
The Panther tank, officially Panzerkampfwagen V Panther with ordnance inventory designation: Sd.Kfz. 171, is a German medium tank of World War II. It was used on the Eastern and Western Fronts from mid-1943 to the end of the war in May 1945.

The AMX-13 is a French light tank produced from 1952 to 1987. It served with the French Army, as the Char 13t-75 Modèle 51, and was exported to more than 26 other nations. Named after its initial weight of 13 tonnes, and featuring a tough and reliable chassis, it was fitted with an oscillating turret built by GIAT Industries with revolver-type magazines, which were also used on the Austrian SK-105 Kürassier. Including prototypes and export versions, over a hundred variants exist, including self-propelled guns, anti-aircraft systems, APCs, and ATGM versions.

The Char 2C, also known as the FCM 2C, was a French post WWI heavy tank landship, later considered a super-heavy tank. It was developed during World War I but not deployed until after the war. It was, in total volume or physical dimensions, the largest operational tank ever made.

The AMX-30 is a main battle tank designed by Ateliers de construction d'Issy-les-Moulineaux and first delivered to the French Army in August 1966. The first five tanks were issued to the 501st Régiment de Chars de Combat in August of that year. The production version of the AMX-30B weighed 36 metric tons, and sacrificed protection for increased mobility. The French believed that it would have required too much armour to protect against the latest anti-tank threats, thereby reducing the tank's maneuverability. Protection, instead, was provided by the speed and the compact dimensions of the vehicle, including a height of 2.28 metres. It had a 105 mm gun, firing a then advanced high-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) warhead known as the Obus G. The Obus G used an outer shell, separated from the main charge by ball bearings, to allow the round to be spin stabilized by the gun without spinning the warhead inside which would disrupt jet formation. Mobility was provided by the 720 horsepower (540 kW) HS-110 diesel engine, although the troublesome transmission adversely affected the tank's performance.

The Entwicklung series, more commonly known as the E-Series, was a late-World War II attempt by Nazi Germany to produce a standardised series of tank designs. There were to be standard designs in five different weight classes from which several specialised variants were to be developed. Design standardisation was envisioned to bring improvements over extreme complexity of previous tank designs that resulted in poor production rates and mechanical unreliability.

The SOMUA S35 was a French cavalry tank of the Second World War. Built from 1936 until 1940 to equip the armoured divisions of the Cavalry, it was for its time a relatively agile medium-weight tank, superior in armour and armament to its French and foreign competitors, such as the contemporary versions of the German Panzer III medium tank. It was constructed from well-sloped, mainly cast, armour sections, that however made it expensive to produce and time-consuming to maintain.

The Char B1 was a French heavy tank manufactured before World War II.

The FCM 36 or Char léger Modèle 1936 FCM, was a light infantry tank that was designed for the French Army prior to World War II. It had a crew of two and was equipped with a short 37mm main armament and a 7.5mm coaxial machine gun.
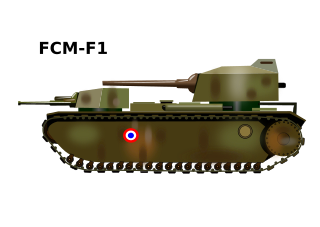
The FCM F1 was a French super-heavy tank developed during the late Interbellum by the Forges et Chantiers de la Méditerranée (FCM) company. Twelve were ordered in 1940 to replace the Char 2C, but France was defeated before construction could begin, a wooden mock-up being all that was finished. The FCM F1 was large and elongated, and had two turrets: one in front and one in the back, with a single high-velocity gun in each turret. The rear turret was superfiring, meaning it was raised higher and fired over the top of the forward one, a common practice in naval vessels. The vehicle was intended to be heavily armoured. Its size and protection level made it by 1940, at about 140 tons, the heaviest tank ever to have actually been ordered for production. Despite two engines its speed would have been low. The primary purpose of the tank was to breach German fortification lines, not to fight enemy tanks. The development path of the FCM F1 was extremely complex, due to the existence of a number of parallel super-heavy tank projects with overlapping design goals, the specifications of which were regularly changed. For each project in turn several companies submitted one or more competing proposals.
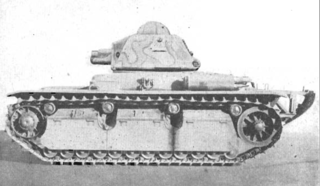
The Renault R40 or Char léger modèle 1935 R modifié 1939 was a French light infantry tank that was used early in World War II, an improvement of the Renault R35, of which it is often considered a variant.

