
The Chincha Islands are a group of three small islands 21 kilometres (13 mi) off the southwest coast of Peru, to which they belong, near the town of Pisco. Since pre-Incan times they were of interest for their extensive guano deposits, but the supplies were mostly exhausted by 1874.

Eupithecia is a large genus of moths of the family Geometridae. There are hundreds of described species, found in all parts of the world, and new species are discovered on a regular basis.

The common pug(Eupithecia vulgata) is a moth of the family Geometridae. It is a common species across the Palearctic region, the Near East and North Africa. It ranges from the Atlantic coast of Ireland and Portugal across Europe, the Middle East and Central Asia to the Russian Far East (Priamurje) and Korea.

The juniper pug or juniper looper(Eupithecia pusillata) is a moth of the family Geometridae. It is found throughout the Palearctic and Nearctic regions and the Near East.

Juan Antonio Pezet was a Peruvian military officer and politician who served in the positions of Secretary of War, Vice President and the 26th and 28th President of Peru throughout his life. As President, his moderate and cautious attitude towards the occupation of the Chincha Islands by a Spanish Fleet in 1864 was used as an excuse to launch a military uprising that drove him out of power.

The Chincha culture consisted of a Native American (Indian) people living near the Pacific Ocean in south west Peru. The Chincha Kingdom and their culture flourished in the Late Intermediate Period, also known as the regional states period of pre-Columbian Peru. They became part of the Inca Empire around 1480. They were prominent as sea-going traders and lived in a large and fertile oasis valley. La Centinela is an archaeological ruin associated with the Chincha. It is located near the present-day city of Chincha Alta.

Tambo Colorado is a well-preserved Inca adobe complex near the coast of Peru, also known under the Quechua names Puka Tampu, Pukallaqta or Pukawasi.

Chincha Alta is a Peruvian city located in the Ica Region. It is the capital of Chincha Province.
Festejo is a festive form of Afro-Peruvian music. The dance is a staple in the Black coastal populations and it celebrates the emancipation of slaves. Festejo is recognized for its high energy and the improvisation carried out by the dancers. Some believe that its origins trace back to competitive dance circles performed by individuals playing cajóns. Despite its African origins, people of all different backgrounds participate in the dance that many regards as one of the greatest representations of Peruvian culture.
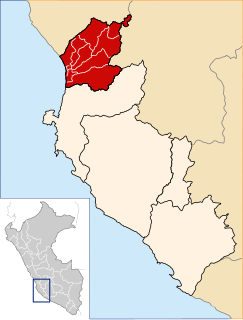
The Chincha Province is one of five provinces of the Ica Region of Peru. The capital of the province is the city of Chincha Alta.
Lunahuaná is a district in the middle Cañete Province in Peru. It is bordered by Imperial District on the west, San Vicente de Cañete District on the north, Pacarán District on the east, and Chincha Province on the south.
Chincha Alta District is one of eleven districts of the province Chincha in Peru.
Chincha Baja District is one of eleven districts of the province Chincha in Peru.

Eupithecia venosata, the netted pug, is a moth of the family Geometridae. It was first described by Johan Christian Fabricius in 1787. It is found across the Palearctic ecozone from Portugal and Morocco in the west to the Lake Baikal in Siberia and Afghanistan and Pakistan in the east.

Eupithecia satyrata, the satyr pug, is a species of moth of the family Geometridae. It was described by Hübner in 1813. It is found from Ireland, through northern and central Europe East to all of Russia and Central Asia and West Siberia to Tibet. It is also present in North Africa and North America.
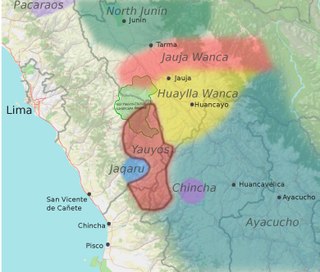
Yauyos–Chincha Quechua or Yauyos Quechua is a dialect cluster of Quechua, spoken in the Yauyos and Chincha districts of Peru. There are numerous dialects: in Yauyos, San Pedro de Huacarpana, Apurí, Madean-Viñac (Madeán), Azángaro-Huangáscar-Chocos (Huangáscar), Cacra-Hongos, Tomás-Alis (Alis), Huancaya-Vitis, Laraos, with similar diversity in Chincha.
Events in the year 1866 in Chile.
The following lists events that happened during 1864 in Chile.













