A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment.

Rosacea is a long-term skin condition that typically affects the face. It results in redness, pimples, swelling, and small and superficial dilated blood vessels. Often, the nose, cheeks, forehead, and chin are most involved. A red, enlarged nose may occur in severe disease, a condition known as rhinophyma.

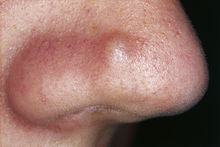
A dermatofibroma, or benign fibrous histiocytomas, is a benign nodule in the skin, typically on the legs, elbows or chest of an adult. It is usually painless.

A papule is a small, well-defined bump in the skin. It may have a rounded, pointed or flat top, and may have a dip. It can appear with a stalk, be thread-like or look warty. It can be soft or firm and its surface may be rough or smooth. Some have crusts or scales. A papule can be flesh colored, yellow, white, brown, red, blue or purplish. There may be just one or many, and they may occur irregularly in different parts of the body or appear in clusters. It does not contain fluid but may progress to a pustule or vesicle. A papule is smaller than a nodule; it can be as tiny as a pinhead and is typically less than 1 cm in width, according to some sources, and 0.5 cm according to others. When merged together, it appears as a plaque.

Hyperkeratosis is thickening of the stratum corneum, often associated with the presence of an abnormal quantity of keratin, and is usually accompanied by an increase in the granular layer. As the corneum layer normally varies greatly in thickness in different sites, some experience is needed to assess minor degrees of hyperkeratosis.

Pearly penile papules are benign, small bumps or spots on the human penis. They vary in size from 1–4 mm, are pearly or flesh-colored, smooth and dome-topped or filiform, and appear in one or, several rows around the corona, the ridge of the head of the penis and sometimes on the penile shaft. They are painless, non-cancerous and not harmful. The medical condition of having such papules is called hirsutoid papillomatosis or hirsuties papillaris coronae glandis.

Pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy (PUPPP), known in United Kingdom as polymorphic eruption of pregnancy (PEP), is a chronic hives-like rash that strikes some women during pregnancy. Some skin changes are known to occur in people who are pregnant while other skin conditions, or dermatoses, that people have prior to getting pregnant will become altered or symptoms will increase. Pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy (PUPPP) is one of many skin conditions that is specific to pregnancy and occurs in about 1 in every 160 (0.625%) of pregnancies.

Granuloma annulare (GA) is a rare, sometimes chronic skin condition which presents as reddish bumps on the skin arranged in a circle or ring. It can initially occur at any age, though two-thirds of patients are under 30 years old, and it is seen most often in children and young adults. Females are two times as likely to have it as males.

Rhinophyma is a condition causing development of a large, bulbous nose associated with granulomatous infiltration, commonly due to untreated rosacea. The condition is most common in older white males.
Papular mucinosis is a rare skin disease. Localized and disseminated cases are called papular mucinosis or lichen myxedematosus while generalized, confluent papular forms with sclerosis are called scleromyxedema. Frequently, all three forms are regarded as papular mucinosis. However, some authors restrict it to only mild cases. Another form, acral persistent papular mucinosis is regarded as a separate entity.

Angiofibroma (AGF) is a descriptive term for a wide range of benign skin or mucous membrane lesions in which individuals have:
- benign papules, i.e. pinhead-sized elevations that lack visible evidence of containing fluid;
- nodules, i.e. small firm lumps usually >0.1 cm in diameter; and/or
- tumors, i.e. masses often regarded as ~0.8 cm or larger.
Cutaneous perforating disorders include the following:

Nevus lipomatosus superficialis is characterized by soft, yellowish papules or cerebriform plaques, usually of the buttock or thigh, less often of the ear or scalp, with a wrinkled rather than warty surface. It is usually congenital in origin or appears within the first three decades.

Atypical fibroxanthoma (AFX) of the skin is a low-grade malignancy related to malignant fibrous histiocytoma, which it resembles histologically. Atypical fibroxanthoma manifests as a hard, pink or red papule or nodule that grows over the course of several months and may bleed or ulcerate. They typically occur on the head and neck. Atypical fibroxanthoma is usually asymptomatic.
Id reactions are types of acute dermatitis developing after days or weeks at skin locations distant from the initial inflammatory or infectious site. They can be localised or generalised. This is also known as an 'autoeczematous response' and there must be an identifiable initial inflammatory or infectious skin problem which leads to the generalised eczema. Often intensely itchy, the red papules and pustules can also be associated with blisters and scales and are always remote from the primary lesion. It is most commonly a blistering rash with itchy vesicles on the sides of fingers and feet as a reaction to fungal infection on the feet, athlete's foot. Stasis dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, acute irritant contact eczema and infective dermatitis have been documented as possible triggers, but the exact cause and mechanism is not fully understood. Several other types of id reactions exist including erythema nodosum, erythema multiforme, Sweet's syndrome and urticaria.
Granulosis rubra nasi is a rare familial disease of children, occurring on the nose, cheeks, and chin, characterized by diffuse redness, persistent excessive sweating, and small dark red papules that disappear on diascopic pressure.

Lichen striatus is a rare skin condition that is seen primarily in children, most frequently appearing ages 5–15. It consists of a self-limiting eruption of small, scaly papules.
Eruptive vellus hair cysts are small lesions that occur most often in the chest wall, abdomen and extremities, often with a crusted surface. EVHC may occur randomly, or it can be inherited as an autosomal dominant trait; sporadic cases usually appear at 4–18 years of age. The cysts appear similar clinically to steatocystoma multiplex, as well as acneiform eruptions and milia. Histopathology is the basis of diagnosis. Retinoids, surgery, and lasers are used as treatment modalities.

Piezogenic papules are protrusions of fat that form within the subcutaneous tissue of the skin. They are typically found on the heels or wrists.
CYLD cutaneous syndrome (CCS) encompasses three rare inherited cutaneous adnexal tumor syndromes: multiple familial trichoepithelioma (MFT1), Brooke–Spiegler syndrome (BSS), and familial cylindromatosis (FC). Cutaneous adnexal tumors are a large group of skin tumors that consist of tissues that have differentiated towards one of the four primary adnexal structures found in normal skin: hair follicles, sebaceous sweat glands, apocrine sweat glands, and eccrine sweat glands. CCS tumors are hair follicle tumors.