
Abae was an ancient town in the northeastern corner of ancient Phocis, in Greece, near the frontiers of the Opuntian Locrians, said to have been built by the Argive Abas, son of Lynceus and Hypermnestra, and grandson of Danaus. This bit of legend suggests an origin or at least an existence in the Bronze Age. Its protohistory supports a continued existence in Iron-Age antiquity. It was famous for its oracle of Apollo Abaeus, one of those consulted by Croesus, king of Lydia, and Mardonius, among others. The site of the oracle was rediscovered at Kalapodi and excavated in modern times. The results confirm an archaeological existence dating from the Bronze Age, as is suggested by the lore.

Voies is a former municipality in Laconia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Monemvasia, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 215.527 km2. It is on the southern tip of Cape Malea. It is a predominantly agricultural region with a few minor villages and one dominant town. Vatika is the common term for the area, but Voies is used in a more official context, particularly for postal situations. Voion, the genitive, is used for description: for example, to differentiate the village of Agios Nikolaos in Voies from other villages and towns of the same name, one would use Agios Nikolaos Voion. Neapoli is the administrative capital of the municipality, and is also the urban center to the numerous villages that surround the hinterland.

Almyros or Halmyros is a town and a municipality of the regional unit of Magnesia, region of Thessaly, Greece. It lies in the center of prosperous fertile plain known as 'Krokio Pedio', which is crossed by torrents. Almyros is an important agricultural and commercial center of Magnesia, and is also developing as a tourist center for the area. The main agricultural products are tomatoes, cotton, wheat, almonds, peanuts and pistachio nuts.

Agrinio is the largest city of the Aetolia-Acarnania regional unit of Greece and its largest municipality, with 89,691 inhabitants (2021). It is the economic center of Aetolia-Acarnania, although its capital is the town of Mesolonghi. The settlement dates back to ancient times. Ancient Agrinion was 3 kilometres northeast of the present city; some walls and foundations of which have been excavated. In medieval times and until 1836, the city was known as Vrachori (Βραχώρι).

Agios Nikolaos, Hagios Nikolaos or Aghios Nikolaos is a coastal city on the Greek island of Crete, lying east of the island's capital Heraklion, north of the city of Ierapetra and west of the city of Sitia.

Serifos is a Greek island municipality in the Aegean Sea, located in the western Cyclades, south of Kythnos and northwest of Sifnos. It is part of the Milos regional unit. The area is 75.207 square kilometres (29.038 sq mi) and the population was 1,241 at the 2021 census. It is located about 170 kilometres ESE of the Athenian port of Piraeus.
Agios Vasileios is a village in the municipal unit of Tenea in Corinthia, Greece.

Arta is a city in northwestern Greece and capital of the regional unit of Arta, which is part of Epirus region. The city was known in ancient times as Ambracia. Arta is known for the medieval bridge over the Arachthos River. Arta is also known for its ancient sites from the era of Pyrrhus of Epirus and its well-preserved 13th-century castle. Arta's Byzantine history is reflected in its many Byzantine churches; perhaps the best known is the Panagia Paregoretissa, built about 1290 by Despot Nikephoros I Komnenos Doukas.

Agios Nikolaos is a village located 110 kilometers south-east of Thessaloniki on the Chalkidiki peninsula in Macedonia, Greece.

Tamassos or Tamasos – names Latinized as Tamassus or Tamasus – was a city-kingdom in ancient Cyprus, one of the ten kingdoms of Cyprus. It was situated in the great central plain of the island, south-east of Soli, on the road from Soli to Tremithus. It is an archaeological site bordering the village of Politiko, about 21 kilometres southwest of Nicosia.

Koufonisia is a former community in the Cyclades, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Naxos and Lesser Cyclades, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 26.025 km2.
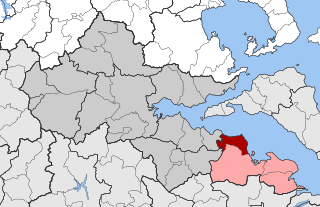
Dafnousia is a former municipality in Phthiotis, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Lokroi, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 77.374 km2. In 2021 its population was 3,387. The seat of the municipality was in Livanates where three quarters of the population live. Dafnousia borders on the municipal unit of Atalanti to the south, and Agios Konstantinos to the west. The name of the municipality comes from the ancient city of "Dafnous" or "Dafnountas".
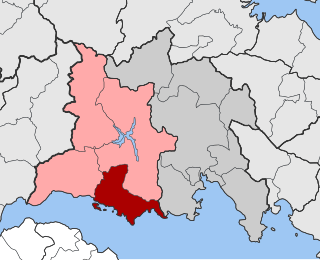
Tolofon is a village and a former municipality in Phocis, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Dorida, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 131.384 km2. The seat of the municipality was in Erateini. The ancient site of Tolophon is located in the northeastern part of the municipal unit. It is situated on the mountainous north coast of the Gulf of Corinth.

Kritsa is one of the oldest and most picturesque villages in Crete, Greece, built amphitheatrically on a rock hill, named Kastellos, surrounded by olive groves, at an altitude of 375 m. It is part of the municipality of Agios Nikolaos. During the Middle Ages, it was thought to be the largest village in Crete. Kritsa has been destroyed many times during the last centuries because it participated in all of Crete's revolutions. It is located 10 km from Agios Nikolaos and has about 2200 inhabitants who live in different neighborhoods named Palemilos, Koukistres, Christos and Pergiolikia.

Kakopetria is a town in Cyprus located 55 kilometres (34 mi) southwest of the capital, Nicosia, on the north-facing foothills of the Troodos Mountains. It stands at an altitude of 667 metres and it is the highest village in the Solea Valley. The community has about 1,200 permanent inhabitants and a couple hundred more who either have a summer house or are originally from Kakopetria but work in Nicosia. Near Kakopetria there is church from 11th century, Agios Nikolaos tis Stegis, UNESCO World Heritage Site.

Kalapodi is a village in the Lokroi municipality, Phthiotis, Central Greece. Lokroi straddles the pass leading over the low mountains between the Bay of Atalantis in the Gulf of Euboea to the plains of Boeotia north of Lake Copais. The road is often termed the Atalanti-Livadeia. The community of Atalanti, the chief deme of Lokroi, overlooks the Bay of Atalantis, while Livadeia is the current capital of Boeotia.
Agios Alexandros is a settlement in the northeastern part of the Aegean island of Lemnos, Greece. It is part of the municipal unit of Moudros and the community of Kontopouli. The population was 0 at the 2011 census. It is located north of the Alyki Lagoon, 4 km southwest of Panagia and 5 km northeast of Kontopouli.
Kontopouli is a village and a community in the municipal unit of Moudros in the northeastern part of the island of Lemnos, Greece. The community includes the small villages Agios Alexandros and Agios Theodoros. Its total area is 37.04 km². Kontopouli is 1 km northwest of Kalliopi, 3 km east of Repanidi and 8 km northeast of Moudros.
Panagia is a village in the northeastern part of the island of Lemnos, Greece. It is part of the municipal unit of Moudros. In 2011 its population was 383 people, including the small village Kortisonas.
Rizovouni is a village of Epirus in the municipality of Ziros in the Preveza regional unit. Its oldest name, 'Podgoras' (until 1927), is of Slavic origin and means at the foot, at the root of the mountain. The late modern "Rizovouni" attributes to the Greek content of the Slavic word.
















