Employment is a relationship between two parties regulating the provision of paid labour services. Usually based on a contract, one party, the employer, which might be a corporation, a not-for-profit organization, a co-operative, or any other entity, pays the other, the employee, in return for carrying out assigned work. Employees work in return for wages, which can be paid on the basis of an hourly rate, by piecework or an annual salary, depending on the type of work an employee does, the prevailing conditions of the sector and the bargaining power between the parties. Employees in some sectors may receive gratuities, bonus payments or stock options. In some types of employment, employees may receive benefits in addition to payment. Benefits may include health insurance, housing, disability insurance. Employment is typically governed by employment laws, organisation or legal contracts.

Recruitment refers to the overall process of identifying, sourcing, screening, shortlisting, and interviewing candidates for jobs within an organization. Recruitment can also refer to the processes involved in choosing individuals for unpaid roles. Managers, human resource generalists and recruitment specialists may be tasked with carrying out recruitment, but in some cases public-sector employment, commercial recruitment agencies, or specialist search consultancies are used to undertake parts of the process. Internet-based technologies which support all aspects of recruitment have become widespread, including the use of artificial intelligence (AI).
Human resource management is the strategic approach to the effective and efficient management of people in a company or organization such that they help their business gain a competitive advantage. It is designed to maximize employee performance in service of an employer's strategic objectives. Human resource management is primarily concerned with the management of people within organizations, focusing on policies and systems. HR departments are responsible for overseeing employee-benefits design, employee recruitment, training and development, performance appraisal, and reward management, such as managing pay and employee-benefits systems. HR also concerns itself with organizational change and industrial relations, or the balancing of organizational practices with requirements arising from collective bargaining and governmental laws.
In human resource development, induction training introduces new employees to their new profession or job role, within an organisation. As a form of systematic training, induction training familiarises and assists new employees with their employer, workforce and job design. The scale of induction training varies between organisations, with smaller firms typically conducting induction in the early months of employment, in comparison to larger corporations who dedicate greater time and resources to its completion.
Investors in People is a standard for people management, offering accreditation to organisations that adhere to the Investors in People Standard. From 1991 to January 2017, Investors in People was owned by the UK government. As of 1 February 2017, Investors in People transitioned into the Investors in People Community Interest Company. Investors in People assessments are conducted locally through local Delivery Centres across the UK and internationally.
Contingent work, casual work, or contract work, is an employment relationship with limited job security, payment on a piece work basis, typically part-time that is considered non-permanent. Although there is less job security, freelancers often report incomes higher than their former traditional jobs.

