Europe, who share a common Russian ancestry, culture, and history. Russian, the most spoken Slavic language, is the shared mother tongue of the Russians; and Orthodox Christianity is their historical religion since the 11th century. They are the largest Slavic nation, as well as the largest European nation.

Krasnodar Krai is a federal subject of Russia, located in the North Caucasus region in Southern Russia and administratively a part of the Southern Federal District. Its administrative center is the city of Krasnodar. The third most populous federal subject, the krai had a population of 5,226,647 as of the 2010 Census.

The Republic of Buryatia is a federal subject of Russia, located in Siberia. Formerly part of the Siberian Federal District, it has been a part of the Russian Far East since 2018. Its capital is the city of Ulan-Ude. Its area is 351,300 square kilometers (135,600 sq mi) with a population of 972,021.

UTC+08:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of +08:00. In ISO 8601 the associated time would be written as 2019-02-07T23:28:34+08:00.

UTC+09:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of +09:00.

UTC+03:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of +03:00. In areas using this time offset, the time is three hours later than the Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). Following the ISO 8601 standard, a time with this offset would be written as, for example, 2019-02-08T23:36:06+03:00.
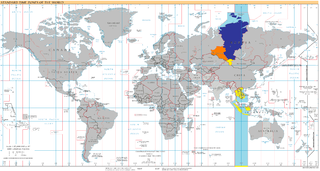
UTC+07:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of +07:00. In ISO 8601 the associated time would be written as 2021-12-31T23:48:02+07:00. It is 7 hours ahead of the UTC, meaning areas in this time zone would be 07:00 while UTC is shown to midnight (00:00).

UTC+05:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of +05:00. This time is used in:
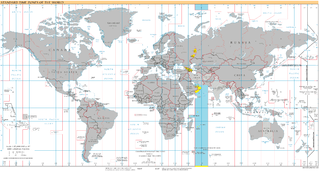
UTC+04:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of +04:00. In ISO 8601 the associated time would be written as 2019-02-07T23:28:34+04:00. This time is used in:
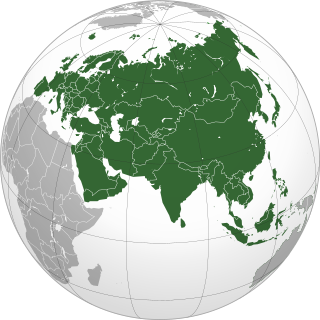
Eurasia is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago in the east. The continental landmass is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean and Africa to the west, the Pacific Ocean to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and by Africa, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Indian Ocean to the south. The division between Europe and Asia as two continents is a historical social construct, as much of their borders is over land; thus, in some parts of the world, Eurasia is recognized as the largest of the six, five, or four continents on Earth. In geology, Eurasia is often considered as a single rigid megablock. However, the rigidity of Eurasia is debated based on paleomagnetic data.

Vladivostok is the largest city and the administrative centre of Primorsky Krai, Russia. The city is located around the Golden Horn Bay on the Sea of Japan, covering an area of 331.16 square kilometres, with a population of 606,561 residents, up to 812,319 residents in the urban agglomeration. Vladivostok is the second-largest city in the Far Eastern Federal District, as well as the Russian Far East, after Khabarovsk.
References
- ↑ "Review of Ethmiidae (Lepidoptera) of the Asian part of Russia and neighbouring territories". Archived from the original on 2012-06-30. Retrieved 2012-01-20.