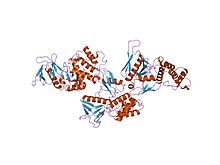
Actin-binding proteins are proteins that bind to actin. This may mean ability to bind actin monomers, or polymers, or both.

Merlin is a cytoskeletal protein. In humans, it is a tumor suppressor protein involved in neurofibromatosis type II. Sequence data reveal its similarity to the ERM protein family.

Gelsolin is an actin-binding protein that is a key regulator of actin filament assembly and disassembly. Gelsolin is one of the most potent members of the actin-severing gelsolin/villin superfamily, as it severs with nearly 100% efficiency.
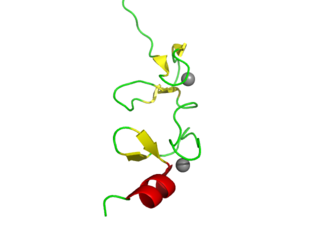
LIM domains are protein structural domains, composed of two contiguous zinc fingers, separated by a two-amino acid residue hydrophobic linker. The domain name is an acronym of the three genes in which it was first identified. LIM is a protein interaction domain that is involved in binding to many structurally and functionally diverse partners. The LIM domain appeared in eukaryotes sometime prior to the most recent common ancestor of plants, fungi, amoeba and animals. In animal cells, LIM domain-containing proteins often shuttle between the cell nucleus where they can regulate gene expression, and the cytoplasm where they are usually associated with actin cytoskeletal structures involved in connecting cells together and to the surrounding matrix, such as stress fibers, focal adhesions and adherens junctions.

Leukosialin also known as sialophorin or CD43 is a transmembrane cell surface protein that in humans is encoded by the SPN (sialophorin) gene.
Talin is a high-molecular-weight cytoskeletal protein concentrated at regions of cell–substratum contact and, in lymphocytes, at cell–cell contacts. Discovered in 1983 by Keith Burridge and colleagues, talin is a ubiquitous cytosolic protein that is found in high concentrations in focal adhesions. It is capable of linking integrins to the actin cytoskeleton either directly or indirectly by interacting with vinculin and α-actinin.

PTK2 protein tyrosine kinase 2 (PTK2), also known as focal adhesion kinase (FAK), is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the PTK2 gene. PTK2 is a focal adhesion-associated protein kinase involved in cellular adhesion and spreading processes. It has been shown that when FAK was blocked, breast cancer cells became less metastatic due to decreased mobility.

Ezrin also known as cytovillin or villin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EZR gene.

Sodium-hydrogen antiporter 3 regulator 1 is a regulator of Sodium-hydrogen antiporter 3. It is encoded by the gene SLC9A3R1. It is also known as ERM Binding Protein 50 (EBP50) or Na+/H+ Exchanger Regulatory Factor (NHERF1). It is believed to interact via long-range allostery, involving significant protein dynamics.

Intercellular adhesion molecule 2 (ICAM2), also known as CD102, is a human gene, and the protein resulting from it.

Sodium-hydrogen exchange regulatory cofactor NHE-RF2 (NHERF-2) also known as tyrosine kinase activator protein 1 (TKA-1) or SRY-interacting protein 1 (SIP-1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC9A3R2 gene.

Moesin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MSN gene.

Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 12 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTPN12 gene.

Radixin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RDX gene.
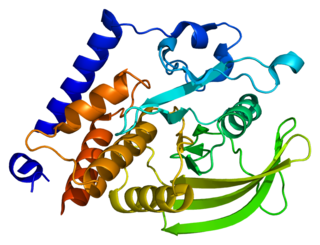
Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 18 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTPN18 gene.
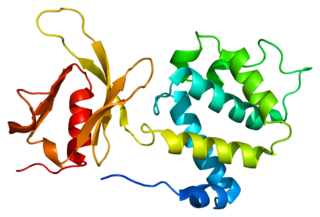
Talin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TLN1 gene. Talin-1 is ubiquitously expressed, and is localized to costamere structures in cardiac and skeletal muscle cells, and to focal adhesions in smooth muscle and non-muscle cells. Talin-1 functions to mediate cell-cell adhesion via the linkage of integrins to the actin cytoskeleton and in the activation of integrins. Altered expression of talin-1 has been observed in patients with heart failure, however no mutations in TLN1 have been linked with specific diseases.

Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 21 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTPN21 gene.

The ERM protein family consists of three closely related proteins, ezrin, radixin and moesin. The three paralogs, ezrin, radixin and moesin, are present in vertebrates, whereas other species have only one ERM gene. Therefore, in vertebrates these paralogs likely arose by gene duplication.

Rho-associated protein kinase (ROCK) is a kinase belonging to the AGC family of serine-threonine specific protein kinases. It is involved mainly in regulating the shape and movement of cells by acting on the cytoskeleton.
Tensin was first identified as a 220 kDa multi-domain protein localized to the specialized regions of plasma membrane called integrin-mediated focal adhesions. Genome sequencing and comparison have revealed the existence of four tensin genes in humans. These genes appear to be related by ancient instances of gene duplication.