Fc fragment of IgE, high affinity I, receptor for; gamma polypeptide is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FCER1G gene. [5]
Fc fragment of IgE, high affinity I, receptor for; gamma polypeptide is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FCER1G gene. [5]
The high affinity IgE receptor, FcεRI, is a key molecule involved in allergic reactions. It is a tetramer composed of 1 alpha, 1 beta, and 2 gamma chains. The gamma chains are also subunits of other Fc receptors. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008].
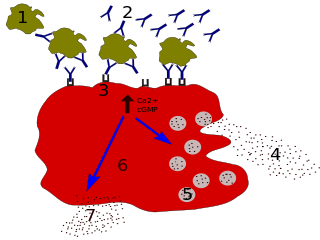
Immunoglobulin E (IgE) is a type of antibody that has been found only in mammals. IgE is synthesised by plasma cells. Monomers of IgE consist of two heavy chains and two light chains, with the ε chain containing four Ig-like constant domains (Cε1–Cε4). IgE is thought to be an important part of the immune response against infection by certain parasitic worms, including Schistosoma mansoni, Trichinella spiralis, and Fasciola hepatica. IgE is also utilized during immune defense against certain protozoan parasites such as Plasmodium falciparum. IgE may have evolved as a defense to protect against venoms.

CD23, also known as Fc epsilon RII, or FcεRII, is the "low-affinity" receptor for IgE, an antibody isotype involved in allergy and resistance to parasites, and is important in regulation of IgE levels. Unlike many of the antibody receptors, CD23 is a C-type lectin. It is found on mature B cells, activated macrophages, eosinophils, follicular dendritic cells, and platelets.

In immunology, an Fc receptor is a protein found on the surface of certain cells – including, among others, B lymphocytes, follicular dendritic cells, natural killer cells, macrophages, neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, human platelets, and mast cells – that contribute to the protective functions of the immune system. Its name is derived from its binding specificity for a part of an antibody known as the Fc region. Fc receptors bind to antibodies that are attached to infected cells or invading pathogens. Their activity stimulates phagocytic or cytotoxic cells to destroy microbes, or infected cells by antibody-mediated phagocytosis or antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Some viruses such as flaviviruses use Fc receptors to help them infect cells, by a mechanism known as antibody-dependent enhancement of infection.

Convulxin is a snake venom toxin found in a tropical rattlesnake known as Crotalus durissus terrificus. It belongs to the family of hemotoxins, which destroy red blood cells or, as is the case with convulxin, induce blood coagulation.

Glycoprotein VI (platelet), also known as GPVI, is a glycoprotein receptor for collagen which is expressed in platelets. In humans, glycoprotein VI is encoded by the GPVI gene. GPVI was first cloned in 2000 by several groups including that of Martine Jandrot-Perrus from INSERM.

Tyrosine-protein kinase SYK, also known as spleen tyrosine kinase, is an enzyme which in humans is encoded by the SYK gene.

Lymphocyte cytosolic protein 2, also known as LCP2 or SLP-76, is a signal-transducing adaptor protein expressed in T cells and myeloid cells and is important in the signaling of T-cell receptors (TCRs). As an adaptor protein, SLP-76 does not have catalytic functions, primarily binding other signaling proteins to form larger signaling complexes. It is a key component of the signaling pathways of receptors with immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs (ITAMs) such as T-cell receptors, its precursors, and receptors for the Fc regions of certain antibodies. SLP-76 is expressed in T-cells and related lymphocytes like natural killer cells.

Fc fragment of IgE, high affinity I, receptor for; alpha polypeptide, also known as FCER1A, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the FCER1A gene.

Platelet glycoprotein Ib alpha chain also known as glycoprotein Ib (platelet), alpha polypeptide or CD42b, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GP1BA gene.

Low affinity immunoglobulin gamma Fc region receptor II-a is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FCGR2A gene.

CD3e molecule, epsilon also known as CD3E is a polypeptide which in humans is encoded by the CD3E gene which resides on chromosome 11.

1-Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate phosphodiesterase gamma-2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PLCG2 gene.

CD84 is a human protein encoded by the CD84 gene.

Glycoprotein V (platelet) (GP5) also known as CD42d (Cluster of Differentiation 42d), is a human gene.

Low affinity immunoglobulin gamma Fc region receptor III-A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FCGR3A gene. It is also known as CD16a as it is part of the cluster of differentiation cell surface molecules.
Fc fragment of IgG receptor IIb is a low affinity inhibitory receptor for the Fc region of immunoglobulin gamma (IgG). FCGR2B participates in the phagocytosis of immune complexes and in the regulation of antibody production by B lymphocytes.

High affinity immunoglobulin gamma Fc receptor I is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FCGR1A gene.

Fc fragment of IgA receptor (FCAR) is a human gene that codes for the transmembrane receptor FcαRI, also known as CD89. FcαRI binds the heavy-chain constant region of Immunoglobulin A (IgA) antibodies. FcαRI is present on the cell surface of myeloid lineage cells, including neutrophils, monocytes, macrophages, and eosinophils, though it is notably absent from intestinal macrophages and does not appear on mast cells. FcαRI plays a role in both pro- and anti-inflammatory responses depending on the state of IgA bound. Inside-out signaling primes FcαRI in order for it to bind its ligand, while outside-in signaling caused by ligand binding depends on FcαRI association with the Fc receptor gamma chain.

FCGR3B, also known as CD16b, is a human gene.

High affinity immunoglobulin epsilon receptor subunit beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MS4A2 gene.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.