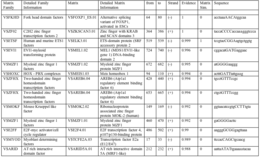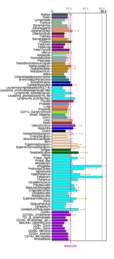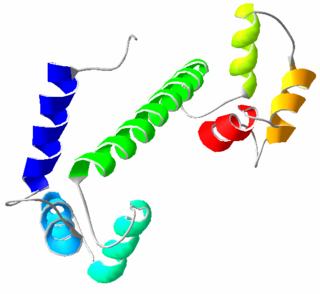
Calmodulin (CaM) (an abbreviation for calcium-modulated protein) is a multifunctional intermediate calcium-binding messenger protein expressed in all eukaryotic cells. It is an intracellular target of the secondary messenger Ca2+, and the binding of Ca2+ is required for the activation of calmodulin. Once bound to Ca2+, calmodulin acts as part of a calcium signal transduction pathway by modifying its interactions with various target proteins such as kinases or phosphatases.

Calmodulin 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CALM3 gene.

UPF0687 protein C20orf27 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the C20orf27 gene. It is expressed in the majority of the human tissues. One study on this protein revealed its role in regulating cell cycle, apoptosis, and tumorigenesis via promoting the activation of NFĸB pathway.

Protein FAM114A1 also known as nervous system overexpressed protein 20 (NOXP20) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FAM114A1 gene. Orthologs of FAM114A1 can be found in organisms as taxonomically distant from Homo sapiens as Drosophila. However, as expected, human FAM114A! is more like that of primates than any other orthologs. FAM114A1 has one paralog, FAM114A2, which also encodes a protein of unknown function.

C8orf48 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the C8orf48 gene. C8orf48 is a nuclear protein specifically predicted to be located in the nuclear lamina. C8orf48 has been found to interact with proteins that are involved in the regulation of various cellular responses like gene expression, protein secretion, cell proliferation, and inflammatory responses. This protein has been linked to breast cancer and papillary thyroid carcinoma.
TMEM156 is a gene that encodes the transmembrane protein 156 (TMEM156) in Homo sapiens. It has the clone name of FLJ23235.

FAM76A is a protein that in Homo sapiens is encoded by the FAM76A gene. Notable structural characteristics of FAM76A include an 83 amino acid coiled coil domain as well as a four amino acid poly-serine compositional bias. FAM76A is conserved in most chordates but it is not found in other deuterostrome phlya such as echinodermata, hemichordata, or xenacoelomorpha—suggesting that FAM76A arose sometime after chordates in the evolutionary lineage. Furthermore, FAM76A is not found in fungi, plants, archaea, or bacteria. FAM76A is predicted to localize to the nucleus and may play a role in regulating transcription.

PRR29 is a protein encoded by the PRR29 gene located in humans on chromosome 17 at 17q23.
Eps15 homology domain-containing protein 3, abbreviated as EHD3 and also known as PAST3, is a protein encoded by the EHD3 gene. It has been observed in humans, mice and rats. It belongs to the EHD protein family, a group of four membrane remodeling proteins related to the Dynamin superfamily of large GTPases. Although the four of them are 70-80% amino acid identical, they all have different locations. Its main function is related to endocytic transport.

Retrotransposon Gag Like 6 is a protein encoded by the RTL6 gene in humans. RTL6 is a member of the Mart family of genes, which are related to Sushi-like retrotransposons and were derived from fish and amphibians. The RTL6 protein is localized to the nucleus and has a predicted leucine zipper motif that is known to bind nucleic acids in similar proteins, such as LDOC1.

Uncharacterized protein C2orf73 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the C2orf73 gene. The protein is predicted to be localized to the nucleus.

Zinc finger CCHC-type containing 18 (ZCCHC18) is a protein that in humans is encoded by ZCCHC18 gene. It is also known as Smad-interacting zinc finger protein 2 (SIZN2), para-neoplastic Ma antigen family member 7b (PNMA7B), and LOC644353. Other names such as zinc finger, CCHC domain containing 12 pseudogene 1, P0CG32, ZCC18_HUMAN had been used to describe this protein.

Cilia- and flagella-associated protein 299 (CFAP299), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CFAP299 gene. CFAP299 is predicted to play a role in spermatogenesis and cell apoptosis.

Golgin subfamily A member 8H, also known as GOLGA8H, is a protein that in Homo sapiens is encoded by the GOLGA8H gene. Function of the GOLGA8H involves a process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of the Golgi apparatus.

C8orf34 is a protein that, in Homo sapiens, is encoded by the C8orf34 gene. Aliases for C8orf34 include vestibule-1 or VEST-1. Within the cell, C8orf34 is localized to the nucleus and nucleoli where it may play a role in the regulation of gene expression as well as the cell cycle.

C12orf24 is a gene in humans that encodes a protein known as FAM216A. This gene is primarily expressed in the testis and brain, but has constitutive expression in 25 other tissues. FAM216A is an intracellular protein that has been predicted to reside within the nucleus of cells. The exact function of C12orf24 is unknown. FAM216A is highly expressed in Sertoli cells of the testis as well as different stage spermatids.

C6orf136 is a protein in humans encoded by the C6orf136 gene. The gene is conserved in mammals, mollusks, as well some porifera. While the function of the gene is currently unknown, C6orf136 has been shown to be hypermethylated in response to FOXM1 expression in Head Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC) tissue cells. Additionally, elevated expression of C6orf136 has been associated with improved survival rates in patients with bladder cancer. C6orf136 has three known isoforms.

Family with sequence 98, member C or FAM98C is a gene that encodes for FAM98C has two aliases FLJ44669 and hypothetical protein LOC147965. FAM98C has two paralogs in humans FAM98A and FAM98B. FAM98C can be characterized for being a Leucine-rich protein. The function of FAM98C is still not defined. FAM98C has orthologs in mammals, reptiles, and amphibians and has a distant orhtologs in Rhinatrema bivittatum and Nanorana parkeri.

Major facilitator superfamily domain containing 6 like (MFSD6L) is a protein encoded by the MFSD6L gene in humans. The MFSD6L protein is a transmembrane protein that is part of the major facilitator superfamily (MFS) that uses chemiosmotic gradients to facilitate the transport of small solutes across cell membranes.

Maestro heat-like repeat-containing protein family member 9 (MROH9) is a protein which in humans is encoded by the MROH9 gene. The word ‘maestro’ itself is an acronym, standing for male-specific transcription in the developing reproductive organs (MRO). MRO genes belong to the MROH family, which includes MROH9.