
The Council of Europe is an international organisation with the goal of upholding human rights, democracy and the rule of law in Europe. Founded in 1949, it brings together 46 member states with a population of approximately 675 million as of 2023; it operates with an annual budget of approximately 500 million euros.
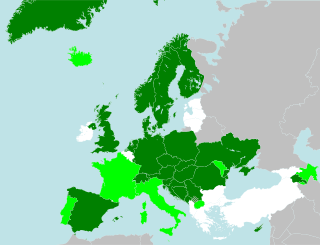
The European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages (ECRML) is a European treaty adopted in 1992 under the auspices of the Council of Europe to protect and promote historical regional and minority languages in Europe. However, the charter does not provide any criterion or definition for an idiom to be a minority or a regional language, and the classification stays in the hands of the national state.

The United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child is an international human rights treaty which sets out the civil, political, economic, social, health and cultural rights of children. The convention defines a child as any human being under the age of eighteen, unless the age of majority is attained earlier under national legislation.

The Schengen Agreement is a treaty which led to the creation of Europe's Schengen Area, in which internal border checks have largely been abolished. It was signed on 14 June 1985, near the town of Schengen, Luxembourg, by five of the ten member states of the then European Economic Community. It proposed measures intended to gradually abolish border checks at the signatories' common borders, including reduced-speed vehicle checks which allowed vehicles to cross borders without stopping, allowing residents in border areas freedom to cross borders away from fixed checkpoints, and the harmonisation of visa policies.

The BernConvention on the Conservation of European Wildlife and Natural Habitats, also known as the Bern Convention, is a binding international legal instrument in the field of Nature Conservation, it covers the natural heritage in Europe, as well as in some African countries. The Convention was open for signature on 19 September 1979 and came into force on 1 June 1982. It is particularly concerned about protecting natural habitats and endangered species, including migratory species.

The Vienna Convention on the Law of Treaties (VCLT) is an international agreement that regulates treaties among sovereign states.

The American Convention on Human Rights (ACHR), also known as the Pact of San José or by its Spanish name used in most of the signatory nations, Convención Americana sobre Derechos Humanos, is an international human rights instrument. It was adopted by many countries in the Western Hemisphere in San José, Costa Rica, on 22 November 1969. It came into force after the eleventh instrument of ratification was deposited on 18 July 1978.

The Bologna Process is a series of ministerial meetings and agreements between European countries to ensure comparability in the standards and quality of higher-education qualifications. The process has created the European Higher Education Area under the Lisbon Recognition Convention. It is named after the University of Bologna, where the Bologna declaration was signed by education ministers from 29 European countries in 1999. The process was opened to other countries in the European Cultural Convention of the Council of Europe, and government meetings have been held in Prague (2001), Berlin (2003), Bergen (2005), London (2007), Leuven (2009), Budapest-Vienna (2010), Bucharest (2012), Yerevan (2015), Paris (2018), and Rome (2020).

The Erasmus Programme is a European Union (EU) student exchange programme established in 1987. Erasmus+, or Erasmus Plus, is the new programme combining all the EU's current schemes for education, training, youth and sport, which was started in January 2014.

The European Higher Education Area (EHEA) was launched in March 2010, during the Budapest-Vienna Ministerial Conference, on the occasion of the 10th anniversary of the Bologna Process.
The Lisbon Recognition Convention, officially the Convention on the Recognition of Qualifications concerning Higher Education in the European Region, is an international convention of the Council of Europe elaborated together with the UNESCO. This is the main legal agreement on credential evaluation in Europe.

European Union culture policies aim to address and promote the cultural dimension of European integration through relevant legislation and government funding. These policies support the development of cultural activity, education or research conducted by private companies, NGO's and individual initiatives based in the EU working in the fields of cinema and audiovisual, publishing, music and crafts.
The European Convention for the Protection of Pet Animals is a treaty of the Council of Europe to promote the welfare of pet animals and ensure minimum standards for their treatment and protection. The treaty was signed in 1987 and became effective on 1 May 1992, after at least four countries had ratified it. Adherence to the treaty is open and not limited to member countries of the Council of Europe. As of August 2023, it has been ratified by 26 states.

The Hague Convention for the Protection of Cultural Property in the Event of Armed Conflict is the first international treaty that focuses exclusively on the protection of cultural property in armed conflict. It was signed at The Hague, Netherlands, on 14 May 1954 and entered into force on 7 August 1956. As of July 2021, it has been ratified by 133 states.
The Valletta Treaty (formally the European Convention on the Protection of the Archaeological Heritage (Revised), also known as the Malta Convention) is a multilateral treaty of the Council of Europe. The 1992 treaty aims to protect the European archaeological heritage "as a source of European collective memory and as an instrument for historical and scientific study". All remains and objects and any other traces of humankind from past times are considered to be elements of the archaeological heritage. The archaeological heritage shall include structures, constructions, groups of buildings, developed sites, moveable objects, monuments of other kinds as well as their context, whether situated on land or under water." (Art. 1)
The European Landscape Convention of the Council of Europe, also known as the Florence Convention, is the first international treaty to be exclusively devoted to all aspects of European landscape. It applies to the entire territory of the Parties and covers natural, rural, urban and peri-urban areas. It concerns landscapes that might be considered outstanding as well as everyday or degraded landscapes. The Convention is aimed at: the protection, management and planning of all landscapes and raising awareness of the value of a living landscape.
The Validation or recognition of foreign studies and degrees is the process whereby a competent authority in one country formally recognises the value of a qualification from a foreign country. This can entail total or partial validation of foreign university and non-university studies, degrees and other qualifications. Particularly within Europe, this is covered by a number of international conventions and agreements.
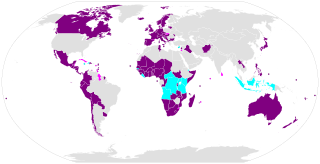
The Convention on Cluster Munitions (CCM) is an international treaty that prohibits all use, transfer, production, and stockpiling of cluster munitions, a type of explosive weapon which scatters submunitions ("bomblets") over an area. Additionally, the convention establishes a framework to support victim assistance, clearance of contaminated sites, risk reduction education, and stockpile destruction. The convention was adopted on 30 May 2008 in Dublin, and was opened for signature on 3 December 2008 in Oslo. It entered into force on 1 August 2010, six months after it was ratified by 30 states. As of December 2023, a total of 124 states are committed to the goal of the convention, with 112 states that have ratified it, and 12 states that have signed the convention but not yet ratified it.a

The Convention on Road Traffic, commonly known as the Geneva Convention on Road Traffic, is an international treaty promoting the development and safety of international road traffic by establishing certain uniform rules among the contracting parties. The convention addresses minimum mechanical and safety equipment needed to be on board and defines an identification mark to identify the origin of the vehicle. The Convention was prepared and opened for signature by the United Nations Conference on Road and Motor Transport held at Geneva from 23 August to 19 September 1949. It came into force on 26 March 1952. This conference also produced the Protocol on Road Signs and Signals.

The Treaties of the European Union are a set of international treaties between the European Union (EU) member states which sets out the EU's constitutional basis. They establish the various EU institutions together with their remit, procedures and objectives. The EU can only act within the competences granted to it through these treaties and amendment to the treaties requires the agreement and ratification of every single signatory.















