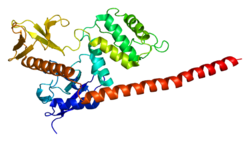
Moesin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MSN gene. [5] [6]
Contents
Moesin (for membrane-organizing extension spike protein) is a member of the ERM protein family which includes ezrin and radixin. ERM proteins appear to function as cross-linkers between plasma membranes and actin-based cytoskeletons. [7]
Moesin is localized to filopodia and other membranous protrusions that are important for cell–cell recognition and signaling and for cell movement. [7]
Moesin has FERM domain at N-terminal.