
In the United States, banking had begun by the 1780s, along with the country's founding. It has developed into a highly influential and complex system of banking and financial services. Anchored by New York City and Wall Street, it is centered on various financial services, such as private banking, asset management, and deposit security.

A financial institution, sometimes called a banking institution, is a business entity that provides service as an intermediary for different types of financial monetary transactions. Broadly speaking, there are three major types of financial institution:
- Depository institution – deposit-taking institution that accepts and manages deposits and makes loans, including bank, building society, credit union, trust company, and mortgage broker;
- Contractual institution – insurance company and pension fund
- Investment institution – investment bank, underwriter, and other different types of financial entities managing investments.

A savings and loan association (S&L), or thrift institution, is a financial institution that specializes in accepting savings deposits and making mortgage and other loans. The terms "S&L" and "thrift" are mainly used in the United States; similar institutions in the United Kingdom, Ireland and some Commonwealth countries include building societies and trustee savings banks. They are often mutually held, meaning that the depositors and borrowers are members with voting rights, and have the ability to direct the financial and managerial goals of the organization like the members of a credit union or the policyholders of a mutual insurance company. While it is possible for an S&L to be a joint-stock company, and even publicly traded, in such instances it is no longer truly a mutual association, and depositors and borrowers no longer have membership rights and managerial control. By law, thrifts can have no more than 20 percent of their lending in commercial loans—their focus on mortgage and consumer loans makes them particularly vulnerable to housing downturns such as the deep one the U.S. experienced in 2007.

The savings and loan crisis of the 1980s and 1990s was the failure of 32% of savings and loan associations (S&Ls) in the United States from 1986 to 1995. An S&L or "thrift" is a financial institution that accepts savings deposits and makes mortgage, car and other personal loans to individual members.

The Community Reinvestment Act is a United States federal law designed to encourage commercial banks and savings associations to help meet the needs of borrowers in all segments of their communities, including low- and moderate-income neighborhoods. Congress passed the Act in 1977 to reduce discriminatory credit practices against low-income neighborhoods, a practice known as redlining.

The Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC) is an independent bureau within the United States Department of the Treasury that was established by the National Currency Act of 1863 and serves to charter, regulate, and supervise all national banks and thrift institutions and the federally licensed branches and agencies of foreign banks in the United States. The acting Comptroller of the Currency is Michael J. Hsu, who took office on May 10, 2021.
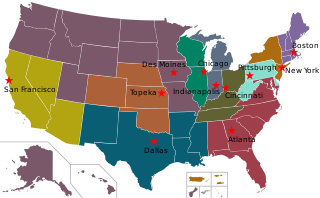
The Federal Home Loan Banks are 11 U.S. government-sponsored banks that provide liquidity to financial institutions to support housing finance and community investment.

The Federal Home Loan Bank Board (FHLBB) was a board created in 1932 that governed the Federal Home Loan Banks also created by the act, the Federal Savings and Loan Insurance Corporation (FSLIC) and nationally-chartered thrifts. It was abolished and superseded by the Federal Housing Finance Board and the Office of Thrift Supervision in 1989 due to the savings and loan crisis of the 1980s, as Federal Home Loan Banks gave favorable lending to the thrifts it regulated leading to regulatory capture.

The Office of Thrift Supervision (OTS) was a United States federal agency under the Department of the Treasury that chartered, supervised, and regulated all federally chartered and state-chartered savings banks and savings and loans associations. It was created in 1989 as a renamed version of the Federal Home Loan Bank Board, another federal agency. Like other U.S. federal bank regulators, it was paid by the banks it regulated. The OTS was initially seen as an aggressive regulator, but was later lax. Declining revenues and staff led the OTS to market itself to companies as a lax regulator in order to get revenue.

The Financial Institutions Reform, Recovery, and Enforcement Act of 1989 (FIRREA), is a United States federal law enacted in the wake of the savings and loan crisis of the 1980s.

The Federal Home Loan Bank Act, Pub. L.Tooltip Public Law 72–304, 47 Stat. 725, enacted July 22, 1932, is a United States federal law passed under President Herbert Hoover in order to lower the cost of home ownership. It established the Federal Home Loan Bank Board to charter and supervise federal savings and loan institutions. It also created the Federal Home Loan Banks which lend to building and loan associations, cooperative banks, homestead associations, insurance companies, savings banks, community development financial institutions, and insured depository institutions in order to finance home mortgages.

The Federal Housing Finance Board (FHFB) was an independent agency of the United States government established in 1989 in the aftermath of the savings and loan crisis to take over management of the Federal Home Loan Banks from the Federal Home Loan Bank Board (FHLBB), and was superseded by the Federal Housing Finance Agency (FHFA) in 2008.
The Senate Banking Subcommittee on Financial Institutions and Consumer Protection is one of five subcommittees within the Senate Committee on Banking, Housing, and Urban Affairs.
Bank regulation in the United States is highly fragmented compared with other G10 countries, where most countries have only one bank regulator. In the U.S., banking is regulated at both the federal and state level. Depending on the type of charter a banking organization has and on its organizational structure, it may be subject to numerous federal and state banking regulations. Apart from the bank regulatory agencies the U.S. maintains separate securities, commodities, and insurance regulatory agencies at the federal and state level, unlike Japan and the United Kingdom. Bank examiners are generally employed to supervise banks and to ensure compliance with regulations.
The New York State Banking Department was created by the New York Legislature on April 15, 1851, with a chief officer to be known as the Superintendent. The New York State Banking Department was the oldest bank regulatory agency in the United States.
Guaranty Bank was a major bank based in Austin, which collapsed in 2009. It was formed in 1988 as part of Temple-Inland and in 2007 became a standalone company. At the time of its collapse, Guaranty was the second largest bank in Texas, with 162 branches across Texas and California, and had $13 billion in assets and held $12 billion in deposits. Major shareholders included billionaire investor Carl Icahn and hotel tycoon Robert Rowling, who jointly invested $600 million in the bank in 2008.
This article details the history of banking in the United States. Banking in the United States is regulated by both the federal and state governments.

Joseph M. Otting is an American businessman and government official. He served as the 31st Comptroller of the Currency from November 27, 2017 to May 29, 2020.
Keith A. Noreika is an American lawyer who specializes in the regulation of financial institutions. He served as Acting Comptroller of the Currency from May 5, 2017, to November 27, 2017, following the 30th Comptroller of the Currency, Thomas J. Curry, and preceding the 31st Comptroller of the Currency, Joseph Otting. Noreika rejoined the law firm of Simpson Thacher on January 8, 2018. He joined Patomak Global Partners as Executive Vice President and Chairman of its Banking Supervision and Regulation Group on July 5, 2022.

Brian P. Brooks is an American lawyer, banker, entrepreneur, technologist, and former government official. He served as Acting Comptroller of the Currency from May 29, 2020, succeeding the 31st Comptroller of the Currency Joseph Otting, until January 14, 2021. Brooks was nominated twice by President Donald Trump for a five-year term as Comptroller of the Currency, once during the 116th Congress, and once in the 117th Congress.











