The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to agriculture:
Agribusiness is the industry, enterprises, and the field of study of value chains in agriculture and in the bio-economy, in which case it is also called bio-business or bio-enterprise. The primary goal of agribusiness is to maximize profit while satisfying the needs of consumers for products related to natural resources such as biotechnology, farms, food, forestry, fisheries, fuel, and fiber.
The Agricultural Marketing Service (AMS) is an agency of the United States Department of Agriculture; it maintains programs in five commodity areas: cotton and tobacco; dairy; fruit and vegetable; livestock and seed; and poultry. These programs provide testing, standardization, grading and market news services for those commodities, and oversee marketing agreements and orders, administer research and promotion programs, and purchase commodities for federal food programs. The AMS enforces certain federal laws such as the Perishable Agricultural Commodities Act and the Federal Seed Act. The AMS budget is $1.2 billion. It is headquartered in the Jamie L. Whitten Building in Washington, D.C.

The food industry is a complex, global network of diverse businesses that supplies most of the food consumed by the world's population. The food industry today has become highly diversified, with manufacturing ranging from small, traditional, family-run activities that are highly labour-intensive, to large, capital-intensive and highly mechanized industrial processes. Many food industries depend almost entirely on local agriculture, animal farms, produce, and/or fishing.
The Commodity Credit Corporation (CCC) is a wholly owned United States government corporation that was created in 1933 to "stabilize, support, and protect farm income and prices". The CCC is authorized to buy, sell, lend, make payments, and engage in other activities for the purpose of increasing production, stabilizing prices, assuring adequate supplies, and facilitating the efficient marketing of agricultural commodities.

Food policy is the area of public policy concerning how food is produced, processed, distributed, purchased, or provided. Food policies are designed to influence the operation of the food and agriculture system balanced with ensuring human health needs. This often includes decision-making around production and processing techniques, marketing, availability, utilization, and consumption of food, in the interest of meeting or furthering social objectives. Food policy can be promulgated on any level, from local to global, and by a government agency, business, or organization. Food policymakers engage in activities such as regulation of food-related industries, establishing eligibility standards for food assistance programs for the poor, ensuring safety of the food supply, food labeling, and even the qualifications of a product to be considered organic.
Food politics is a term which encompasses not only food policy and legislation, but all aspects of the production, control, regulation, inspection, distribution and consumption of commercially grown, and even sometimes home grown, food. The commercial aspects of food production are affected by ethical, cultural, and health concerns, as well as environmental concerns about farming and agricultural practices and retailing methods. The term also encompasses biofuels, GMO crops and pesticide use, the international food market, food aid, food security and food sovereignty, obesity, labor practices and immigrant workers, issues of water usage, animal cruelty, and climate change.

Farmland Industries was the largest agricultural cooperative in North America when it eventually sold all of its assets in 2002–04. During its 74-year history, Farmland served its farmer membership as a diversified, integrated organization, playing a significant role in agricultural markets both domestically and worldwide.
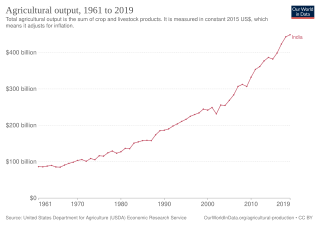
The history of agriculture in India dates back to the Neolithic period. India ranks second worldwide in farm outputs. As per the Indian economic survey 2020 -21, agriculture employed more than 50% of the Indian workforce and contributed 20.2% to the country's GDP.

Roughly one-third of Iran's total surface area is suitable for farmland, but because of poor soil and a lack of adequate water distribution in many areas, most of it is not under cultivation. Only 12% of the total land area is under cultivation but less than one-third of the cultivated area is irrigated; the rest is devoted to dryland farming. Some 92 percent of agricultural products depend on water. The western and northwestern portions of the country have the most fertile soils. Iran's food security index stands at around 96 percent.
Title 7 of the United States Code outlines the role of agriculture in the United States Code.

The Ministry of Food Processing Industries (MOFPI) is a ministry of the Government of India responsible for the formulation and administration of the rules, regulations, and laws related to food processing in India.

Agriculture in Ghana consists of a variety of agricultural products and is an established economic sector, providing employment on a formal and informal basis. It is represented by the Ministry of Food and Agriculture. Ghana produces a variety of crops in various climatic zones which range from dry savanna to wet forest which run in east–west bands across Ghana. Agricultural crops, including yams, grains, cocoa, oil palms, kola nuts, and timber, form the base of agriculture in Ghana's economy. In 2013 agriculture employed 53.6% of the total labor force in Ghana.

Agricultural marketing covers the services involved in moving an agricultural product from the farm to the consumer. These services involve the planning, organizing, directing and handling of agricultural produce in such a way as to satisfy farmers, intermediaries and consumers. Numerous interconnected activities are involved in doing this, such as planning production, growing and harvesting, grading, packing and packaging, transport, storage, agro- and food processing, provision of market information, distribution, advertising and sale. Effectively, the term encompasses the entire range of supply chain operations for agricultural products, whether conducted through ad hoc sales or through a more integrated chain, such as one involving contract farming.
Market information systems are information systems used in gathering, analyzing and disseminating information about prices and other information relevant to farmers, animal rearers, traders, processors and others involved in handling agricultural products. Market information systems play an important role in agro-industrialisation and food supply chains. With the advance of information and communication technologies for development (ICTs) in developing countries, the income- generation opportunities offered by market information systems have been sought by international development organizations, non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and businesses alike.
The School of Agricultural and Life Sciences is a French public and national Grande Ecole in agricultural and life sciences, funded by the Ministry of Higher Education and Research and member of Toulouse Tech. The ENSAT is a school of the National Polytechnic Institute of Toulouse (INPT), a university federating several schools dealing with engineering, agriculture and veterinary sciences, chemistry, meteorology.
The Agricultural Development and Marketing Corporation, usually known as ADMARC, was formed in Malawi in 1971 as a government-owned corporation or parastatal to promote the Malawian economy by increasing the volume and quality of its agricultural exports, to develop new foreign markets for the consumption of Malawian agricultural produce and to support Malawi's farmers. it was the successor of a number of separate marketing boards of the colonial-era and early post-colonial times, whose functions were as much about controlling African smallholders or generating government revenues as in promoting agricultural development. At its foundation, ADMARC was given the power to finance the economic development of any public or private organisation, agricultural or not.

Kuih lidah is a traditional kuih for the Bruneian Malay people in Papar in the states of Sabah in Malaysia.

The Ministry of Agriculture and Food Security, abbreviated MAFS, is a ministry of the Government of Malaysia that is responsible for agriculture, agro-based industry, agritourism, livestock, veterinary services, fisheries, quarantine, inspection, agricultural research, agricultural development, agricultural marketing, pineapple industry, agribusiness, botanical garden, food security, food sovereignty.
Punjab Agri Export Corporation Limited (PAGREXCO) is a government enterprise established by the Government of Punjab in the year 1997 as the nodal agency for agricultural export from the state of Punjab, India. The company works for export of fresh and processed agricultural produce, infrastructural development and policy implementation in the state.It is a subsidiary of Punjab Agro Industries Corporation.