Employee engagement is a fundamental concept in the effort to understand and describe, both qualitatively and quantitatively, the nature of the relationship between an organization and its employees. An "engaged employee" is defined as one who is fully absorbed by and enthusiastic about their work and so takes positive action to further the organization's reputation and interests. An engaged employee has a positive attitude towards the organization and its values. In contrast, a disengaged employee may range from someone doing the bare minimum at work, up to an employee who is actively damaging the company's work output and reputation.
Kronos Incorporated was an American multinational workforce management and human capital management cloud provider headquartered in Lowell, Massachusetts, United States, which employed more than 6,000 people worldwide.
Talent management (TM) refers to the anticipation of required human capital for an organization and the planning to meet those needs. The field has been growing in significance and gaining interest among practitioners as well as in the scholarly debate over the past 10 years, particularly after McKinsey's 1997 research and the 2001 book on The War for Talent. Talent management in this context does not refer to the management of entertainers. Talent management is the science of using strategic human resource planning to improve business value and to make it possible for companies and organizations to reach their goals. Everything done to recruit, retain, develop, reward and make people perform forms a part of talent management as well as strategic workforce planning. A talent-management strategy should link to business strategy and to local context to function more appropriately
Employee voice refers to the participation of employees in influencing organisational decision-making. Because research and analysis have grown around the voice concept in a variety of disciplines, ‘employee voice’ has become an elastic term meaning somewhat different things to different policy, academic and practitioner actors. In the many disciplines that cover voice, such as human resource management, political science, economics, organisational behaviour, psychology or law, perspectives toward the concept differ. Drawing on Dundon et al. voice can be seen with different lenses. First, voice is an articulation of individual dissatisfaction or concern that aims to address a specific problem or issue with management. Second, voice takes the form of collective organisation, where voice provides a countervailing source of power to management. Third, there is the role of voice as a contribution to management decision-making. Here the purpose is to gain employee input to improve work organisation and efficiency more generally, perhaps through quality circles or teamwork, or eliciting workforce engagement. Fourth, voice can be seen as an instrument for mutual gain, with productive collaboration between capital and labour increasing the long-term viability of an organisation and economic well-being of employees.
The International Organisation of Employers (IOE) was created in 1920 to advocate for employers and the business community in the tripartite governance structure of the International Labour Organization (ILO). Today, from its headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, IOE continues to defend and promote these same interests across a wide range of UN agencies, international organisations, intergovernmental processes and the media. As of September 2019, IOE had 156 national employer organisations members in 145 countries. It remains involved in the activities of the International Labour Organization, acting as Secretariat to the Employers' Group, as well as representing business in international forums, including the G20 intergovernmental process on labour and social policy. It describes itself as "the largest network of the private sector in the world" and "the global voice of business".
Global workforce refers to the international labor pool of workers, including those employed by multinational companies and connected through a global system of networking and production, foreign workers, transient migrant workers, remote workers, those in export-oriented employment, contingent workforce or other precarious work. As of 2012, the global labor pool consisted of approximately 3 billion workers, around 200 million unemployed.
The Transfers of Undertakings Directive2001/23/EC is a European Union law that protects the contracts of employment of people working in businesses that are transferred between owners. It replaced and updated the law previously known as the Acquired Rights Directive 77/187/EC.
Ibec is Ireland’s largest lobby and business representative group. Its purpose is to help build a better, sustainable future by influencing, supporting and delivering for business success. Ibec positions are shaped by its diverse membership, which range from small to large, domestic to multinational and 38 trade associations which cover a wide range of industry sectors. As well as lobbying, Ibec provides a wide range of professional services and management training to members on all aspects of human resource management, occupational health and safety, employee relations and employment law.
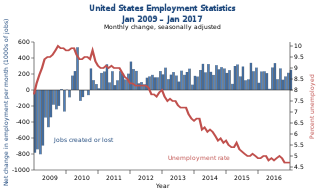
Unemployment in the United States discusses the causes and measures of U.S. unemployment and strategies for reducing it. Job creation and unemployment are affected by factors such as economic conditions, global competition, education, automation, and demographics. These factors can affect the number of workers, the duration of unemployment, and wage levels.
The Association of Swedish Engineering Industries is a Swedish trade organization representing employers of multinational engineering and industrial manufacturing companies. The member companies operate in a range of sectors that include telecommunications, fabricated metal products, electronics, machinery and equipment, office machinery and apparatus, power industry, instrument technology, optics, motor cars and transport equipments. The association’s main objective is to assist the employers of its member companies with various industry policies and labor law guidelines, collective agreement negotiations with labor unions as well as regular publication of economic policy and trend analysis reports. The association also maintains an established task force to promote initiatives in technological innovation, research collaboration between universities and companies as well as design thinking that ultimately can enhance the global competitiveness of Sweden’s industrial sector. The association has 4,000 member companies with over 300,000 employees.
The American Benefits Council (the Council) is a national trade association based in Washington, D.C. that advocates for employer-sponsored benefit plans. The Council's members represent the private employee benefits community and either sponsor directly or provide services to retirement and health benefit plans both nationally and internationally.

The Global Apprenticeship Network (GAN) is a Swiss independent and neutral not-for-profit association based in Geneva. The GAN is a network of companies, employer organisations, associations and international organisations with the mission of promoting quality apprenticeships and the goal of creating job opportunities for youth and ensuring skills for business.
Gig workers are independent contractors, online platform workers, contract firm workers, on-call workers and temporary workers. Gig workers enter into formal agreements with on-demand companies to provide services to the company's clients.
Corporate language policy is a broad category covering the internal governance and management of language in private organisations. This differs from other definitions, such as official language and working language, as this category considers a broader set of organisational policy and actions directed towards language.



