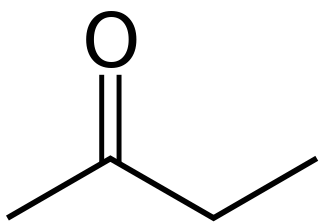
Butanone, also known as methyl ethyl ketone (MEK) or ethyl methyl ketone, is an organic compound with the formula CH3C(O)CH2CH3. This colorless liquid ketone has a sharp, sweet odor reminiscent of acetone. It is produced industrially on a large scale, but occurs in nature only in trace amounts. It is partially soluble in water, and is commonly used as an industrial solvent. It is an isomer of another solvent, tetrahydrofuran.

Palmitic acid is a fatty acid with a 16-carbon chain. It is the most common saturated fatty acid found in animals, plants and microorganisms. Its chemical formula is CH3(CH2)14COOH, and its C:D ratio is 16:0. It is a major component of palm oil from the fruit of Elaeis guineensis, making up to 44% of total fats. Meats, cheeses, butter, and other dairy products also contain palmitic acid, amounting to 50–60% of total fats.

Ethyl oleate is a fatty acid ester formed by the condensation of oleic acid and ethanol. It is a colorless oil although degraded samples can appear yellow.

Ethyl acetate is the organic compound with the formula CH3CO2CH2CH3, simplified to C4H8O2. This colorless liquid has a characteristic sweet smell and is used in glues, nail polish removers, and the decaffeination process of tea and coffee. Ethyl acetate is the ester of ethanol and acetic acid; it is manufactured on a large scale for use as a solvent.
The chemical compound ethyl nitrite is an alkyl nitrite with a chemical formula C2H5NO2. It may be prepared from ethanol.

Ethyl formate is an ester formed when ethanol reacts with formic acid. Ethyl formate has the characteristic smell of rum and is partially responsible for the flavor of raspberries, occurring naturally in some plant oils, fruits, and juices. Ethyl formate does not occur naturally in the animal kingdom.
Cetyl alcohol, also known as hexadecan-1-ol and palmityl alcohol, is a C-16 fatty alcohol with the formula CH3(CH2)15OH. At room temperature, cetyl alcohol takes the form of a waxy white solid or flakes. The name cetyl derives from the whale oil (cetacea oil, from Latin: cetus, lit. 'whale', from Ancient Greek: κῆτος, romanized: kētos, lit. 'huge fish') from which it was first isolated.

Retinyl palmitate, or vitamin A palmitate, is the ester of retinol (vitamin A) and palmitic acid, with formula C36H60O2. It is the most abundant form of vitamin A storage in animals.

Ascorbyl palmitate is an ester formed from ascorbic acid and palmitic acid creating a fat-soluble form of vitamin C. In addition to its use as a source of vitamin C, it is also used as an antioxidant food additive. It is approved for use as a food additive in the EU, the U.S., Canada, Australia, and New Zealand.
In enzymology, a fatty-acid peroxidase (EC 1.11.1.3) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a retinyl-palmitate esterase (EC 3.1.1.21) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction.
The molecular formula C18H36O2 (molar mass: 284.48 g/mol, exact mass: 284.2715 u) may refer to:

Ethyl iodoacetate is an organic compound with the chemical formula ICH2CO2CH2CH3. It is a derivative of ethyl acetate. Under normal conditions, the compound is a clear, light yellow to orange liquid.

Pipotiazine (Piportil), also known as pipothiazine, is a typical antipsychotic of the phenothiazine class used in the United Kingdom and other countries for the treatment of schizophrenia. Its properties are similar to those of chlorpromazine. A 2004 systematic review investigated its efficacy for people with schizophrenia:

Propetandrol, or propethandrol, also known as 17α-ethyl-19-nortestosterone 3β-propionate or 17α-ethyl-19-nor-4-androstenediol 3β-propionate, as well as 17α-ethylestr-4-en-3β,17β-diol 3β-propionate, is a synthetic and orally active anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS) and progestogen and a 17α-alkylated derivative of 19-nortestosterone. It is an androgen ester – specifically, the 3β-propionate ester of norethandrolone (17α-ethyl-19-nortestosterone).

Azinphos-ethyl was a broad-spectrum organophosphate insecticide.
Estradiol palmitate, or estradiol monopalmitate, also known as estradiol 17β-hexadecanoate, is a naturally occurring steroidal estrogen and an estrogen ester – specifically, the C17β palmitate ester of estradiol. It occurs in the body as a very long-lasting metabolite and prohormone of estradiol. The compound has no affinity for the estrogen receptor, requiring transformation into estradiol for its estrogenic activity. In addition to its endogenous role, estradiol palmitate was formerly used as a fattening agent in chickens under the brand name Esmopal.
Lipoidal estradiol (LE2) is the variety of endogenous C17β long-chain fatty acid esters of estradiol which are formed as metabolites of estradiol. Important examples of these esters include estradiol arachidonate, estradiol lineolate, estradiol oleate, estradiol palmitate, and estradiol stearate. LE2 are estrogens but do not bind to the estrogen receptor, instead acting as prohormones of estradiol. Relative to estradiol, they have far longer-lasting durations of effect due to their much slower rates of metabolism and clearance. It has been hypothesized that LE2 may serve as a store of estrogen for when estradiol levels become low. LE2 are highly lipophilic and hydrophobic and are found in highest concentrations in adipose tissue and other estrogen-sensitive tissues and in low but detectable concentrations in circulation, with none excreted in urine. They have been referred to as the "endogenous counterparts of the synthetic esters of estrogens" like estradiol valerate and estradiol cypionate.











