
A supercomputer is a type of computer with a high level of performance as compared to a general-purpose computer. The performance of a supercomputer is commonly measured in floating-point operations per second (FLOPS) instead of million instructions per second (MIPS). Since 2017, supercomputers have existed, which can perform over 1017 FLOPS (a hundred quadrillion FLOPS, 100 petaFLOPS or 100 PFLOPS). For comparison, a desktop computer has performance in the range of hundreds of gigaFLOPS (1011) to tens of teraFLOPS (1013). Since November 2017, all of the world's fastest 500 supercomputers run on Linux-based operating systems. Additional research is being conducted in the United States, the European Union, Taiwan, Japan, and China to build faster, more powerful and technologically superior exascale supercomputers.
Floating point operations per second is a measure of computer performance in computing, useful in fields of scientific computations that require floating-point calculations.

Blue Gene was an IBM project aimed at designing supercomputers that can reach operating speeds in the petaFLOPS (PFLOPS) range, with low power consumption.

EPCC, formerly the Edinburgh Parallel Computing Centre, is a supercomputing centre based at the University of Edinburgh. Since its foundation in 1990, its stated mission has been to accelerate the effective exploitation of novel computing throughout industry, academia and commerce.

The TOP500 project ranks and details the 500 most powerful non-distributed computer systems in the world. The project was started in 1993 and publishes an updated list of the supercomputers twice a year. The first of these updates always coincides with the International Supercomputing Conference in June, and the second is presented at the ACM/IEEE Supercomputing Conference in November. The project aims to provide a reliable basis for tracking and detecting trends in high-performance computing and bases rankings on HPL benchmarks, a portable implementation of the high-performance LINPACK benchmark written in Fortran for distributed-memory computers.
Kittyhawk is an IBM supercomputer. The proposed project entails constructing a global-scale shared supercomputer capable of hosting the entire Internet on one platform as an application, whereas the current Internet is a collection of interconnected computer networks.
The Green500 is a biannual ranking of supercomputers, from the TOP500 list of supercomputers, in terms of energy efficiency. The list measures performance per watt using the TOP500 measure of high performance LINPACK benchmarks at double-precision floating-point format.

IBM Sequoia was a petascale Blue Gene/Q supercomputer constructed by IBM for the National Nuclear Security Administration as part of the Advanced Simulation and Computing Program (ASC). It was delivered to the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) in 2011 and was fully deployed in June 2012. Sequoia was dismantled in 2020, its last position on the top500.org list was #22 in the November 2019 list.
The National Center for Computational Sciences (NCCS) is a United States Department of Energy (DOE) Leadership Computing Facility that houses the Oak Ridge Leadership Computing Facility (OLCF), a DOE Office of Science User Facility charged with helping researchers solve challenging scientific problems of global interest with a combination of leading high-performance computing (HPC) resources and international expertise in scientific computing.
Shaheen is the name of a series of supercomputers owned and operated by King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST), Saudi Arabia. Shaheen is named after the Peregrine Falcon. The most recent model, Shaheen II, is the largest and most powerful supercomputer in the Middle East.
A lightweight kernel (LWK) operating system is one used in a large computer with many processor cores, termed a parallel computer.
New York Blue is an 18 rack Blue Gene/L and a 2 rack Blue Gene/P massively parallel supercomputer based on the IBM system-on-chip technology. It is located in the New York Center for Computational Sciences (NYCCS). The supercomputer is owned by Stony Brook University and is located at Brookhaven National Laboratory in Upton, Long Island, New York. The funds for this machine were provided by the New York state, with the leadership of the NYS Assembly. It began operating on July 15, 2007, when it was the fifth most powerful supercomputer dedicated to general research. According to Stony Brook provost Robert McGrath, it would also rank within the top 10 when including supercomputers available only for military research. The renovation of laboratory space was supported by the New York state and U.S. DOE fund. As of June 2010, the Blue Gene/L was ranked 67th in the Top 500 supercomputing rankings. Together with the Computational Center for Nanotechnology Innovations at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, New York Blue provides New York state with more computing power available for general research than any state in the nation.
The Slurm Workload Manager, formerly known as Simple Linux Utility for Resource Management (SLURM), or simply Slurm, is a free and open-source job scheduler for Linux and Unix-like kernels, used by many of the world's supercomputers and computer clusters.

The K computer – named for the Japanese word/numeral "kei" (京), meaning 10 quadrillion (1016) – was a supercomputer manufactured by Fujitsu, installed at the Riken Advanced Institute for Computational Science campus in Kobe, Hyōgo Prefecture, Japan. The K computer was based on a distributed memory architecture with over 80,000 compute nodes. It was used for a variety of applications, including climate research, disaster prevention and medical research. The K computer's operating system was based on the Linux kernel, with additional drivers designed to make use of the computer's hardware.

Several centers for supercomputing exist across Europe, and distributed access to them is coordinated by European initiatives to facilitate high-performance computing. One such initiative, the HPC Europa project, fits within the Distributed European Infrastructure for Supercomputing Applications (DEISA), which was formed in 2002 as a consortium of eleven supercomputing centers from seven European countries. Operating within the CORDIS framework, HPC Europa aims to provide access to supercomputers across Europe.

Compute Node Kernel (CNK) is the node level operating system for the IBM Blue Gene series of supercomputers.
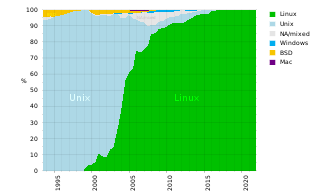
A supercomputer operating system is an operating system intended for supercomputers. Since the end of the 20th century, supercomputer operating systems have undergone major transformations, as fundamental changes have occurred in supercomputer architecture. While early operating systems were custom tailored to each supercomputer to gain speed, the trend has been moving away from in-house operating systems and toward some form of Linux, with it running all the supercomputers on the TOP500 list in November 2017. In 2021, top 10 computers run for instance Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL), or some variant of it or other Linux distribution e.g. Ubuntu.

POWER9 is a family of superscalar, multithreading, multi-core microprocessors produced by IBM, based on the Power ISA. It was announced in August 2016. The POWER9-based processors are being manufactured using a 14 nm FinFET process, in 12- and 24-core versions, for scale out and scale up applications, and possibly other variations, since the POWER9 architecture is open for licensing and modification by the OpenPOWER Foundation members.

Galileo is a 1.1 petaFLOPS supercomputer located at CINECA in Bologna, Italy.

Fugaku(Japanese: 富岳) is a petascale supercomputer at the Riken Center for Computational Science in Kobe, Japan. It started development in 2014 as the successor to the K computer and made its debut in 2020. It is named after an alternative name for Mount Fuji.













