Related Research Articles

The Second Crusade (1147–1150) was the second major crusade launched from Europe. The Second Crusade was started in response to the fall of the County of Edessa in 1144 to the forces of Zengi. The county had been founded during the First Crusade (1096–1099) by King Baldwin I of Jerusalem in 1098. While it was the first Crusader state to be founded, it was also the first to fall.

Imad al-Din Zengi, also romanized as Zangi, Zengui, Zenki, and Zanki, was a Turkoman atabeg of the Seljuk Empire, who ruled Mosul, Aleppo, Hama, and, later, Edessa. He was the namesake and founder of the Zengid dynasty of atabegs.

Nūr al-Dīn Maḥmūd Zengī, commonly known as Nur ad-Din, was a member of the Zengid dynasty, who ruled the Syrian province of the Seljuk Empire. He reigned from 1146 to 1174. He is regarded as an important figure of the Second Crusade.

Baldwin II, also known as Baldwin of Bourcq or Bourg, was Count of Edessa from 1100 to 1118, and King of Jerusalem from 1118 until his death. He accompanied his cousins Godfrey of Bouillon and Baldwin of Boulogne to the Holy Land during the First Crusade. He succeeded Baldwin of Boulogne as the second count of Edessa when he left the county for Jerusalem following his brother's death. He was captured at the Battle of Harran in 1104. He was held first by Sökmen of Mardin, then by Jikirmish of Mosul, and finally by Jawali Saqawa. During his captivity, Tancred, the Crusader ruler of the Principality of Antioch, and Tancred's cousin, Richard of Salerno, governed Edessa as Baldwin's regents.
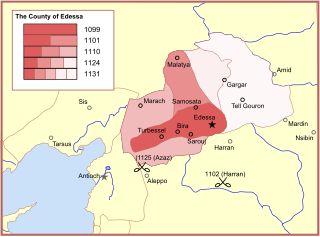
The County of Edessa was a 12th-century Crusader state in Upper Mesopotamia. Its seat was the city of Edessa.

The Principality of Antioch was one of the Crusader states created during the First Crusade which included parts of modern-day Turkey and Syria. The principality was much smaller than the County of Edessa or the Kingdom of Jerusalem. It extended around the northeastern edge of the Mediterranean, bordering the County of Tripoli to the south, Edessa to the east, and the Byzantine Empire or the Kingdom of Armenia to the northwest, depending on the date.

Joscelin II was the fourth and last ruling count of Edessa. He was son of his predecessor, Joscelin I, and Beatrice, daughter of Constantine I of Armenia.
Thoros II, also known as Thoros the Great, was the sixth lord of Armenian Cilicia from the Rubenid dynasty from 1144/1145 until 1169.

The Sultanate of Rûm was a culturally Turco-Persian Sunni Muslim state, established over conquered Byzantine territories and peoples (Rûm) of Anatolia by the Seljuk Turks following their entry into Anatolia after the Battle of Manzikert (1071). The name Rûm was a synonym for the medieval Eastern Roman Empire and its peoples, as it remains in modern Turkish. The name is derived from the Aramaic (rhōmī) and Parthian (frwm) names for ancient Rome, via the Greek Ῥωμαῖοι (Romaioi).

The Battle of Inab, also called Battle of Ard al-Hâtim or Fons Muratus, was fought on 29 June 1149, during the Second Crusade. The Zengid army of Atabeg Nur ad-Din Zangi destroyed the combined army of Prince Raymond of Poitiers and the Assassins of Ali ibn-Wafa. The Principality of Antioch was subsequently pillaged and reduced in size as its eastern border was pushed west.

The Artuqid dynasty was established in 1102 as an Anatolian Beylik (Principality) of the Seljuk Empire. It formed a Turkoman dynasty rooted in the Oghuz Döğer tribe, and followed the Sunni Muslim faith. It ruled in eastern Anatolia, Northern Syria and Northern Iraq in the eleventh through thirteenth centuries. The Artuqid dynasty took its name from its founder, Artuk Bey, who was of the Döger branch of the Oghuz Turks and ruled one of the Turkmen beyliks of the Seljuk Empire. Artuk's sons and descendants ruled the three branches in the region: Sökmen's descendants ruled the region around Hasankeyf between 1102 and 1231; Ilghazi's branch ruled from Mardin and Mayyafariqin between 1106 and 1186 and Aleppo from 1117–1128; and the Harput line starting in 1112 under the Sökmen branch, and was independent between 1185 and 1233.

The siege of Edessa took place from 28 November to 24 December 1144, resulting in the fall of the capital of the County of Edessa to Zengi, the atabeg of Mosul and Aleppo. This event was the catalyst for the Second Crusade.

The Battle of Harim (Harenc) was fought on 12 August 1164 at Harim, Syria, between the forces of Nur ad-Din, and a combined army from the County of Tripoli, the Principality of Antioch, the Byzantine Empire, and Armenia. Nur ad-Din won a crushing victory, capturing most of the leaders of the opposing army.

The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Christian Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these military expeditions are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that had the objective of reconquering Jerusalem and its surrounding area from Muslim rule after the region had been conquered by the Rashidun Caliphate centuries earlier. Beginning with the First Crusade, which resulted in the conquest of Jerusalem in 1099, dozens of military campaigns were organised, providing a focal point of European history for centuries. Crusading declined rapidly after the 15th century.
In the Battle of Aintab in August 1150, a Crusader force commanded by King Baldwin III of Jerusalem repelled the attacks of Nur ad-Din Zangi of Aleppo and evacuated the Latin Christian residents of the County of Edessa. This was both a tactical victory and a strategic defeat for the Crusaders.

Belek Ghazi was a Turkish bey in the early 12th century.
Beatrice of Saone was countess consort of Edessa from 1134 to 1150 by marriage to Count Joscelin II of Edessa. She served as regent of the remnants of the County of Edessa in the absence of her spouse in 1150.

Husam al-Din Timurtash was an Artuqid emir of Mardin (1122–1154) and ruler of Aleppo (1124–1125).
Gündoğan, historically Turbessel, is a neighbourhood in the municipality and district of Oğuzeli, Gaziantep Province, Turkey. Its population is 374 (2022). It was originally a fortress that played an important role in the Crusades, remnant of which is a tumulus.
The Lordship of Marash was a territorial lordship in northeastern Cilicia between 1104 and 1149, centred on the city of Marash. One of the lesser Crusader states, it played a major role in the defence of the northern frontier in the 1130s and 1140s under Lords Geoffrey and Baldwin. Its position became untenable after the fall of Edessa in 1146.
References
- 1 2 3 4 Nicholson, Robert Lawrence. Joscelyn III and the Fall of the Crusader States 1134-1199. Netherlands: Brill, 1973.
- 1 2 3 Eydoux, Henri Paul. "Le château franc de Turbessel." Bulletin Monumental 139, no. 4 (1981): 229-232.
- ↑ Altan, Ebru. "Nur Al-Din Mahmud B. Zangi (1146-1174): One Of The Prominent Leaders Of The Struggle Against The Crusaders." Tarih Dergisi 59 (2014): 57-78.