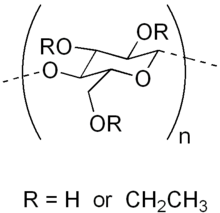
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula (C
6H
10O
5)
n, a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wall of green plants, many forms of algae and the oomycetes. Some species of bacteria secrete it to form biofilms. Cellulose is the most abundant organic polymer on Earth. The cellulose content of cotton fibre is 90%, that of wood is 40–50%, and that of dried hemp is approximately 57%.
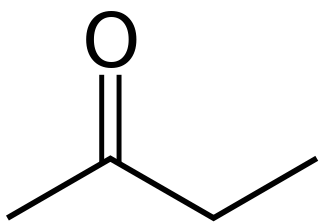
Butanone, also known as methyl ethyl ketone (MEK) or ethyl methyl ketone, is an organic compound with the formula CH3C(O)CH2CH3. This colorless liquid ketone has a sharp, sweet odor reminiscent of acetone. It is produced industrially on a large scale, but occurs in nature only in trace amounts. It is partially soluble in water, and is commonly used as an industrial solvent. It is an isomer of another solvent, tetrahydrofuran.

Ethyl butyrate, also known as ethyl butanoate, or butyric ether, is an ester with the chemical formula CH3CH2CH2COOCH2CH3. It is soluble in propylene glycol, paraffin oil, and kerosene. It has a fruity odor, similar to pineapple, and is a key ingredient used as a flavor enhancer in processed orange juices. It also occurs naturally in many fruits, albeit at lower concentrations.
An excipient is a substance formulated alongside the active ingredient of a medication. They may be used to enhance the active ingredient’s therapeutic properties; to facilitate drug absorption; to reduce viscosity; to enhance solubility; to improve long-term stabilization ; or to add bulk to solid formulations that have small amounts of potent active ingredients. During the manufacturing process, excipients can improve the handling of active substances and facilitate powder flow. The choice of excipients depends on factors such as the intended route of administration, the dosage form, and compatibility with the active ingredient.
Microencapsulation is a process in which tiny particles or droplets are surrounded by a coating to give small capsules, with useful properties. In general, it is used to incorporate food ingredients, enzymes, cells or other materials on a micro metric scale. Microencapsulation can also be used to enclose solids, liquids, or gases inside a micrometric wall made of hard or soft soluble film, in order to reduce dosing frequency and prevent the degradation of pharmaceuticals.
An anticaking agent is an additive placed in powdered or granulated materials, such as table salt or confectioneries, to prevent the formation of lumps (caking) and for easing packaging, transport, flowability, and consumption. Caking mechanisms depend on the nature of the material. Crystalline solids often cake by formation of liquid bridge and subsequent fusion of microcrystals. Amorphous materials can cake by glass transitions and changes in viscosity. Polymorphic phase transitions can also induce caking.
Resinous glaze is an alcohol-based solution of various types of food-grade shellac. The shellac is derived from the raw material sticklac, which is a resin scraped from the branches of trees left from when the small insect, Kerria lacca, creates a hard, waterproof cocoon. When used in food and confections, it is also known as confectioner's glaze, pure food glaze, natural glaze, or confectioner's resin. When used on medicines, it is sometimes called pharmaceutical glaze.

Hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) is a derivative of cellulose with both water solubility and organic solubility. It is used as an excipient, and topical ophthalmic protectant and lubricant.

A thickening agent or thickener is a substance which can increase the viscosity of a liquid without substantially changing its other properties. Edible thickeners are commonly used to thicken sauces, soups, and puddings without altering their taste; thickeners are also used in paints, inks, explosives, and cosmetics.

Carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) or cellulose gum is a cellulose derivative with carboxymethyl groups (-CH2-COOH) bound to some of the hydroxyl groups of the glucopyranose monomers that make up the cellulose backbone. It is often used in its sodium salt form, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose. It used to be marketed under the name Tylose, a registered trademark of SE Tylose.
An enteric coating is a polymer barrier applied to oral medication that prevents its dissolution or disintegration in the gastric environment. This helps by either protecting drugs from the acidity of the stomach, the stomach from the detrimental effects of the drug, or to release the drug after the stomach. Some drugs are unstable at the pH of gastric acid and need to be protected from degradation. Enteric coating is also an effective method to obtain drug targeting. Other drugs such as some anthelmintics may need to reach a high concentration in a specific part of the intestine. Enteric coating may also be used during studies as a research tool to determine drug absorption. Enteric-coated medications pertain to the "delayed action" dosage form category. Tablets, mini-tablets, pellets and granules are the most common enteric-coated dosage forms.

Methyl cellulose is a compound derived from cellulose. It is sold under a variety of trade names and is used as a thickener and emulsifier in various food and cosmetic products, and also as a bulk-forming laxative. Like cellulose, it is not digestible, non-toxic, and not an allergen. In addition to culinary uses, it is used in arts and crafts such as papier-mâché and is often the main ingredient of wallpaper paste.
Glycol ethers are a class of chemical compounds consisting of alkyl ethers that are based on glycols such as ethylene glycol or propylene glycol. They are commonly used as solvents in paints and cleaners. They have good solvent properties while having higher boiling points than the lower-molecular-weight ethers and alcohols.
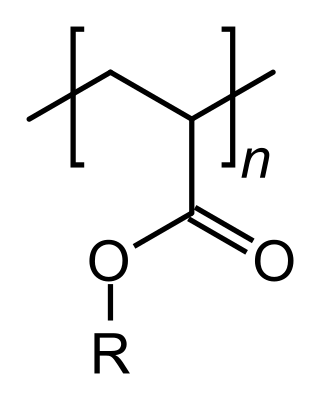
An acrylate polymer is any of a group of polymers prepared from acrylate monomers. These plastics are noted for their transparency, resistance to breakage, and elasticity.

Hypromellose (INN), short for hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC), is a semisynthetic, inert, viscoelastic polymer used in eye drops, as well as an excipient and controlled-delivery component in oral medicaments, found in a variety of commercial products.

Hydroxyethyl cellulose is a gelling and thickening agent derived from cellulose. It is widely used in cosmetics, cleaning solutions, and other household products. Hydroxyethyl cellulose and methyl cellulose are frequently used with hydrophobic drugs in capsule formulations, to improve the drugs' dissolution in the gastrointestinal fluids. This process is known as hydrophilization.

Nanocellulose is a term referring to a familly of cellulosic materials that have at least one of their dimensions in the nanoscale. Examples of nanocellulosic materials are microfibrilated cellulose, cellulose nanofibers or cellulose nanocrystals. Nanocellulose may be obtained from natural cellulose fibers through different production processes. This family of materials possess various interesting properties for a wide range of potential applications.

Bacterial cellulose is an organic compound with the formula (C
6H
10O
5)
n produced by certain types of bacteria. While cellulose is a basic structural material of most plants, it is also produced by bacteria, principally of the genera Komagataeibacter, Acetobacter, Sarcina ventriculi and Agrobacterium. Bacterial, or microbial, cellulose has different properties from plant cellulose and is characterized by high purity, strength, moldability and increased water holding ability. In natural habitats, the majority of bacteria synthesize extracellular polysaccharides, such as cellulose, which form protective envelopes around the cells. While bacterial cellulose is produced in nature, many methods are currently being investigated to enhance cellulose growth from cultures in laboratories as a large-scale process. By controlling synthesis methods, the resulting microbial cellulose can be tailored to have specific desirable properties. For example, attention has been given to the bacteria Komagataeibacter xylinus due to its cellulose's unique mechanical properties and applications to biotechnology, microbiology, and materials science.

Ethyl methyl cellulose is a thickener, vegetable gum, foaming agent and emulsifier. Its E number is E465.