The ARL 44 was a French heavy tank and tank destroyer, the development of which started just before the end of the Second World War. Only sixty of these tanks were ever completed, from 1949 onwards. The type proved to be unsatisfactory and only entered limited service. The tank was phased out in 1953.
The Char G1 was a French replacement project for the Char D2 medium tank. Several prototypes from different companies were developed from 1936 onwards, but not a single one had been fully completed at the time of the Fall of France in 1940. The projects represented some of the most advanced French tank design of the period and finally envisaged a type that would have been roughly equal in armament and mobility to later World War II standard tanks of other nations, such as the Soviet T-34 and the American M4 Sherman, but possessing several novel features, such as gun stabilisation, a semi-automatic loader and an optical rangefinder.

A super-heavy tank or super heavy tank is any tank that is notably beyond the standard of the class heavy tank in either size or weight relative to contemporary vehicles.

The AMX-40 was a French main battle tank developed by GIAT during the latter stages of the Cold War as an export tank to replace the earlier AMX-32. Designed to be an inexpensive tank orientated towards militaries with smaller defence budgets, the AMX-40 featured a lightly armoured hull and good mobility reminiscent of previous French MBTs with a powerful 120 mm cannon. It however failed to attract interest and sales, rendering the project a failure, being discontinued in 1990.

The AMX 50 or AMX-50 is a French heavy tank designed in the immediate post Second World War period. It was proposed as, in succession, the French medium, heavy, and main battle tank, incorporating many advanced features. It was cancelled in the late 1950s however, due to unfavourable economic and political circumstances after serious delays in development.

French development into tanks began during World War I as an effort to overcome the stalemate of trench warfare, and largely at the initiative of the manufacturers. The Schneider CA1 was the first tank produced by France, and 400 units were built. The French also experimented with various tank designs, such as the Frot-Laffly landship, Boirault machine and Souain experiment. Another 400 Saint-Chamond tanks were manufactured from April 1917 to July 1918 but they were underpowered and were of limited utility because the caterpillar tracks were too short for the tank's length and weight. The most significant French tank development during the war was the Renault FT light tank, which set the general layout for future tank designs and was used or redesigned by various military forces, including those of the United States.
The AMX 38 was a prototype French tank designed in 1937 at the AMX works. Designed as AMX's response to the 20-tonne tank programme intended to replace the aging Char D2, it was a faster and heavier alternative to Renault R35, in practice a cross-over between a light tank and medium tank.

The "ARL Tracteur C", or ARL Char C, was a French super-heavy tank design developed during the late Interbellum by the Atelier de Construction de Rueil (ARL) company. A full-scale wooden mock-up was part produced, but the project was terminated in favor of FCM F1, a directly competing design, which proved to be superior. The vehicle was meant to be extremely heavy and for that time period, very heavily armored. ARL C was intended to be very long to meet the requirement to cross trenches up to 7 meters wide. The tank was multi-turreted like FCM F1; however, unlike FCM F1, ARL C had the main turret in front of the very long hull right behind the secondary turret, not in the back of vehicle. The development path of the ARL C was extremely complex, due to the existence of a number of parallel super-heavy tank projects with overlapping design goals, the specifications of which were regularly changed. For each project in turn several companies submitted one or more competing proposals.
The AMX 40 was a proposed French cruiser tank. It was intended to replace the SOMUA S35 and S40 tanks. The tank never went beyond design stage after the Fall of France.
The AMX Tracteur C was a super-heavy tank designed by Ateliers de construction d'Issy-les-Moulineaux(AMX).















